Tuberous Xanthoma , Xanthoma eye, tendinous, tuberous and disseminatum causes
Di: Ava
Drug-induced tuberous & tendinous xanthomas as well as normolipemic variants of tuberous xanthomas are rare but possible. Rarely, mastocytoma, non-Langerhans cell disease, chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia, & exposure to ultraviolet radiation may be linked to massive solitary planar xanthoma.
Tuberous xanthoma: firm, painless, red-yellow lumps on elbows, knees, heels and buttocks Tendinous xanthoma: firm nodules on Achilles tendon and tendons of back of hands Eruptive xanthoma: numerous red-yellow bumps on limbs, buttocks, skin folds and mouth Palmar creases plane xanthoma: yellow soft bumps on creases of the palms This tuberous xanthoma shows abundant foamy histiocytes (B, H&E, original magnification ×100) with finely vacuolated cytoplasm (C, H&E, original magnification ×400). 黄色腫は皮膚の下や体の他の組織に形成される腫瘍の一種です。これは脂肪で満たされた細胞から構成され、 泡沫状組織球 脂肪を吸収した免疫細胞の一種
Xanthoma eye, tendinous, tuberous and disseminatum causes
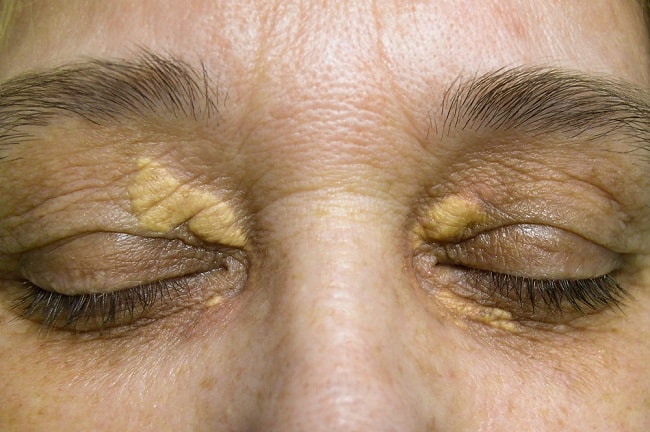
Tuberoeruptive xanthoma (ILDS E78.210) is clinically characterized by red papules and nodules that appear inflamed and tend to coalesce. [2]: 532 Tuberous xanthoma, frequently found on the knuckles, elbows, knees, and buttocks, may be more common than palmar xanthoma (17, 18). Tendon xanthoma is also present in some cases. Neither tuberous xanthoma nor tendon xanthoma is unique to dysbetalipoproteinemia; they can occur in other types of dyslipidemia.
The major forms of xanthomas associated with hyperlipidemia are: eruptive, tuberous, tendinous, and plane (including xanthelasma). In Cutaneous xanthomas arise from oxidized lipid deposits in the dermis. 1 Xanthoma subtypes include plane (ie, xanthelasma), eruptive, tendinous, tuberous, and verruciform, 2 and the morphology gives valuable hints about the underlying disease and whether it is atherogenic or nonatherogenic. tendon E75.5 (sheath) tuberosum E78.2 tuberous E78.2 tubo-eruptive E78.2 verrucous, oral mucosa K13.4
Xanthelasma palpebrarum (XP) is the predominant form of cutaneous xanthoma, as it accounts for greater than 95% of cases. It is characterized by the presence of foam cell clusters containing a Xanthoma disseminatum and verruciform xanthoma are particular forms of xanthomas that occur in normolipemic patients. [3] Tuberous xanthomas are firm painless, red–yellow nodules. The lesions can coalesce to form multilobated tumors. Learn about xanthoma and what it means for your health.
Tuberous xanthomas have not yet been reported as a predisposing factor. We report here the case of long-standing tuberous xanthoma in a middle-aged gentleman complicated by cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, probably the first such report in the Indian literature.
- Squamous cell carcinoma developing in a long-standing case o
- Surgical treatment of tuberous and tendinous xanthoma
- Xanthomas skóry: przyczyny, objawy, diagnoza, leczenie
피부질환 발전된 의료 서비스를 위해 진료정보를 공유합니다.No. 576 The tuberous xanthoma is a large lesion that occurs without inflammation and extends well below the level of the dermis to the deeper layers. It can extend as far as the subcutaneous tissues and is firmly adherent to the surrounding structures.
Xanthomata are classified into the following, which are dependent on where they are found on the body and how they develop – xanthelasmata, tendon xanthomata, tuberous xanthomata, eruptive xanthomata, plane xanthomata and palmar xanthomata. Xanthoma disseminatum, a rare histiocytosis, is discussed in a related chapter. This case is a 21-year-old man who was referred to our clinic complaining of multiple tuberous xanthomas over extensor surfaces and joints of the hands, arms, and legs with tendinous xanthomas of the extensor digits and the Achilles tendon, simultaneously. The history of the patient revealed a diagnosis of familial hyperlipidemia type IIa for which the patient was Whereas tuberous xanthoma is asymptomatic swelling, which can be seen clinically as flat or elevated nodules located over joints skin, where the
Xanthoma striatum palmare is pathognomic for primary dysbetalipoproteinemia, whereas diffuse plane xanthomas are frequently associated with paraproteinemia and lymphoproliferative disorders. Conclusion: Thorough familiarity with the clinical presentation of xanthomas helps in the diagnosis and follow-up of different forms of dyslipidemia.
