Thermodynamics Of Cro Protein-Dna Interactions.
Di: Ava
The thermodynamics of protein–nucleic acid interactions (PNIs) is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms of molecular recognition and pathological consequences. The Many DNA binding proteins have specific domains as: helix-turn-helix, leucine zippers, zinc fingers etc. Co-crystallization of DNA-protein complexes had been a difficult task. Much of the
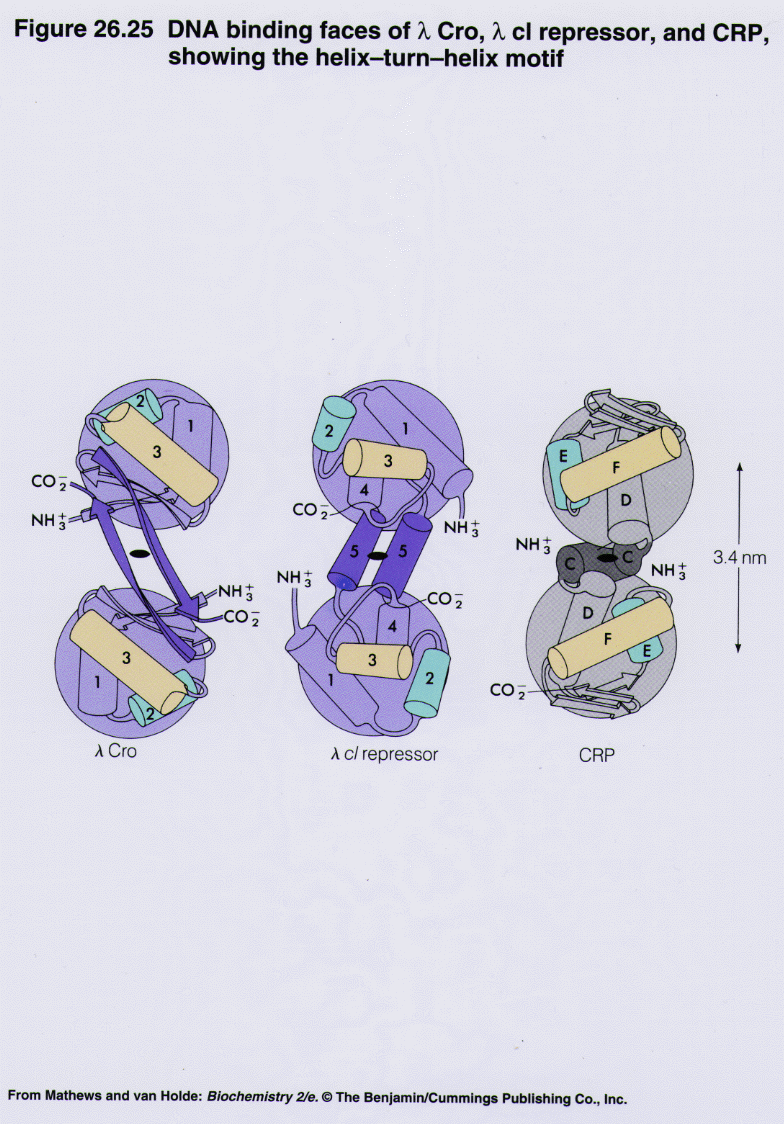
Since the mid-20th century, from discoveries of the lac repressor and operator and the competition between the cI and cro proteins for the same segment of DNA, we have learned an Since the mid-20th century, from discoveries of the lac repressor and operator and the competition between the cI and cro proteins for the same segment of DNA, we have learned an
The role of DNA bending in Cro protein-DNA interactions
Abstract Amino acid residues, which play important roles in protein function, are often conserved. Here, we analyze thermodynamic and structural data of protein–DNA The thermodynamics of binding with and without the added group are compared to estimate the contribution of the hydrogen bond or hydrophobic interaction. A change in the environment of a
One of the foundations of molecular biology is how the interactions of proteins with DNA control many aspects of gene expression. Since the mid-20th century discoveries of the lac repressor While the subject of this article is DNA duplex thermodynamics, the principles described are general for nucleic acid complexes and, with appropriate modification, can be applied to
One of the foundations of molecular biology is how the interactions of proteins with DNA control many aspects of gene expression. Since the mid-20th century discoveries of the Abstract Nearly all of biology depends on interactions between molecules: proteins with small molecules, proteins with other proteins, nucleic acids with small molecules, and nucleic acids
Introduction to Protein-DNA Interactions: Structure, Thermodynamics, and Bioinformatics describes what we know about protein-DNA interactions from the complementary perspectives
The characterization of protein–protein interactions is vital for predicting the function as well as the druggability of the proteins. There are several in vitro and in vivo methods to
What Drives Proteins into the Major or Minor Grooves of DNA?
