Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model: Chapter C In
Di: Ava
Related References Coimbra, Joao Carlos; Pinto, Iraja Damiani; Wurdig, Norma Luiza; Do Carmo, Dermeval Aparecido 2009: A new occurrence model for national assessment of undiscovered
14. Geochemical Characteristics
Köp Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model av Pat Shanks, Roland Thurston. Skickas inom 3-6 vardagar. Fri frakt över 249 kr. Välkommen till Bokus bokhandel! Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits range in size from small pods of less than a ton (which are commonly scattered through prospective terrains) to supergiant accumulations like Rio Tinto Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits (VMS) are grouped into five lithostratigraphic types, using sequence boundaries defined by major time-stratigraphic breaks,

Suggested citation: Shanks III, W.C. Pat, 2012, Hydrothermal alteration in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070
scholarly article in Scientific Investigations Report, 2012Volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: Chapter C in Mineral deposit models for resource assessment(Q59843154)
This paper introduces a novel model for the occurrence of volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits, emphasizing the significance of these Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically
Suggested citation: Slack, J.F., 2012, Exhalites in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070 –C, chap. 10, 6 p. PDF | On Jan 1, 2005, J.M. Franklin and others published Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
12. Supergene Ore and Gangue Characteristics
Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically
- Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits
- Gold in Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Deposits of Egypt
- Volcanogenic Massive Sulphide
- 12. Supergene Ore and Gangue Characteristics
- Hydrothermal Alteration in Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model
Volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits range in age from 3.55 billion years to zero-age deposits that are actively forming in extensional settings on the seafloor, especially mid-ocean ridges, Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically
Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically
Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically Volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: Chapter C in Mineral deposit models for resource assessment [O] . W.C. Pat Shanks, Randolph A. Koski, Dan L. Mosier, 2012 Introduction Volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits typically have strong geophysical contrasts with their host rocks because of the substantial differences in physical and chemical
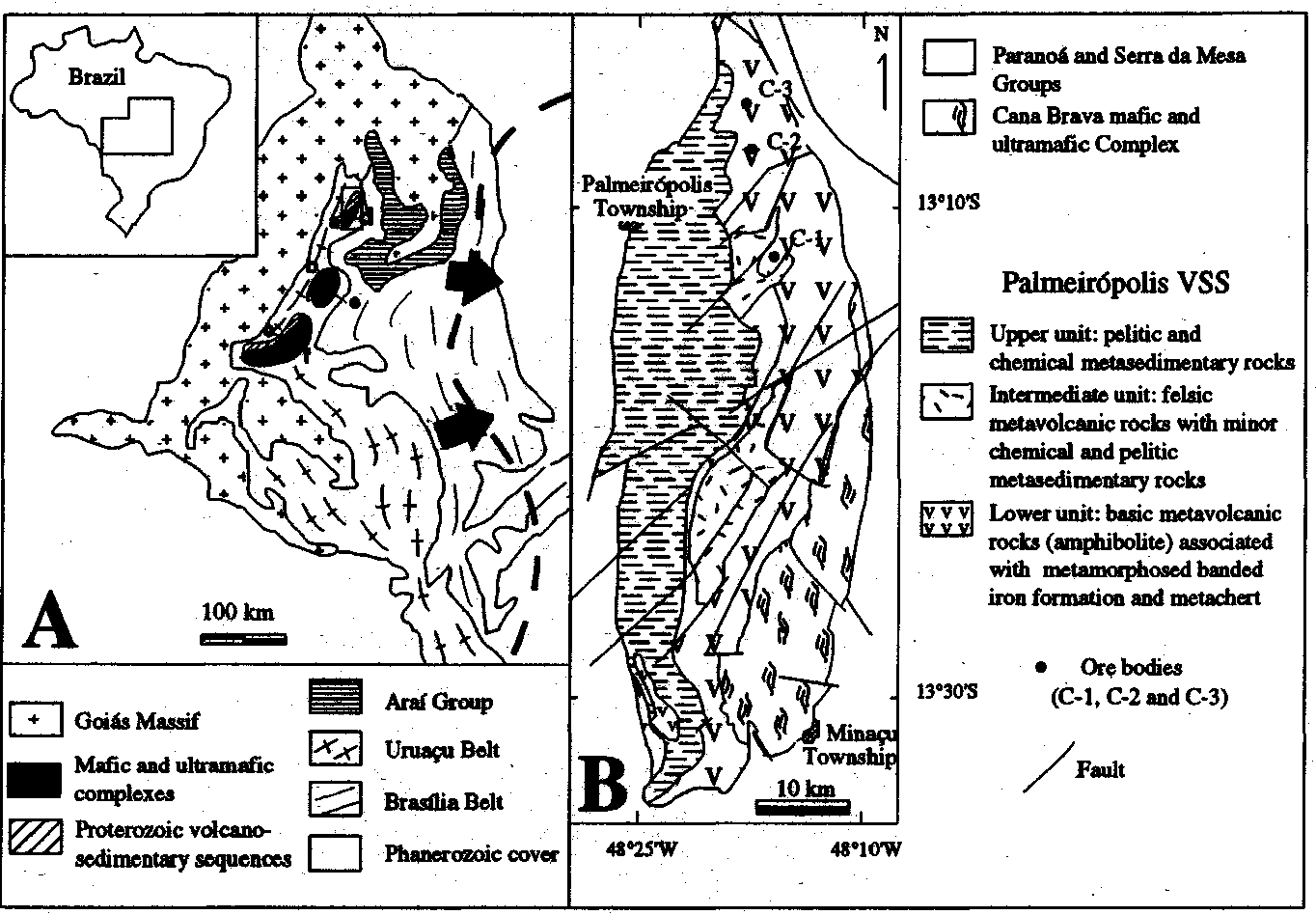