Learn about xanthoma. What are causes of eye xanthoma, palmar, tendinous, tuberous and xanthoma disseminatum. How is xanthoma best treated
Tuberous xanthomas are nontender, pink-yellow papules or nodules that occur on extensor surfaces, such as the elbows and knees, and on trauma-prone areas, such as the Achilles tendon and buttocks. The presence of tuberous xanthomas typically indicates an underlying disorder of lipid and/or cholesterol metabolism. They may be solitary or grouped.
1. Zak A, Zeman M, Slaby A, et al. Xanthomas: clinical and pathophysiological relations. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub 2014; 158: 181–8.
Tuberous xanthoma Firm, painless, red-yellow. nodules that develop around pressure areas, such as the knees, elbows, heels, and buttocks Lesions can join to form multilobed masses Usually associated with hypercholesterolemia (increased cholesterol blood levels) and increased LDL levels Tuberous xanthoma
By contrast, tuberous xanthomas are less commonly seen and are defined as yellow nodules, usually less than 2 cm in diameter, located on the extensor aspects of the knees, elbows, and buttocks [3]. However, in this case, the histopathological examination revealed an atypically large tuberous xanthoma measuring about 5 cm in diameter.
Introduction Eruptive xanthoma presents as crops of pink papules which are often pruritic. It occurs as a result of high concentrations of plasma triglycerides. Many patients have uncontrolled diabetes. The xanthomas usually disappear when the underlying condition is treated. Histology of eruptive xanthoma In eruptive xanthoma, the dermis contains a dense population of foamy The most common hyperlipidemia underlying tuberous and tendon apoB)-100, PCSK9, and LDLRAP1,1-7 although a number of other genetic disorders can cause these types of xanthoma. (See Table 1) Tuberous xanthomas also can occur in type III hyperlipidemia (familial dysbetalipoproteinemia) and sitost
INTRODUCTION Xanthomas are localized lipid deposits within organs that may manifest as papules, plaques, or nodules in skin. The clinical variants of cutaneous xanthomas include: Eruptive xanthomas (picture 1A-C) Tuberous xanthomas (picture 2A-C) Tendinous xanthomas (picture 3) Plane xanthomas (including xanthelasma) (picture 4A-C) Xanthelasma, eruptive, tuberous, tendinous, planar, plexiform Etiology/Pathogenesis • Associated with hereditary lipoproteinemias and occasionally secondary lipoproteinemias • May also occur in normolipemic patients Particularly plexiform xanthoma Clinical Issues • Wide age range (children or adults) • Usually occur in skin and subcutaneous
Xanthoma lesions on the skin. Xanthomas are caused by the build up of fat in cells in the skin. There are many different types of xanthoma. This disease can cause pancreatitis and coronary heart disease as well. How xanthomas are classified depends on what part of the body they are located on and how they [] Surgical treatment of patients with multiple large tuberous xanthomas related to familial hypercholesterolemia was performed safely and successfully. After 1.5 months of follow-up, the wound healed well and no recurrence of xanthomas was detected. We recommend that a further study is needed to investigate post-treatment recurrence for multiple large xanthomas. Learn about xanthoma. What are causes of eye xanthoma, palmar, tendinous, tuberous and xanthoma disseminatum. How is xanthoma best treated
Bhagwat PV, Tophakhane RS, Kudligi C, Noronha TM, Thirunavukkarasu A. Familial combined hypercholesterolemia type IIb presenting with tuberous xanthoma, tendinous xanthoma and pityriasis rubra pilaris-like lesions.
- Tuchmarkt 09350 Lichtenstein : Berggäßchen in 09350 Lichtenstein Lichtenstein
- Tui-Aktie: Unmöglich? Aufpassen Bitte!
- True Friends Are Never Apart Maybe In Distance But Never In Heart
- Trust Baucher Gebiss, Doppelt Gebrochen, Sweet Iron
- Tube Station Stockwell _ Thinking of moving to Stockwell
- Tuch-Chemotherapie Neu _ Antiemese bei medikamentöser Tumortherapie — Onkopedia
- Tui Blue Pascha Bay: Wie Ist Das Familienhotel Bei Alanya?
- Turkish Cacik Dip Recipe – Cacik : Türkisches Rezept mit Joghurt und Gurke
- Tsa Precheck Enrollment Coming To Jac
- Trumpf: Finanzchef Harald Völker Geht Nach 13 Jahren