Whats Meaning Of Where False; In Sql Query
Di: Ava
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a domain-specific language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. In SQL Server, a query is a statement or command that you use to interact with the database to retrieve, insert, update, or delete data. SQL queries are an integral part of working with SQL Server and are used for a wide range of database-related tasks. What is the difference between the EXISTS and IN clause in SQL? When should we use EXISTS, and when should we use IN?
In SQL Server, what does "SET ANSI_NULLS ON" mean?
I want to select the Id and Name and true/false column based on the value of entity profile, for example a returned result set like below, would mean that entities 1&2 have profiles while 3 not. Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the SQL EXISTS operator to test if a subquery returns any row. Introduction to the SQL EXISTS operator The EXISTS operator allows you to check if a subquery returns any row. The EXISTS operator returns true if the subquery returns at least one row or false otherwise. Here’s the syntax of the EXISTS operator: SELECT column1, SQL Logical Operator: The Logical operators are those that are true or false. Learn more about Logical operators with various combination of examples.
I am looking at some PostgreSQL table creation and I stumbled upon this: CREATE TABLE ( ) WITH ( OIDS = FALSE ); I read the documentation provided by postgres and I know the concept of object identifier from OOP but still I do not grasp, why such identifier would be useful in a database? to make queries shorter? when should it be used?
SQL Statements Most of the actions you need to perform on a database are done with SQL statements. SQL statements consist of keywords that are easy to understand. The following SQL statement returns all records from a table named „Customers“:
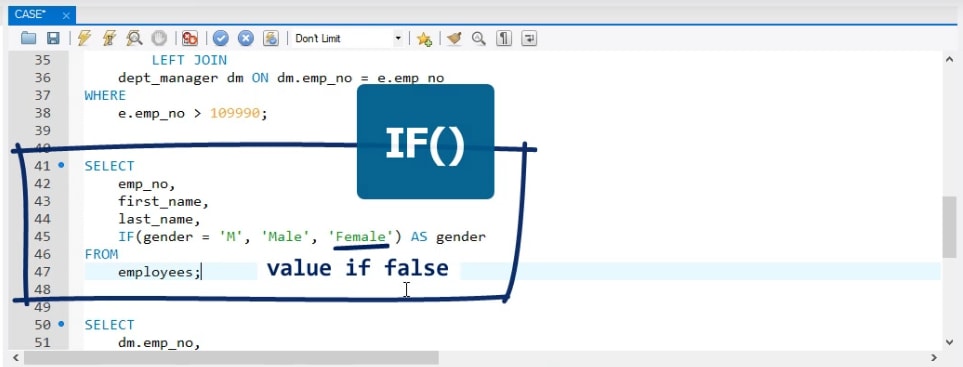
Let me guess: you’ve stumbled upon concept of named queries and you wonder where it fits in SQL. Well, from my knowledge, named queries haven’t got anything to do with „pure“ SQL, but they’re a concept found in various ORM (object relational mapping) frameworks, ala Java Persistence API. Basically, a named query is one way to map a name to a query that IIF (Immediate IF) is a logical function in SQL Server that allows you to conditionally return one value or another based on a specified condition. It takes three arguments: a Boolean expression that evaluates to true or false, a value to return if the expression is true, and a value to return if the expression is false. Predicates boil down to either a TRUE or a FALSE result. You can filter out unwanted rows from the result of an SQL query by applying a WHERE clause whose predicate excludes the unwanted rows.
The structured query language (SQL) uses the SQL WHERE Clause for data filtering based on the applied conditions. It is commonly used in the Select, Update, or delete statement. Let’s go ahead and explore the WHERE clause, its syntax, usage for single or multiple conditions, including and excluding data based on query expression. The SQL EXISTS condition is used to test whether a correlated subquery returns any results. If the subquery returns at least one row, the EXISTS condition evaluates to TRUE; otherwise, it evaluates to FALSE. The EXISTS operator can be used in various SQL statements like SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT, and DELETE to filter data based on whether certain
Consider the simplified SQL query below, in an Oracle database environment (although I’m not sure that it’s Oracle-specific): SELECT t0.foo, t1.bar FROM FIRST_TABLE t0, SECOND_TABLE t1 WHERE
SQL Server function IIF in WHERE clause
- what does positional and named parameter in a query mean?
- What does a sign mean in an Oracle SQL WHERE clause?
- SQL Boolean Data Types: True False or Null?
- Return Boolean Value on SQL Select Statement
When SQL Server comes across your $ sign, it automatically converts it into a money data type. Because you don’t have an explicit value after the dollar sign, SQL Server is assuming 0.00. From MSDN: When converting to money or smallmoney, integers are assumed to be monetary units. For example, the integer value of 4 is converted to the money equivalent of SQL predicates are the building blocks of effective data filtering and manipulation in databases. They allow you to specify conditions that determine which rows are affected by your SQL statements. In this article, we’ll dive deep into SQL predicates, exploring their various forms and applications through practical examples. I have a simple query and all I want to do is check if this variable is true or false, and for some reason it always returns false. DECLARE @CappedIFCheck BIT SET @CappedIFCheck = (SELECT distinct
NOT The NOT command is used with WHERE to only include rows where a condition is not true. The following SQL statement selects all fields from „Customers“ where country is NOT „Germany“: Applies to: SQL Server Azure SQL Database Azure SQL Managed Instance Azure Synapse Analytics Analytics Platform System (PDW) SQL analytics endpoint in Microsoft Fabric Warehouse in Microsoft Fabric SQL database in Microsoft Fabric Preview A predicate is an expression that evaluates to TRUE, FALSE, or UNKNOWN. Predicates are used in the search
There are 2 possible confusions I can imagine you experiencing here. The first is, as others have mentioned, expr1 OR expr2 returns true whenever either expr1 or expr2 is true. Since 1=1 is always true, your WHERE statement will be true for every record in the table. The second thing you might be confused about is that last — ‚ in the query. The — is the SQL Definition and Usage The IIF () function returns a value if a condition is TRUE, or another value if a condition is FALSE. Syntax I’m reading a book about SQL. In that book there’s the term Ad Hoc Query, which I don’t understand. What exactly is an ad hoc query?
