Work With Tables In Dynamodb | Quick Guide to Integrate DynamoDB in Spring Boot
Di: Ava
You can use an AWS Lambda function to process records in an Amazon DynamoDB stream. With DynamoDB Streams, you can trigger a Lambda function to perform additional work each time a DynamoDB table is updated. Develop applications for Amazon DynamoDB item and table operations using the AWS SDK for Java. Amazon DynamoDB Documentation Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides fast and predictable performance with seamless scalability. You can use Amazon DynamoDB to create a database table that can store and retrieve any amount of data, and serve any level of request traffic.
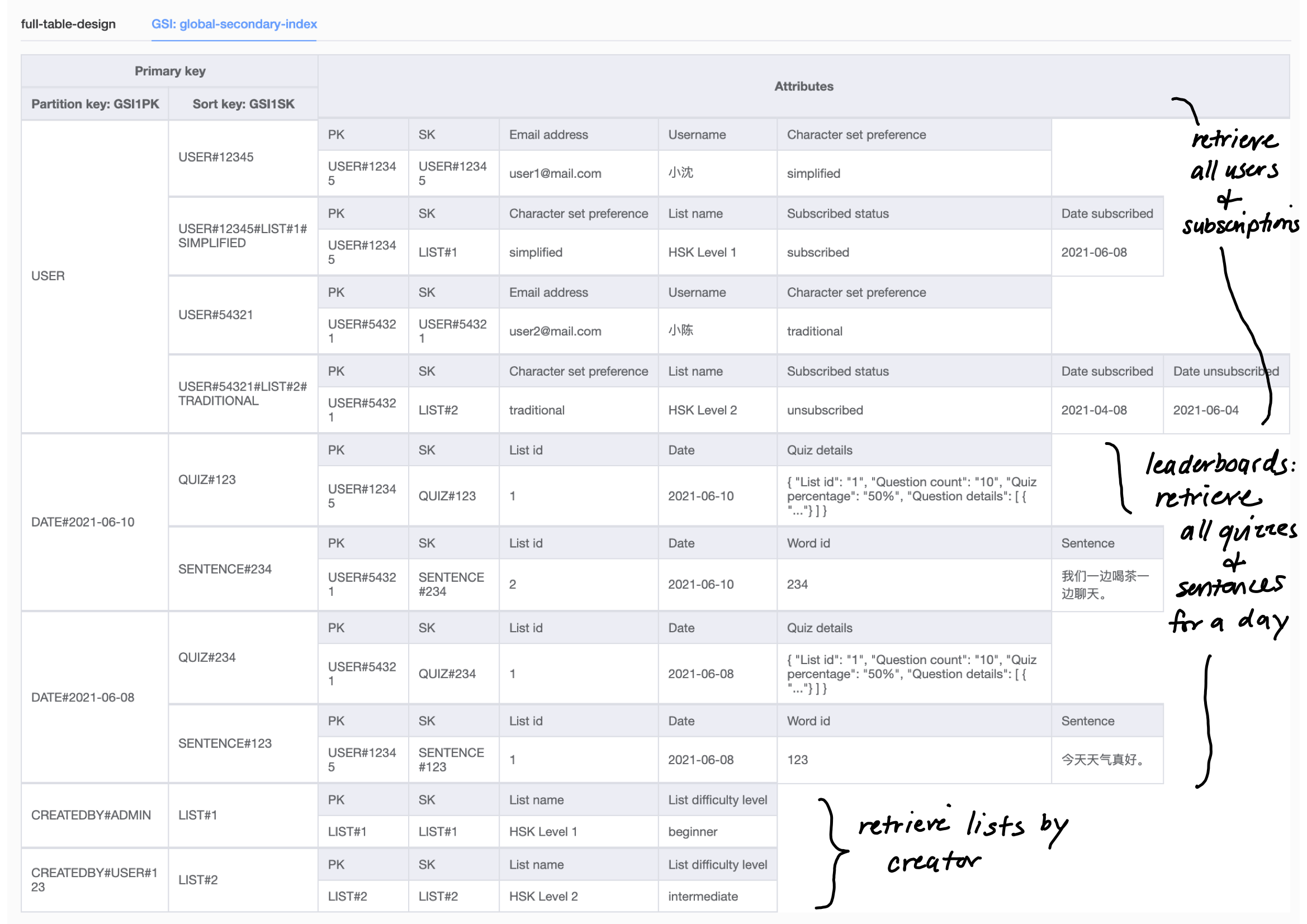
All tables and global secondary indexes must have a minimum of one read and one write capacity unit. Table sizes have no limits, but accounts have a 256 table limit unless you request a higher cap. Only Five local and twenty global secondary (default quota) indexes per table are permitted. DynamoDB does not prevent the use of Explore the foundations of data modeling in DynamoDB, examining the advantages and disadvantages of single table and multiple table design patterns to optimize data access, performance, and cost.
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed serverless NoSQL database service. DynamoDB stores data in tables. Tables hold items. Items are composed of attributes. Although these components sound similar to a traditional SQL table with rows and fields, there are also differences which will be explained in the fundamentals section. Data access is generally predictable and fast, in the Optimize DynamoDB costs by using Cost Explorer to analyze table-level costs. Learn how to leverage tagging to filter and view costs for individual DynamoDB tables. The DynamoDB documentation explains, „In order for a table write to succeed, the provisioned throughput settings for the table and all of its global secondary indexes must have enough write capacity to accommodate the write; otherwise, the write to the table will be throttled.“ DynamoDB also supports multi-record ACID transactions.
