Which Of The Following Complexes Are Low Spin And Diamagnetic?
Di: Ava
Click here?to get an answer to your question ️ 145 UULIT Which of the following complexes are low spin and mplex plex diamagnetic ? (a) K, (Os (CN),] (b) [Mo (CO), (c) [Mn (CN), 14- Select the correct answer using the codes given below: (1) a, b and c To determine which of the following complex ions is diamagnetic, we need to analyze the electronic configurations and the number of unpaired electrons in each complex ion. A complex is considered diamagnetic if all of its electrons are paired. 1. Identify the Complex Ions: We have four complex ions to analyze. Let’s denote them as: – (i) (FeF6
A low spin complex is one in which the electrons are paired up to give a maximum number of doubly occupied d orbitals and a minimum number of unpaired electrons. Outer orbital complexes are high spin complexes and inner orbital complexes are low spin complexes. N H 3 and H 2 O are weak field ligands and do not cause pairing of electrons in the Click here?to get an answer to your question ️ which of the following complexes is diamagnetic and low spin Here , the oxidation state of Mn 3+ is +3 and it contributes to d2sp3 hybridisation ,hence it is inner orbital complexes. These are electronic arrangement of the
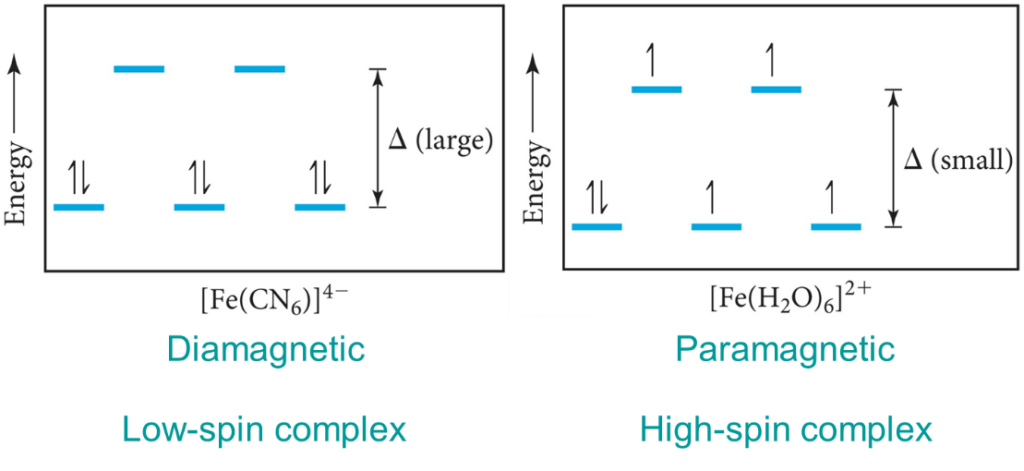
Depict high spin and low spin configurations for each of the following complexes. Tell whether each is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Give the number of unpaired electrons of the paramagnetic complexes: [C r F 6] 4 − We find that the square planar complexes have the greatest crystal field splitting energy compared to all the other complexes. This means that most square planar complexes are low spin, strong field ligands. Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field. How are the following conversions carried out? Benzoic acid into metanitrobenzoic acid. State the superiority of crystal field theory over valence bond theory. Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes rarely observed? Complete and balance the following reactions: (1) P 4 + H 2 SO 4 → ____ + _____ + _____ +
Is cobalt hexaaqua paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
Diamagnetic complexes have no unpaired electrons. Use crystal field theory to determine the spin state based on the ligand field strength.
What are the high-spin complexes?When crystal field splitting energy is smaller than electron pairing energy, the complexes formed are high-spin complexes.
Complete step by step answer: The diamagnetic term is used for those complexes in which the central atom has paired electrons in its d-orbital. So, more the number of paired electrons more will be the diamagnetism of complexes. The strong field ligands form low spin complexes and weak field ligands form high spin complexes. CO being strong field ligand causes pairing thereby making it diamagnetic. Hence, is a low spin complex.
Which of the following sets of complexes is`//` are correct with respect to the properties indicated `+2` oxidation state of central metal atom. A low-spin complex is a type of coordination compound characterized by a small crystal field splitting energy, which leads to the pairing of electrons in the lower energy d-orbitals before occupying the higher energy d-orbitals. This results in a configuration with fewer unpaired electrons, often leading to diamagnetism. The properties of low-spin complexes are influenced
- 19.3 Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination
- 4.3: High Spin and Low Spin Complexes
- Which of the following statement about `Fe_` is correct
Click here?to get an answer to your question ️ which of the following complex is diamagnetic 2.87 BM 1.73 BM 0 BM 2.87 BM = 2 Unpaired electrons , Mn3+, d4 low spin 1.73 BM = 1 Unpaired electron , Co2+, d7 low spin 0 BM = 0 Unpaired electron , Fe2+, d6 low spin Draw the crystal filed splitting diagram of d orbitals in a linear complex MX2, assuming the ligands (X) to be along the z axis. Soln. Electron-electron repulsion between M and X will be there only for d For instance, the d6 complexes of Fe2+ are diamagnetic in the low-spin state while having four unpaired electrons in the high-spin state. Thus, a variation in the magnitude of the magnetic moment is expected as we after spin crossover.
