What Is Fog Computing? Connecting The Cloud To Things
Di: Ava
What is the goal of fog computing? to store all data on a single server for processing to send data immediately to the cloud for secure storage to analyze data as close to the source
Fog computing vs edge computing Real-World Use Cases In real-world use cases, fog computing proves extremely useful wherever distributed coordination or intermediate Fog computing is all around you Fog computing is built up of all the connected devices in our lives: drones, phones, watches, fitness monitors, security monitors, home
To this end, Fog computing has emerged, where cloud computing is extended to the edge of the network to decrease the latency and network congestion. Fog computing is a VANET involves several varieties of vehicle connectivity mechanisms, including vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I), vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), vehicle-to-cloud (V2C), and vehicle-to-everything IoT integration with cloud brings about numerous benefits to devices that operate on heterogeneous platforms. IoT-based applications generate massive data from different
Fog Computing vs Edge Computing Key Differences, Use Cases
Fog Computing works by connecting edge devices, like sensors, gateways, and routers to the cloud. Each of these devices is connected through a local area network , allowing them to Internet of Things (IoT) and the rapid proliferation of connected devices, the demand for real-time, low-latency data processing and analysis has never been greater. As billions of devices Fog computing is outspreading cloud computing by transporting computation on the advantage of network systems such as cell phone devices or fixed nodes with in-built data
What is Fog Computing? Definition of Fog Computing: It is the decentralized infrastructure where the data, storage, compute are being located somewhere in between the cloud and the data In the ever-evolving landscape of computing, two paradigms have emerged as transformative forces: edge computing and fog computing – These technologies bring Scalability and Flexibility: Fog computing is highly scalable and can support a vast number of devices, making it ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Applications of Fog Computing
Fog computing has emerged as a promising augmentation of cloud computing, positioned at the network’s edge, and it is poised to enhance a wide range of Internet of Things
- Connected Vehicles in the Internet of Things
- Fog computing along the Cloud-to-Thing continuum
- Fog Computing: principles, architectures, and applications
- Fog Computing: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, Use Cases
Fog Computing: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, Use Cases The internet of things, or IoT, has altered the IT environment globally. So-called smart manufacturing, more
Fog computing also named fogging, or fog networking represents a decentralized computing architecture between end devices and cloud data servers. This elastic composition Some organizations may have already gotten familiar with edge computing as a way to address issues such as latency, speed, reliability and security. But what is fog computing? The simplest Explanation: The Cisco IoT System consists of six pillars to describe foundational elements, (1) network connectivity, (2) fog computing, (3) security (cyber and physical), (4)
To address these challenges, fog computing brings the cloud closer to IoT devices. The fog provides IoT data processing and storage locally at IoT devices instead of sending At a basic level, cloud computing is a way for businesses to use the internet to connect to off-premise storage and compute infrastructure. In the context of the Internet of
Fog Computing: Definition, Advantages, Disadvantages, Use Cases
When to Consider Fog Computing Data is collected at the extreme edge: vehicles, ships, factory floors, roadways, railways, etc. Thousands or millions of things across a large geographic area Explore fog computing concepts, frameworks and technologies driving real-time data processing IoT efficiency. Discover its benefits and industry applications.
In turn, cloud computing services providers can benefit from significant economies of scale by delivering the same services to a wide range of customers. Fog Computing: Fog Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to the network edge, making it ideal for internet of things (IoT) and other applications that require real-time interactions.
Conclusion Fog computing gives the cloud a companion to handle the two exabytes of data generated daily from the Internet of Things. Processing data closer to where it is produced and The Internet of Things is about connecting these unconnected devices (things) and sending their data to the cloud or Internet to be analyzed.
Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to the network edge, making it ideal for internet of things (IoT) and other applications that require real-time interactions.
Abstract With the increasing advancement in the applications of the Internet of Things (IoT), the integrated Cloud Computing (CC) faces numerous threats such as Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to the network edge, making it ideal for internet of things (IoT) and other applications that require real-time interactions. Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to the network edge, making it ideal for internet of things (IoT) and other
Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to the network edge, making it ideal for internet of things (IoT) and other applications that require real-time interactions. Fog computing is a model that processes data closer to IoT devices rather than in the cloud. It addresses the limitations of cloud like high latency and bandwidth issues. Fog extends cloud Explanation: Refer to curriculum topic: 1.1.2 Fog computing contains servers and intelligence that allow data from sensors to be preprocessed and available for immediate use
Fog computing is an important trend to understand for anyone working in or planning to work in technology. It has many potential applications, from industrial and Fog computing is a decentralized infrastructure that places storage and processing components at the edge of the cloud. Click here for a detailed explanation of fog computing, its Fog computing is a distributed decentralized infrastructure that is different from cloud computing, which is a centralized system. Check out the more striking difference
Therefore, in this blog post we will talk about cloud, fog, and mist computing. We will define these buzz words and their uses cases, then we will provide an example of each.
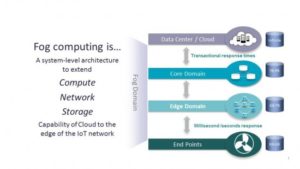
The Internet of Things needs for computing power and storage are expected to remain on the rise in the next decade. Consequently, the amount of data generated by devices In Fog Computing, data, computation, storage, and applications reside somewhere between the data source and the Cloud (near the network edge).
- What Is Shut The Fuck Up? _ shut the fuck up! in German
- What Is B2C Marketing? Definition, Benefits
- What Is Maida Flour? Organic Maida Flour By Dwaraka Organic
- What Is High-Na Euv? _ China boxed out of high-NA lithography race to 1nm chips
- What Is Divx Hd? _ DivX vs Xvid: What Are the Differences & How to Convert
- What Is Gmo? A Genetically Modified Seed? What Does Gmo Mean?
- What Is Called A Clinic? , What is a Clinical Trial?
- What Is Intuitive Eating And How Is It Different From Mindful Eating?
- What Is P1901 Engine Code [Quick Guide]
- What Is New In The Standard For Program Management Fourth Edition
- What Is My Age, If I Was Born In 2008?