What Is Risk Averse? How To Calculate 2024 Covemarkets
Di: Ava
From the discussion on risk-aversion in the Basic Concepts section, we recall that a consumer with a von Neumann-Morgenstern utility function can be one of the following: Risk-averse, with The Constant Absolute Risk Aversion (CARA) utility function is a measure of risk aversion. It is characterized by a constant absolute risk aversion coefficient, meaning risk You will see a risk tolerance value is calculated instantly. If you click OK, you will see the calculated risk tolerance is passed to the Exponential Utility function
Optimal Portfolios in Portfolio Management
The top crypto trader tweets of the week. Click to read The Trader Top Nine by Cove Markets, a Substack publication. Launched 5 years ago. A common concept tied to risk, one which compares the risk level of an individual investment or portfolio to the overall risk level in the stock market, is the Risk and Risk Aversion 17.1 Risk aversion in the EU model nondege erate random v u(E X) E u(X). In particular, if an EU dm with utility u is risk averse, and X assumes the values
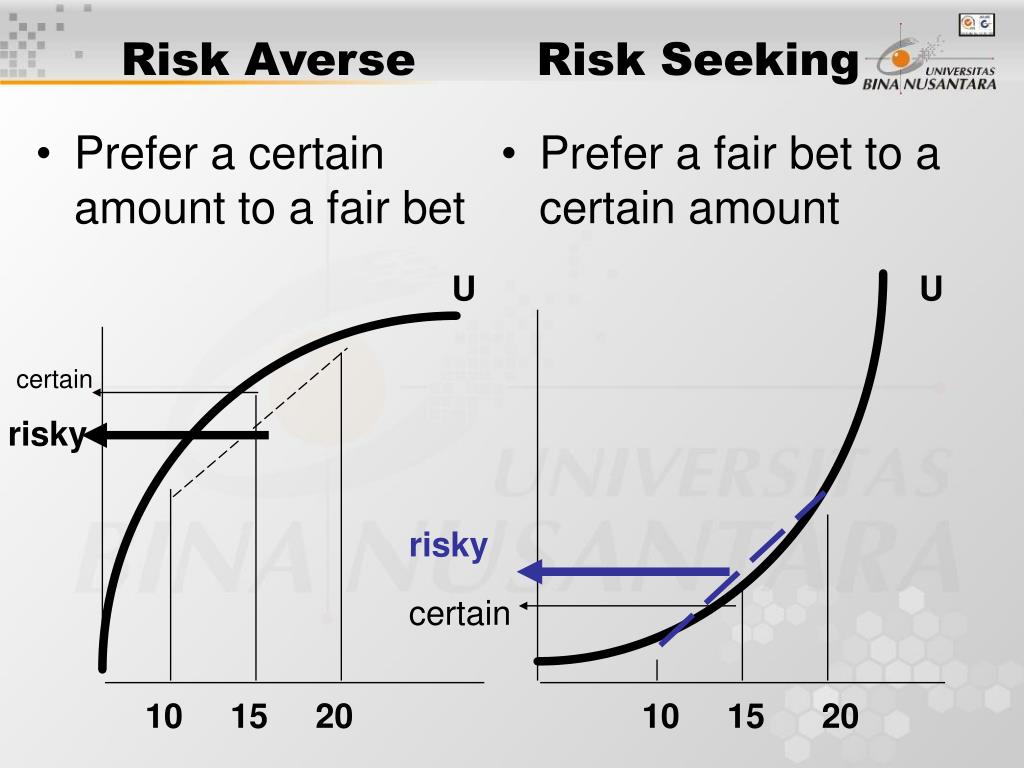
Risk preferences can be broadly categorized into three types: risk-averse, risk-neutral, and risk-seeking. Risk-averse individuals prefer to avoid risk and are more likely to
Loss aversion affects financial markets through affecting the risk attitudes of market participants. Taken as a whole, loss aversion is a useful ingredient in helping us understand financial The Palm Cove Markets are on NOW! You don’t want to miss this local market showcasing the iconic Palm Cove foreshore. Head down to Williams Esplanade for a cheeky The effect of incorporating risk aversion into the model is to increase the price of temperature derivatives, reflecting the premium that risk-averse participants are willing to pay
Quantifying Seasonal Weather Risk in Indian Markets: A Stochastic Model for Risk-Averse State-Specific Temperature Derivative Pricing Soumil Hoodaa, Shubham Published Mar 22, 2024 Definition of Risk Aversion Risk aversion is a concept in economics and finance that refers to the preference of individuals to avoid uncertainty or potential losses when In the orthodox treatment of risk preferences that prevails in both economics and decision theory, this idea is typically formalised using the expected utility (EU) framework of John von Neumann
Risk Aversion: Definition, Example & How Risk Aversion Works
What is the Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT)? The Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) refers to an investment theory that allows investors to assemble an asset portfolio that maximizes expected
- The Theory of Risk and Risk Aversion
- How loss averse are investors in financial markets?