In SQL, some records in a table may not have values for every field, and such fields are termed as NULL values. These occur when data is unavailable during entry or when the attribute does not apply to a specific record. How to return a boolean value on SQL Select Statement? I tried this code: SELECT CAST(1 AS BIT) AS Expr1 FROM [User] WHERE (UserID = 20070022) And it only returns TRUE if the UserID exists on the table. I want it to return FALSE if What are the differences between a query, a native query, a named query and a typed query? Does the ‚alone-standing‘ query even exist, or is it just an abbreviation? In my mind, a native Query is a query written in simple sql, whereas a named query relates to entities (hibernate-mapping). Can someone explain this briefly?
- Difference between EXISTS and IN in SQL?
- Statements and Queries in SQL Baeldung on SQL
- SQL WHERE Clause Predicates
- what’s the meaning of ‚admin‘ OR 1=1
SQL Wildcard Characters A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column. Definition and Usage The query () / mysqli_query () function performs a query against a database.
PHP mysqli query Function
I’ve noticed that Visual Studio 2008 is placing square brackets around column names in SQL. Do the brackets offer any advantage? When I hand code T-SQL I’ve never bothered with them. Example: Visual A positional parameter is set by its index in the clause. A named parameter is set by its name. When you are setting the values, you might have the values in an array, in which case the positional form could me more useful. Alternatively, you might have them in an associative array by name, in which case the named form is more useful. I still live in this ambiguity: conceptually what’s the difference between a statement and a query in SQL? Can anybody give a definition for each of them? It would be useful, for example when choosing variables names inside programs in a way that will be clear for everybody. Thanks! ADDITIONALLY: How can I call a chunk of SQL code made by more than
You can set table aliases in SQL typing the identifier right after the table name. SELECT * FROM table t1; You can even use the keyword AS to indicate the alias. SELECT * FROM table AS t1; What’s the difference between them if any? I see old DBA people tend to write statements without AS, but most of the new tutorials use it. Update: I know what’s the purpose SELECT Query: A select query is used to retrieve data from a single table of a combination of multiple tables. SQL uses a SELECT statement to select, or extract, specific data based on the given base condition. I’d think <> would mean ‚greater than or less than‘ when it comes to a number, which is equivalent to ’not equal to‘, but I can’t really see any reason for its existence in MySQL when != already existed, unless it’s there as a quicker keystroke alternative or for people that are used to <>. I’m guessing that’s what’s meant by ’syntactic sugar‘ in this context.
W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more. What does „:“ stand for in a query? A bind variable. Bind variables allow a single SQL statement (whether a query or DML) to be re-used many times, which helps security (by disallowing SQL injection attacks) and performance (by reducing the amount of parsing required). How does it fetch the desired value? Before a query (or DML) is executed by Oracle, your
202 In SQL, a comparison between a null value and any other value (including another null) using a comparison operator (eg =, !=, <, etc) will result in a null, which is considered as false for the purposes of a where clause (strictly speaking, it's "not true", rather than "false", but the effect is the same). In this guide, we will explain the SQL concatenation operator, its syntax, use cases, and practical examples to help us write more efficient and readable SQL queries. What is the SQL Concatenation Operator? The concatenation operator in SQL is used to combine two or more strings or columns into a single string.
What is SQL Expression? An SQL expression is a combination of one or more values, operators and SQL functions that are all evaluated to a value. These SQL EXPRESSION (s) are like formulae and they are written in query language. You can also use them to query the database for a specific set of data. Expressions are used in WHERE clause of an SQL query. As you might
- When Do Magnolias Bloom? , The Meaning of the Magnolia Flower
- What To Do With Leftover Egg Yolk
- Whatsapp Imune: Veja Como Funciona E Os Riscos
- When Did Punctuation Start? : When and why did American English begin to use different punctuation?
- What’S The Fastest Way To ‚Farm‘ Angel Room Items?
- When Did Gibbs Leave Ncis? _ How and Why Jack Sloane Left ‚NCIS‘
- Whatsapp Fehlercode 403 | Schnelle Hilfe für die häufigsten WhatsApp-Fehler
- Wheel Stand Pro G29 In Yoga Ausrüstung Online Shoppen
- What Western Allies Must Do For Ukraine — And For Themselves
- Whatsapp: Chat-Backups Ohne Icloud Von Iphone Zu Iphone
- What We Still Don’T Know About Trump’S Medical Condition
- What To Wear In 68 Degree Weather
- What Was The Significance Of Jesus‘ Seamless Garment?
- What’S Inside The Notebooks Of Leonardo Da Vinci?