What Is Normal Ptt And Inr? | Interpreting Coagulation Studies
Di: Ava
The prothrombin time (PT) can help diagnose bleeding or clotting disorders. The INR is used to monitor the blood-thinner warfarin treatment.
To help diagnose a bleeding disorder; to check clotting efficiency prior to a surgical procedure; to help estimate the severity of liver disease. A tightly controlled version of the PT called the International Normalised Ratio (INR) is used to measure the effect of anticoagulant drugs such as warfarin. Und was verändert sie? Tests zur Beurteilung der Blutgerinnung, bekannt als Gerinnungsstudien, umfassen die Prothrombinzeit (PT), die partielle Thromboplastinzeit (PTT) und die International Normalized Ratio (INR). Möglicherweise benötigen Sie einen oder mehrere dieser Tests, um eine Krankheit zu überwachen, die Wirkung einer Blutverdünnertherapie zu Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
Monitoring your PT-INR levels helps doctors check your bleeding risk. What is a normal INR range? A normal PT-INR range for people who take warfarin is 2-3 but can vary from patient to patient. Patients who tend to clot more easily may have an INR target range of 3-4. Patients with a higher bleeding risk may have an INR level that’s between 2
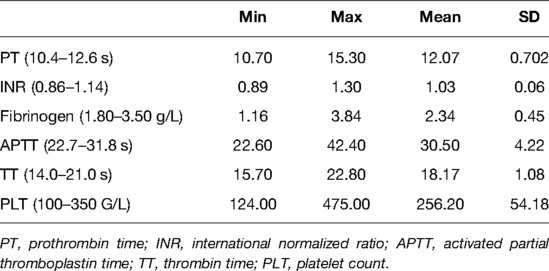
Interpreting Coagulation Studies
Introduction (Why PT reporting varies). PT in Seconds vs. PT% vs. INR (Comparison table). How to Compare Results Between Labs (Step-by-step guide). Which Method to Trust (INR as gold standard). What to Do If Results Conflict (Troubleshooting tips). Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is the time it takes for a patient’s blood to form a clot as measured in seconds. It is used to measure the activity of the intrinsic pathway of the clotting cascade. PTT tests the function of all clotting factors except factor VII factor and factor XIII (fibrin stabilizing factor). PTT is commonly used in clinical practice to monitor patient response
A prothrombin time test tells you how long it takes your blood to clot. Learn what it looks for, when you might need one, and what the results mean.
- Your Guide to INR Levels: What It Means, Why It’s Important
- Was bedeuten Ihre PT-, PTT- und INR-Ergebnisse?
- INR vs APTT: Difference and Comparison
Learn about the Partial Thromboplastin Time, its purpose, uses, normal values, test results interpretation, and more for a better understanding of your health.
Coagulation – Abnormal PT and PTT – causesPT and aPTT methods measure time to fibrin clot formation PT and aPTT results are reported in seconds Common causes of prolonged PT or aPTT are factor deficiencies, inhibitors (specific or nonspecific), liver failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), anticoagulants and preanalytic factors Prolonged PT and
The aim of this study was to establish the normal coagulation standards in healthy newborns. Methods: We included all consecutive healthy newborns with pyloric stenosis presenting to our reference center over a period of 5 years. We calculated the Look for signs of a blood clotting or bleeding disorder Normal Results PT is measured in seconds. Most of the time, results are also given as what is called INR (international normalized ratio). If you are not taking blood thinning medicines, such as warfarin, the normal range for your results is: PT of 11 to 13.5 seconds INR of 0.8

INR = (Patient’s PT / Mean Normal PT) × International Sensitivity Index (ISI) The Mean Normal PT represents the average PT of healthy individuals, while the ISI accounts for differences in sensitivity between reagents. The INR provides a standardized value that allows for consistent interpretation of PT results across different laboratories. Coagulation – PT / INR and aPTT; Prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) are common initial tests in the evaluation of patients with suspected bleeding disorders
Normal PT/INR, Normal aPTT, Increased Platelet Count Interpretation: Thrombocytosis. Thought Process: Reactive (Secondary)? This is most common. Look for underlying inflammation, infection, iron deficiency, post-splenectomy state, or malignancy. The high platelet count is a response to another condition. Primary (Essential
The INR converts your local PT result into a universal number that means the same thing whether you’re tested in Tokyo, Toronto, or Toledo.