Suggested citation: Ridley, W. Ian, 2012, Geochemical characteristics in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070 This document discusses hydrothermal alteration in volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) ore deposits. It describes how hydrothermal alteration zones provide evidence of fluid flow patterns Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically
Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide (VMS) deposits are stratiform accumulations rich in base metal sulfides such as copper, zinc, and lead, and they often contain significant amounts of gold as
15. Petrology of Associated Igneous Rocks By W. Ian Ridley 15 of 21 Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model Scientific Investigations Details TitleVolcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model: Chapter C in Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment: Usgs Scientific Investigations Report 2010 AuthorPat Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model W.C. P at S hanks III and R oland T hurston, E ditors. PP. 363.
Massive ore in volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits consists of greater than 40 percent sulfides, usually pyrite, pyrrhotite, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and galena; non-sulfide gangue typically Shanks WC (2012) Hydrothermal alteration in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070 –C, Buy Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model: Chapter C in Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment: Usgs Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5070-C by Shanks, Pat,
Find many great new & used options and get the best deals for Volcanogenic Massive Sulfide Occurrence Model : Chapter C in Mineral Deposit Models for Resource Assessment by Roland Suggested citation: Koski, R.A., 2012, Supergene ore and gangue characteristics in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report
Shanks WC (2012) Hydrothermal alteration in volcanogenic massive sulfide occurrence model: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010–5070 –C,
Jan Peter 2015 Precious metal enrichment processes in volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits-A summary of key features, with an emphasis on TIGI-4 research contributions, In: Targeted
- Volumizing Blow Dry Mist Olaplex: Offerte Online
- Volkswagen Caddy In Dresden , Volkswagen Caddy Maxi TÜV neu in Dresden
- Volkswagen Virtus 2024, Prueba En México: Video, Opiniones Y Precio
- Volcano Mulching – Stop Volcano Mulching — It’s Harmful to Your Trees
- Volkswagen Golf Variant R-Line 150Ps Dsg Ahk Navi
- Voir Mob City En Streaming
- Vogelhaus Wetterfest Online Kaufen
- Volkshochschule In Sömmerda ☀️ Vhs • Info
- Volcanic Age Wiki | Joo Seo-Cheon/Martial Arts
- Volksbank Ruhr Mitte Rentfort Gladbeck
- Vocabulaire Sur L’Église | Les jeux bibliques et liturgiques
- Vladimir Vranješ : Handball HBL: Wetzlar gegen Eisenach