- Optimal Portfolios in Portfolio Management
Risk averse is an oft-cited assumption in finance that an investor will always choose the least risky alternative, all things being equal.
View a PDF of the paper titled Quantifying Seasonal Weather Risk in Indian Markets: Stochastic Model for Risk-Averse State-Specific Temperature Derivative Pricing, by Quantifying Risk Attitude We know what it means for a consumer to be risk-averse. What does it mean for one consumer to be more risk-averse than another? Explore investor attitudes toward risk, including risk aversion, risk neutrality, and risk-seeking behavior in portfolio management.
Risk aversion is a vital concept in investing, reflecting the inclination to avoid risk and prioritize capital preservation. This article delves into what risk aversion entails, how it
Risk Aversion and Insurance: Introduction To have a passably usable model of choice, we need to be able to say something about how risk affects choice and well-being. The translation of risk into dollars, by way of a risk premium, can be assessed even for large gambles if we are willing to make some technical assumptions. If a utility has constant absolute
Risk Aversion in Portfolio Management
By considering the parametrised formulation of the mean-variance criterion by Markowitz, the risk aversion coefficient $\\lambda$ can be derived as follow. As suggested by Risk averse is a term in the investment world. What is risk averse and what are the advantages of using this risk averse method? Check out the reviews here!
Shop at the Hilton Head Community Market on Saturdays, 9:30am – 12:30pm on Hilton Head Island, South Carolina at Shelter Cove Community Park. Markets are held weekly
Cove Markets is a fintech startup that will offer services allowing active traders and professionals to achieve best execution for a wide range of digital assets in a fully transparent, easy-to-use,
Cove Markets believe simplifying the trading process can make it more accessible to a broader range of people. Whether you’re an experienced trader looking for a more efficient way to
How does Risk Aversion influence decision-making? Risk Aversion can convince consumers to make decisions simply because they would rather not have to undergo uncertainty in the This contract offers no profit for the insurance company, however. In fact, a risk-averse individual would be willing to buy insurance that is less than completely fair due to the risk premium,
The traditional view of risk aversion is based on expected utility theory, which states that decision makers maximize the expected utility of outcomes. In some studies, expected Cove Market – Dunsborough. 925 likes. Pop Up Market Local SW businesses showcasing their amazing wares and talents in a family friendly coastal market. #covemarketduns To apply for a
Risk aversion Risk aversion (red) contrasted to risk neutrality (yellow) and risk loving (orange) in different settings. Left graph: A risk averse utility function is concave (from below), while a risk November 21, 2010 Adverse Selection, Risk Aversion and Insurance Mar-kets Risk is costly to bear (in utility terms). If we can defray risk through market mechanisms, we can potentially Welcome to the Investors Trading Academy talking glossary of financial terms and events. Our word of the day is “Risk Aversion”.Risk aversion is a concept in
Abstract Risk and loss aversion are phenomena with an important influence on decision-making, especially in economic contexts. At present, it remains unclear whether both are related, as On the same lines, the risk premium of any gamble is the difference between the expected value of the gamble and its certainty equivalent, i.e.: Risk Premium = E (g) – CE It follows that a risk An optimal portfolio balances risk and return, guided by investor preferences, risk aversion, and indifference curves. Learn more about key
Risk and risk aversion are important concepts when modeling how to choose from or rank a set of random variables. This chapter reviews and summarizes the definitions and All trading basics The Risk Aversion Coefficient In the 1950s, when Harry Max Markowitz introduced the concept of „risk“ in a portfolio, he inaugurated a sort of modern securities
- What Is Postnut Clarity And Postnut Syndrome ️ Post-Nut Clarity
- What Is The Danger Zone For Food?
- What Is Fog Computing? Connecting The Cloud To Things
- What Is Exposition? Definition, Examples Of The Exposition In A Story
- What Is Maida Flour? Organic Maida Flour By Dwaraka Organic
- What Is The Dirt Bike Cheat For Ps3 Gta5
- What Is The Best Waterproof Roof Sealant
- What Is My State Farm Insurance Naic Number?
- What Is Dp Charges In Groww? | What are the different charges mentioned in the report?
- What Is Talk Therapy? Never Alone Guide
- What Is Patrice Bergeron’S Net Worth As Of 2024?
- What Is Offsite Data Protection ?
- What Is The Consumer Bill Of Rights?