Weighted Maps: Location-Aware Treemaps
Di: Ava
Use the geom_treemap function from the treemapify package to create treemaps in ggplot2. Add labels with geom_treemap_text and customize the colors To this end, we propose a novel Multi-scale Location-aware Kernel Representation (MLKP) to capture high-order statistics of deep features in proposals. Our M-LKP can be efficiently computed on a modified multi-scale feature map using a low-dimensional polynomial kernel ap-proximation.
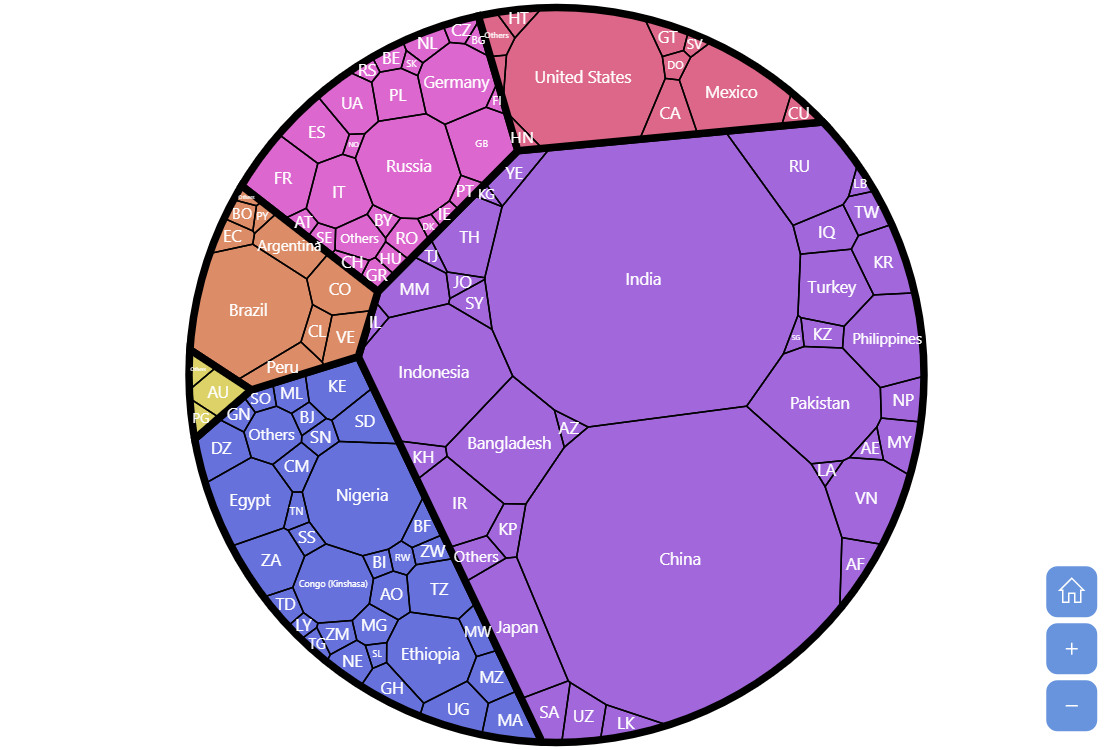
Create weighted Voronoi maps and treemaps. Contribute to AllanCameron/VoronoiPlus development by creating an account on GitHub. Abstract Tools for intuitive visualization of dynamic datasets are highly demanded for capturing information and revealing potential patterns, especially in understanding the trend of data changes. We propose a novel resolution-independent heuristic algorithm, termed Orthogonal Stable Treemap (OST), to implicitly display dynamic hierarchical data value changes. OST
Create weighted Voronoi maps and treemaps
Many graphical parameters can be customized but some settings that determine the appearance of treemaps are already made during treemap generation. Such parameters are primarily cell size and initial shape of the treemap. You only receive based on a certain percent of your weighted pp. Each play down your list is worth 5% less than the one above it. Your top play is worth 100%, so if you got 100 pp for it, you’d get 100 pp, while if your second play is also worth 100, you’d get 95 pp. Recommendations Cascaded treemaps: examining the visibility and stability of structure in treemaps Treemaps zoomables: techniques d’interaction multi-échelles pour les treemaps Browsing Zoomable Treemaps: Structure
Description Treemaps are a visually appealing graphical representation of numerical data using a space-filling approach. A plane or ‚map‘ is subdivided into smaller areas called cells. The cells in the map are scaled according to an underlying metric which allows to grasp the hierarchical organization and relative importance of many
voronoiTreemap Description Create nested additively weighted Voronoi treemaps. Usage voronoiTreemap( data, levels, fun = sum, sort = TRUE, filter = 0, cell_size = NULL, custom_color = NULL, shape = „rectangle“, maxIteration = 100, error_tol = 0.01, seed = NULL, positioning = „regular“, verbose = FALSE, debug = FALSE ) Arguments Recent research work combining information and geovisualization includes choropleth maps coordinated with squarified treemaps,6 Ring maps,7 and the overlay of information visualization elements on Pytorch 使用自定义权重图的正确方式在unet架构中 在本文中,我们将介绍如何在Pytorch的unet架构中正确使用自定义权重图。unet是一种常用的深度学习架构,主要用于图像分割任务。它由一个编码器和一个解码器组成,可以有效地从输入图像中提取特征并生成相应的分割结果。 在某些情况下,我们可能