` [Co (H_ (2)O)_ (6)]^ (3+)=d^ (2)sp^ (3)`
low spin, diamagnetic,magntic moment = zero `BM` . The complexes formed are called inner orbital complex (low spin complex) and outer orbital complex (high spin complex) respectively. Further, the complexes can be paramagnetic or diamagnetic in nature. The drawbacks of this theory are that this involves number of assumptions and also does not explain the colour of the complex.
Inner orbital complexes and diamagnetic behavior:Inner orbital complexes, also known as low spin complexes, are formed when the ligands occupy the inner d-orbitals of the central metal ion. These complexes have a stable electronic configuration due to the pairing of electrons in Complexes in which the electrons are paired because of the large crystal field splitting are called low-spin complexes because the number of unpaired electrons (spins) is minimized. Figure 19.35 Iron (II) complexes have six electrons in the 5d orbitals. In the absence of a crystal field, the orbitals are degenerate.
2) Here you need to know that for Co3+ all complexes are low spin except [CoF6]3- and [Co (H2O)3F3]. So, the complex given will be low spin with all 6 electrons paired & thus it will be diamagnetic. A. 4:1 B. 1:1 C. 2:1 D. 1:2 E. 1:4, For which of the following metal ions would there be no distinction between low spin and high spin in octahedral complexes? A.
Which of the following statement is correct ? (CFSE = Crystal Field Splitting Energy) A Lower CFSE favours formation of low spin complex Step 1/21. Diamagnetic complexes have all their electrons paired up, meaning there are no unpaired electrons.Answer2. Low spin complexes have a smaller number of unpaired electrons compared to high spin complexes. Now let’s analyze each option: a) Cr3+ (3d3) – low spin: In this case, there are 3 unpaired electrons, so it is not diamagnetic. b) Ni2+ (3d8) – high spin: In this (d) In high spin octahedral complexes, oct is less than the electron pairing energy, and is relatively very small. (e) Low spin complexes contain strong field ligands. 16. (Crystal Field Theory) When the valence d orbitals of the central metal ion are split in energy in an octahedral ligand field, which orbitals are raised least in energy?
Click here?to get an answer to your question ️ Which of the following complexes is diamagnetic and low spin? [CoF, (H,0),] Cr (C,04), 7 [AuCl] [Fe (CN).]\“ The complex ion $\ce { [Co (H2O)6]^3+}$ has $\ce {Co}$ in the $+3$ oxidation state, meaning it has an electron configuration of $ [Ar] 4s^0 3d^6$. Therefore it has 4 unpaired electrons and would be paramagnetic. In a low-spin complex, the electrons will pair up as much as possible, but there will still be one unpaired electron, making this complex paramagnetic. B) High-spin [Fe (H2O)6]3+: Again, Fe is in the +3 oxidation state. In a high-spin complex, the electrons will fill up all the available orbitals before pairing up.
of unpaiÑd = 2 l: No. = 2 kJ mol-I complex will have high spin configuration it has more negative value of CFSE and hencN‘ more stable than low spin configuration. 1.6 x 342 -416+342 = -0.6×260 156 kJ CFSE CFSE = 3<0.4 A;) + connguranon low spin high spin is 342 kJ mol-I. Predict whether the complex will have low spin or high spin configuraHon.
Which of the following species is diamagnetic? (1) An isolated, gas-phase V3+ ion [Ar] 4s03d2 (2) A high spin octahedral Fe+2 complex A. 4536 (3) An isolated, gas phase Cu2+ ion (4) A low spin octahedral Co3+ complex [ ito 45∘ 15 antic
In [N i(N H 3)6]3+, the N i3+(d7) ion udergoes sp3d2 hybridization to form outer orbital complex or high-spin (spin-free) with 3 unpaired electrons. In [T i(H 2O)6]3+, the T i3+(d1) ion contains only 1 d electron and cannot form low-spin (spin-paired) complex. [Cr(N H 3)6]3+ undergoes d2sp3 hybridization and contains only 3 electrons. Thus the term low-spin (spin-paired) complex is In the complexes K4[F e(CN)6],K3[Co(CN)6]andK2[N i(CN)4], all the electrons are paired. These complexes are low spin inner orbital complexes. Hence, they are diamagnetic complexes. Was this answer helpful? (c) A particular metal ion in a particular oxidation state can form either diamagnetic complexes only or paramagnetic complexes only.
High spin and low spin are two possible classifications of spin states that occur in coordination compounds. These classifications come from either the ligand The correct answer is Since K4O8(CN)6,Mo(CO)6 has no unpaired electrons they are diamagnetic and low spin while Mn(CN)64− has one unpaired electron they are paramagnetic in nature and have high spin. The option B is correct.
- White Sox Hoodie | Chicago White Sox Authentic Collection
- Which Do You Select First – Is there an onSelect event or equivalent for HTML <select>?
- White Lipped Python: Feiten, Info
- White Chocolate Toffee – White Chocolate Toffee Cashews
- Where’S The Option To Upload .Ovpn File Under Services>Openvpn
- White Christmas At An Amc Theatre Near You.
- Which Progress Products Can Be Downloaded For Free?
- Whisky Live Paris 2024 Wieder In Der Grande Halle De La Villette
- White Folia Tall Vase 30Cm | Tall White Vase Buy at Molly Florence blog
- Who Has The Most Rings In Sports History?