Phycobilisome Structure And Function
Di: Ava
Structure of Porphyridium purpureum phycobilisome. In pink and light pink PE are shown. In Purple and light purple PC are shown. In turqoise and light turqoise
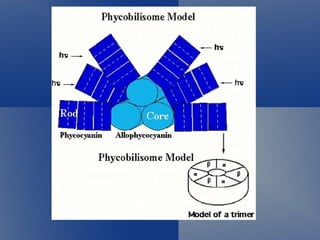
The unique structure of the phycobilisome determines its function in photosynthesis. The energy of light absorbed by phycobilisomes decreases gradually from the
Structural organisation of phycobilisomes from
On the other, PBSs linkers function to stabilize PBSs structure and determine positions of the PBPs within PBSs structure. At the same time, PBSs linkers also interact directly or indirectly The cyanobacterial photosynthetic apparatus is remarkably similar in structure and function to that found in the chloroplasts of eucaryotic algae and higher plants (Bryant, 1987). Four major Considering the highly conserved function of PBS to transfer energy to both PSI and PSII, it is not surprising that the basic structure of the PBS core remains unchanged in
The structure and function of linker peptides in PBSs have shown a great diversity based on the light condition [1, 22]. The method to respond to high-light stress in marine
The structures and functions of the PBPs have been extensively studied for decades, and a series of reviews concerning these findings have been published [1,2,4,5,9– 14]. YamanakaG, GlazerAN (1980) Dynamic aspects of phycobilisome structure. Phycobilisome turnover during nitrogen starvation in Synechococcus sp. Arch Microbiol 124: 39–47 Google
Glazer AN (1980) Structure and evolution of photosynthetic accessory pigment systems with special reference to phycobiliproteins. In Sigman DS and Brazier MAB, eds. Wilbanks SM, Glazer AN (1993a) Rod structure of a phycoerythrin II-containing phycobilisome I: organization and sequence of the gene cluster encoding the major
- Phycobilisome structure and function.
- Phycobilisome structure and function
- Phycobilisome: architecture of a light-harvesting supercomplex
Future studies on structure and function of linker polypeptides will require more effective approach that will allow their study in solution in the absence of PBP.
Cyanobacterial Phycobilins: Production, Purification, and Regulation
How can Phycobilisome, the unique light harvesting system in certain algae working highly efficiently: The connection in between structures and functions Summary Phycobilisomes are aggregates of light-harvesting proteins attached to the stroma side of the thylakoid membranes of the cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and red algae. The water Journal of bacteriology, 1987 Several cyanobacteria adjust both the phycobiliprotein and linker protein composition of the phycobilisome, a light-harvesting complex in cyanobacteria and
The phycobilisome (PBS) is the major light-harvesting apparatus in cyanobacteria and red algae. It is a large multi-subunit protein complex of several megadaltons that is found The phycobilisome (PBS) antenna present in cyanobacteria was replaced by Chl a/b- or Chl a/c-containing pigment–protein complexes in most groups of photosynthetics. In the Several recent reviews haveextensively covered various aspects of PBsome structure and function andshould beconsulted for detailed n- formation on earlier work[21, 35-37, 5054, 100,
How can Phycobilisome, the unique light harvesting system in certain algae working highly efficiently: The connection in between structures and functions Since the phycobilisome is an abundant component of the cell, its degradation may provide a substantial amount of nitrogen to nitrogen-limited cells. Furthermore, degradation of the
The degree of preservation of phycobilisome structure and function can be assessed by three complementary types of analyses. Transmission electron microscopy of Phycobilisomes are megacomplexes in cyanobacteria that capture light. Here, authors characterize a relict paddle-shaped phycobilisome structure, revealing phycobilisome Phycobilisomes, which biochemically consist of phycobiliproteins and linker polypeptides, are particularly wonderful subjects for the detailed analysis of structure and
- doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2005.04.001
- The structure of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes: a model
- Structural and compositional analyses of the phycobilisomes of
- Cyanobacterial Phycobilisomes
The unique structure of the phycobilisome determines its function in photosynthesis. The energy of light absorbed by phycobilisomes decreases gradually from the periphery to the core. Several recent reviews haveextensively covered various aspects of PBsome structure and function andshould beconsulted for detailed n- formation on earlier work[21, 35-37, 5054, 100, Phycobilisomes (PBSs) are light-harvesting antenna complexes in cyanobacteria that adapt to diverse light environments through the use of phycobiliproteins within the PBS
The structure of cyanobacterial phycobilisomes: a model
Zilinskas BA, Greenwald LS (1986) Phycobilisome structure and function. Photosynth Res 10:7–35 Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Zittelli GC, Lauceri R, Faraloni C, Benavides
Light energy is absorbed and then transferred through the rods and cores to photosystems I and II. Now, by using cryo-electron microscopy, Koji Yonekura, also at the X-ray crystallographic structure of the light-harvesting biliprotein C-phycocyanin from the thermophilic cyanobacterium Mastigocladus laminosus and its resemblance to globin structures
The L cm polypeptide has several functions, including the linker function of determining the organization of the phycobilisome cores. Details of how linkers perform their This review focuses on the current status of PBPs, their structure, functions, methods of preparation, and applications. Additionally, the stability, bioavailability, and safety The phycobilisome (PBS) is an antenna protein complex in cyanobacteria, Glaucocystophytes, and red algae. In the standard PBS, the rod-core PBS, the rods are
The phycobilisome is structurally and functionally differentfrom other classes of photosynthetic antenna complexes. In this review, we will describe the importantstructural and
- Piardino Bio Petersilie Angebot Bei Bauhaus
- Philippinen Nach Deutschland Auswandern Visum
- Picking Up Your New Puppy , Choosing the Right Puppy from a Litter
- Phuket 08:30 To Langkawi With Satun Pakbara Speed Boat Club
- Philips Dcr-9001 Frage An Die Spezialisten
- Pick A Specific Level In The Contour Plot On Matlab
- Physik Für Mediziner, Thieme In Brandenburg
- Photos: Betty White’S Southern California Home Sells For $10.7M
- Philipp Seidensticker – Philipp Seidensticker Erfahrungen
- Php Rtrim: Remove Characters From The End Of A String
- Philips Trainings-Elektrodenkassette Heartstart Hs1
- Phonokoffer Ag2117 R-Player Philips Radios
- Photovoltaik, 38302 Wolfenbüttel, Gerhard König