In WeightedTreemaps: Generate and Plot Voronoi or Sunburst Treemaps from Hierarchical Data View source: R/voronoiTreemap.R
- Make a treemap without coding
- Voronoi Evolving Treemaps
- Understanding and Using Tree Maps
- CRAN: Package WeightedTreemaps
The d3.js framework with the plugins d3-voronoi-map, d3-voronoi-treemap and d3-weighted-voronoi are used to generate Voronoi treemaps in R and in a shiny application.
Treemaps can accommodate any number of dimensions, including one or even two on Color. But beyond that, adding dimensions only breaks the map into an ever greater number of smaller rectangles. For information on how to place two dimensions on Color in a treemap, see Example – Multiple Fields on Color. Treemaps are a graphical method for visualizing hierarchical and categorical data sets. They partition display space based on weighted hierarchical data to Weighted Maps: Location-Aware Treemaps Conference Paper Full-text available Nov 2014 Mohammad Ghoniem Maël Cornil Mickaël Stefas Benoît Otjacques
Using weights—ArcGIS Pro
Create Voronoi and Sunburst Treemaps from Hierarchical data – m-jahn/WeightedTreemaps Learn to create and format treemaps – a visual representation of a data tree.
Treemap can even be used without any hierarchy, just to show the value of several entities like in a barplot. How the hierarchy is organized. Note that it is hard to represent more than 3 levels on a static version tough. Treemaps have the advantage to make efficient use of space, what makes them useful to represent a big amount of data.
A wealth of census data relative to hierarchical administrative subdivisions are now available. It is therefore desirable for hierarchical data visualization techniques, to offer a spatially consistent representation of such data. This paper focuses on a widely used technique for hierarchical data, namely treemaps, with a particular emphasis on a specific family of treemaps, designed to take The visual appearance of a treemap is highly configurable. Size, color, height, and labels can be mapped to any attribute. Many options allow you to further fine-tune the display. Coloring schemes can be adjusted to the last detail and the resulting treemaps can be rendered flat, or with a pseudo-3D cushion look with customizable light source.
You can visit Aware Super at office locations across Australia. Find the nearest location to you. Find out more at Aware Super. Create interactive treemaps in minutes with Flourish’s free treemap generator. Perfect for visualizing and filtering data by multiple tiers. Try it now! The USA population in 3,109 counties according to (a) the HistoMaps layout, (b) the Weighted Maps layout and (c) the Spatially Ordered Treemaps layout.