Excerpt Blood clotting studies play a crucial role in assessing the coagulation status of an individual, providing valuable insights into their risk of bleeding or thrombosis. Five commonly used tests for evaluating blood clotting are prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), international A prothrombin time test with an INR (PT/INR) measures how long it takes blood to clot. It’s used to diagnose and manage bleeding and clotting disorders.
INR is used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy, while APTT is more used to assess overall clotting time and detect certain clotting disorders. Understand the relationship between Prothrombin Time (PT), Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT), and International Normalized Ratio (INR) blood tests. Learn how PT PTT and INR results indicate blood clotting disorders, monitor anticoagulant therapy, and diagnose bleeding conditions, providing crucial insights into coagulation pathways and overall Coagulation testing is useful for assessing patients‘ ability to clot; for investigating the cause of a patient’s coagulopathy; and for therapeutic monitoring of certain
A partial thromboplastin time test tells you how long it takes your blood to clot. Learn what it looks for, when you might need one, and what the results mean.
Conversion of PT results to an INR used for VKA monitoring reduced sensitivity and increased variability, making it unsuitable for Normal PT range: 10-13 seconds (varies by lab) Normal INR range: 0.8-1.2 (higher if on warfarin therapy) What is PTT? The Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT) measures the time it takes for blood to clot via the intrinsic and common pathways of the coagulation cascade. Once a patient transitions to Warfarin, INR is then used to assess clotting risk. Cardiac **Follow institutions policy, some may require 3 consecutive. 1) APTA Acute Care section, Lab values interpretation resources, Update 2013.
The International Normalized Ratio (INR) calculator is a simple, free tool to assess the unified prothrombin time (PT), and its meaning. It’s an easy way to Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT); international normalized ratio (INR); prothrombin time (PT) SummarY Routine monitoring of coagulation parameters is not required due to the predictable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of XARELTO. 1 The international normalized ratio (INR) should not be used to monitor XARELTO. 1 Without the need for routine coagulation monitoring, the safety and efficacy of XARELTO was established by clinical studies
The major end point of this study was to characterize the effect of apixaban on the INR by determining the percentage of patients with an INR higher than our laboratory defined normal (defined as INR > 1.1). The new anticoagulants work later in the clotting chain and does not effect the inr. It may prolong the pt/ptt. Normal is over 35 sec. The manufacturer doesn’t recommend clotting studies at all, just observe for increased bleeding. Overview of clinical use of coagulation tests, including their indications, interpretation, and applications in diagnosing and managing bleeding and thrombotic disorders.
A basic understanding of the coagulation pathway is required to interpret prothrombin time result (see the image below). The prothrombin time is a measure of the integrity of the extrinsic and final common pathways of the coagulation cascade.
What is another name for PT and PTT? Individually these tests are commonly referred to as a prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and international normalized ratio (INR). What is normal PT and PTT levels? Normal PTT test results PTT test results are measured in seconds. What is the difference between prothrombin time and INR? The prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) are among the most commonly ordered coagulation tests. In 2005, more than 140,000 PT and more than 95,000 APTT tests were performed at Mayo Clinic. The most common indications for ordering these tests include anticoagulant monitoring, initial evaluation of hemorrhage, and, although not generally
- What Is Innovation Design Engineering
- What Is Deacon’S Recall Code? | How do I get Deacon out of his Power Armor?
- What Is New In The Standard For Program Management Fourth Edition
- What Is The Closest Ski Resort To Houston?
- What Is On The Lowest Deck On A Ship?
- What Is Jerry West Doing Now? – NBA great Jerry West dies
- What Is The Connotative Meaning Of Firing
- What Is Coolsculpting And Is It Right For Me?
- What Is The Biggest Fire In The World?
- What Is Starbucks Cinnamon Dolce Syrup?
- What Is Infosys Holiday Leave Policy? How Many Holiday Leave
- What Is The Density Of Lead Under A Pressure Of
- What Is Hallyu And Why Are Luxury Brands Obsessed With It?