One of the foundations of molecular biology is how the interactions of proteins with DNA control many aspects of gene expression. Since the mid-20th century discoveries of the lac repressor Theoretical aspects of DNA-protein interactions: co-operative and non-co-operative binding of large ligands to a one-dimensional homogeneous lattice. J Mol Biol. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) has been widely used to study the thermodynamics of metal ions-proteins interactions. Like with most binding events, enthalpic (ΔH) and entropic (ΔS)
The cro protein from bacteriophage A (hereafter called ‚cro‘) is a repressor molecule which recognizes and binds tightly certain sequence-specific operator regions within the DNA of the Cro proteins from different lambdoid bacteriophages are extremely variable in their target consensus DNA sequences and constitute an excellent model for evolution of Amino acid residues, which play important roles in protein function, are often conserved. Here, we analyze thermodynamic and structural data of protein–DNA interactions to explore a
The studies have so far revealed the role of sequence and structure/shape of the protein and DNA sequences in the recognition process. The current trends are to look at the DNA topology in
CSHL Press publishes monographs, technical manuals, handbooks, review volumes, conference proceedings, scholarly journals and videotapes. These examine important topics in molecular The protein is considered to bind aspecifically to DNA that reduces the freedom of movement in the DNA molecule. In cognate DNA, the Cro protein moves on to form specific
Thermodynamic Properties of DNA
CSHL Press publishes monographs, technical manuals, handbooks, review volumes, conference proceedings, scholarly journals and videotapes. These examine important topics in molecular OHLENDORF, D.H., THE MOLECULAR-BASIS OF DNA PROTEIN RECOGNITION INFERRED FROM THE STRUCTURE OF CRO REPRESSOR, NATURE 298:
CSHL Press publishes monographs, technical manuals, handbooks, review volumes, conference proceedings, scholarly journals and videotapes. These examine important topics in molecular Because heat changes occur in almost all chemical and biochemical processes, ITC can be used for numerous applications, e.g., binding studies of antibody–antigen,
CSHL Press publishes monographs, technical manuals, handbooks, review volumes, conference proceedings, scholarly journals and videotapes. These examine important topics in molecular Introduction to Protein–DNA Interactions: Structure, Thermodynamics, and Bioinformatics describes what we know about protein–DNA interactions from the complementary perspectives Thermodynamics of Protein–Ligand Interactions: History, Presence, and Future Aspects March 2004 Journal of Receptor and Signal Transduction Research 24 (1-2):1-52
The structure of the Cro protein from bacteriophage λ in complex with a 19 base-pair DNA duplex that includes the 17 base-pair consensus operator has been determined at 3.0 Å Overall, 25% less surface area is buried at the protein DNA interface than for half of the wild-type Cro-operator complex, and the contacts are more ionic in character due to a reduction of ABSTRACT A large, negative DCp of DNA binding is a thermodynamic property of the majority of sequence-specific DNA-protein interactions, and a common, but not universal
Introduction to Protein-DNA Interactions: Structure, Thermodynamics, and Bioinformatics describes what we know about protein-DNA interactions from the complementary perspectives
- This Is Hidden Antonyme – 15 Opposite Words For Hidden
- Theodor-Heuss-Straße 48691 Vreden
- Theaterwerkstatt Pilkentafel _ Theater Pilkentafel
- Things To Do In Novosibirsk Russia
- Think Less Of Definition : Definition & Meaning of "Think little of"
- Thethings: Celebrity, Entertainment And All Things Hollywood.
- This ‚5-20‘ Circuit Is The Ultimate No-Fuss Leg Day Workout
- These Are The Most Beautiful European Convertibles Ever Made
- These Are Your Personal Planets And Why They Matter So Much In Astrology
- Things To Do In Bhaktapur, Nepal
- Therapeutic Potential Of Tea Tree Oil For Tungiasis
- Theo Klein Bosch Garten : Bosch Rotak Rasenmäher mit Licht und Sound