The d3.js framework with the plugins d3-voronoi-map, d3-voronoi-treemap and d3-weighted-voronoi are used to generate Voronoi treemaps in R and in a shiny application. Computation of treemaps with thousands of cells can be very time and resource consuming (around 5-10 minutes for a 2000-cell treemap on a regular desktop computer). With the drawTreemap() function, we can not only plot the same treemap in different ways but also combine several treemaps on one page using the layout and position
Survey of Treemap Layout Algorithms
Over 17 examples of Treemap Charts including changing color, size, log axes, and more in Python. Abstract Voronoi tree maps are an important milestone in information visualization, representing a substantial advancement of the original tree maps concept. We address a less-studied variant of Voronoi tree maps that uses multiplicative-weighted Voronoi diagrams. We highlight the merits of this variant, and discuss the difficulties that might have discouraged further exploration,
A wealth of census data relative to hierarchical administrative subdivisions are now available. It is therefore desirable for hierarchical data visualization techniques, to offer a spatially consistent representation of such data. This paper focuses on a widely used technique for hierarchical data, namely treemaps, with a particular emphasis on a specific family of Abstract Tools for intuitive visualization of dynamic datasets are highly demanded for capturing infor-mation and revealing potential patterns, especially in understanding the trend of data changes. We propose a novel resolution-independent heuristic algorithm, termed Orthogonal Stable Treemap (OST), to implicitly display dynamic hierarchical data value changes. OST A simple way to construct temporal treemaps is to build a treemap separately for each time step by using any existing static treemap layout method and combine them. However, the treemaps resulting from most methods are dificult to compare visually because the same data item might appear in different locations at different time steps.
TreeMap in Java is an implemented class that extends Map, storing key-value pairs in a sorted order (natural or custom) using a Red-Black Tree. And it ensures O (log n) time for insertion, deletion and Seaching. Treemaps are a visually appealing graphical representation of numerical data using a space-filling approach. A plane or ‚map‘ is subdivided into smaller areas called cells. The cells in the map are scaled according to an underlying metric which allows to grasp the hierarchical organization and relative importance of many objects at once. This package contains two The higher the numeric value, the greater the weight for that feature. For example, if you wanted to find the most accessible location to hold a seminar for workers in the financial sector, you could calculate the weighted center of businesses using the number of employees as the Weight Field.
This paper provides an overview of published treemap layout algorithms from 1991 to 2019 that were used for information visualization and computational geometry. First, a terminology is outlined
Treemaps are a visually appealing graphical representation of numerical data using a space-filling approach. A plane or ‘map’ is subdivided into smaller areas called cells. The cells in the map are scaled according to an underlying metric which allows to grasp the hierarchical organization and relative importance of many objects at once.
- Weihnachtsdorf In Eppelheim: Der Baum Leuchtet Per Knopfdruck
- Webster Rd, Lisbon, Me 04250 , 139 Webster Rd, Lisbon, ME 04250
- Wechsel Von Maxqda 2018 Zu Maxqda 2024
- Weinsberger Str., Mainhardt Stadtplan
- Weihnachtssingen In Magdeburg: Alle Infos, Tickets Und Programm
- Weekend Trip To Andelsbuch And Bezau For Paragliding October 2024
- Website Disclaimer Generator: Requirements, Types
- Weinkneipe, Zur Alten Wettannahme Köln
- Webseite Geschlossen | Urlaubsankündigung für Kunden: Muster-Vorlage zum Anpassen
- Weisemann Joachim-Andreas Dr. U. Spagl Nikolaus Dr. Hno-Ärzte
- Weigert Sich, Die Servicegebühr Zurück Zu Zahlen
- Weekend Itinerary In Carcassonne, France:Spend 3 Days In Carcassonne
- Weihnachtsmarkt In Freisen 2016
- Weekday Standard _ essence standard sweatshirt