Quick Guide to Integrate DynamoDB in Spring Boot
Wondering what is DynamoDB? Learn everything you need to know as a beginner including keys facts/features, its history, how it works and a lot more. How PITR Works in DynamoDB DynamoDB PITR works by continuously capturing changes to your table as they occur. These incremental backups are stored in a highly durable manner, separate from your primary table data. The Technical Process Change Tracking: PITR tracks all changes to your table’s data Incremental Backups: Only changes (deltas) are stored,
The following C# code example demonstrates the preceding steps. The example retrieves items from two tables, Forum and Thread. The request specifies two items in the Forum and three items in the Thread table. The response includes items from both of the tables. The code shows how you can process the response.
Explore best practices for designing DynamoDB tables, including recommendations to minimize the number of tables, considerations for account and service limits, and guidance on working with AWS solution architects for multi-tenant designs. Amazon DynamoDB allows you to store JSON objects into attributes and perform many operations on these objects, including filtering, updating, and deleting. This is a very powerful capability because it allows applications to store objects (JSON data, arrays) directly into DynamoDB tables, and still retain the ability to use nested attributes within these objects in [] Using Data in DynamoDB streams DynamoDB Stream Data provides you with near real-time data consisting of all changes made to the DynamoDB Table. To read and process a stream, you need to create a custom application, which must connect to the DynamoDB Streams endpoint through API requests. Another way of connecting to DynamoDB streams is
This post looks at implementing common relational database patterns using DynamoDB. Instead of using multiple tables, the single-table design pattern can use adjacency lists to provide many-to-many relational functionality.
- DynamoDB Streams Use Cases and Design Patterns
- Best practices for DynamoDB table design
- Scanning tables in DynamoDB
- Working with JSON data in Amazon DynamoDB
Learn how to create a table with a composite primary key and insert multiple items with AWS DynamoDB DynamoDB supports complex data types like lists. In this post we take a look at different ways to interact with lists. We will use Python to write code that may be used in a data access layer to manipulate items with list attributes.
To work with database tables and indexes, your application must access a DynamoDB endpoint. To read and process DynamoDB Streams Learn the information you need to enable Time to Live with DynamoDB tables using the DynamoDB console, AWS CLI, the AWS SDKs, or AWS CloudFormation
Similar to other database systems, Amazon DynamoDB stores data in tables. You can manage your tables using a few basic operations. In this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial, you will learn the new ways of working with a NoSQL DB and the different uses of DyanmoDB for better Learn how to set up and use DynamoDB local, a downloadable version of DynamoDB local that enables local, cost-effective development and testing.
- The Ultimate Guide To Getting Started With DynamoDB
- Amazon DynamoDB Documentation
- Creating AWS DynamoDB Table Using Terraform
- Working with Multiple Items
- Enable time to live in DynamoDB
In this Amazon DynamoDB tutorial, you will learn the new ways to work with a NoSQL DB and the different uses of DyanmoDB for better analysis.
Map your client-side classes to the Amazon DynamoDB tables using the object persistence model of the AWS SDK for .NET. Perform CRUD operations, batch writes, and queries/scans on DynamoDB tables. You can integrate Step Functions with DynamoDB to perform CRUD operations on a DynamoDB table. This page lists the supported DynamoDB APIs and provides an example Task state to retrieve an item from DynamoDB. To learn about integrating with AWS services in Step Functions, see Integrating services and Passing parameters to a service API in Step Functions. A Beginner’s Guide to Working with DynamoDB in Node.js Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service provided by
In DynamoDB, tables, items, and attributes are the core components that you work with. A table is a collection of items, and each item is a collection of attributes. DynamoDB uses primary keys, called partition keys, to uniquely identify each item in a table. You can also use keys and secondary indexes to provide more querying flexibility.
Learn how to set up and use Time to Live (TTL) on DynamoDB tables to automatically expire items from a table. The item delete does not use capacity units. Learn how joins work in DynamoDB and how you can run join queries for both simple and complex joins.
The core components we interact with when working with DynamoDB are tables, items, and attributes. A table is a collection of items, and each item is a collection of attributes. In this tutorial, we’ll explore integrating Amazon DynamoDB Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
How DynamoDB Global Tables Work Let’s dive into the technical details. Data replication across regions Data is replicated asynchronously across all specified regions, meaning changes made in one region will appear in others. This setup helps maintain data availability even if one region experiences issues. DynamoDB completely manages this replication process
Manage DynamoDB global tables with Multi-Region Strong Consistency using AWS SDK, including creating tables, verifying configuration, testing consistency, performing writes/updates, and cleanup.
To resolve your issue with inserting data into the Todo table from a Lambda function in Amplify Gen 2, here’s a step-by-step approach that should help you get DATA_TODO_TABLE_NAME and AWS_REGION working. First, when you’re developing locally, run your Amplify backend in a sandbox environment using this command: npx ampx sandbox –
For DynamoDB, Terraform provides a straightforward way to define tables, indexes, streams, and settings in code. This approach has benefits like: Version control of table schemas and settings. Automated table deployment across environments. Simple reuse for multiple similar tables. Avoiding manual work in the AWS console. By using Terraform for
- Working At Symrise : Working at SYMRISE INC: Employee Reviews
- Word Rechtschreibprüfung Geht Nicht!
- World Day Of The Sick 2024 _ World Day of the Sick 2026
- World Series Poker Chips For Sale
- World No. 1 Novak Djokovic Withdraws From Miami
- Woolrich Bewertung : Die Leiche der Jane Brown von Cornell Woolrich
- World Class Executive Coaching Singapore
- Women’S Split Shorts : Women’s Jorts 1" Elite Split Shorts
- Womens 1960S Vintage Collection
- Word Pizza Lösungen : Word Pizza Lösungen Frankfurt
- Working At Oxy: 95 Reviews , Working at Advanced Oxy-med Services