The Survival Time Of The Ventriculo-Peritoneal-Shunt In Children With
Di: Ava
This study intends to assess the survival status and scrutinize the predictive factors of mortality among children after a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Methods: A retrospective cohort study was Hydrocephalus is common among children with myelomeningocele and is most frequently treated with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS). Although much is known about factors related to first
Analysis of factors affecting ventriculoperitoneal shunt survival in pediatric patients January 2013 Child’s Nervous System 29 (5):791-802 DOI: 10.1007/s00381-012-2004-5 Source Hydrocephalus; children; survival status; ventriculoperitoneal shunt; Ethiopia placed annually in Africa, where 17,789 were ventric-uloperitoneal [5,6]. In the past five decades, VP shunt METHODS In this retrospective cohort study, all patients undergoing externalization of a VPS at a single institution between 2005 and 2020 were grouped according
Ventriculoperitoneal shunts in children on peritoneal dialysis:
The prognosis of all the children was good, and there were no significant changes in eight cases. Conclusion: Ventriculoperitoneal shunt is
Abstract Purpose The ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt has become the procedure of choice for treatment of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). We aimed An analysis of factors determining the requirement of ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in the children suffering from posterior fossa tumour: a single centre retrospective review Correlation between cerebrospinal fluid abnormalities before ventriculoperitoneal shunt and postoperative intracranial infection in adult patients with hydrocephalus: A clinical study
Shunt related complications occurred in 11 (30%) children and 3 children had undergone revision of the shunt multiple times. Good outcome
Shunt surgery in children is associated with high revision and complication rates. We investigated revision rates and postoperative complications to specify current challenges associated with Mean survival after intra-abdominal metastasis detection was 3.8 months suggesting that glioma intra-abdominal metastasis carries adverse prognosis, although three
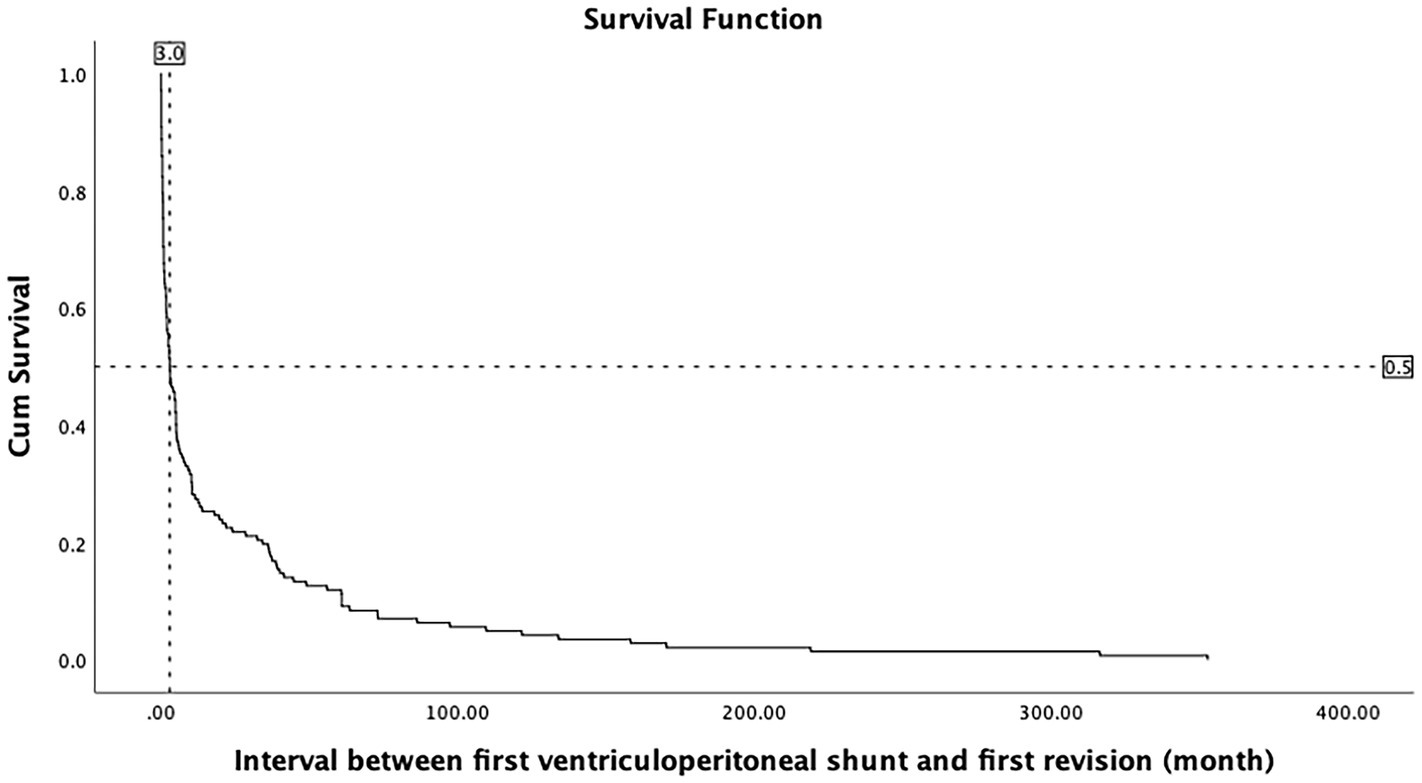
Purpose Management of hydrocephalus with insertion of ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is associated with significant complications in both adult and pediatric patients. These The Kaplan-Meier method of survival analysis was used to compare etiologies on the 5-year survival (revision-free) rate and the median 5-year survival time. A total of 253 The durability of endoscopic third ventriculostomy and ventriculoperitoneal shunts in children with hydrocephalus following posterior fossa tumor resection: a systematic review and time-to
Ventriculoperitoneal shunts in children: factors affecting shunt survival
Background: Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt therapy is a crucial intervention for normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH). This meta-analysis Cureus, 2021 Ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) is the most commonly used procedure for the treatment of hydrocephalus (HDC), especially in children. However, this is prone to many Children with a PVP shunt should not undergo school hearing screening with earphones and should be referred directly to the local Audiology service for testing using inserts.
The findings of the study indicate that age at shunt placement, etiology of hydrocephalus, type of hydrocephalus, and previous treatments before shunt surgery were independently significantly
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, all patients undergoing externalization of a VPS at a single institution between 2005 and 2020 were grouped according to the new Aim: To study the clinical outcome of shunt surgeries in children with hydrocephalus and evaluate the risk factors for ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt failure. Materials and methods: Patients who
Purpose Ventriculoatrial (VA) and ventriculopleural (VPL) shunts are used as alternatives when CSF diversion to the peritoneal compartment with a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Abstract The authors reviewed 175 paediatric patients with posterior fossa tumours treated at the Hospital for Sick Children at Great Ormond Street, London, between 1983 and 1993, in an MeSH terms Adolescent Child Child, Preschool Female Follow-Up Studies Glasgow Coma Scale Hospitals, University Humans Hydrocephalus / epidemiology Hydrocephalus / surgery* Infant
Descriptive statistics summarized the demographic and clinical information. The Chi-square test, independent t-tests, and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis were performed to
End stage renal disease (ESRD) is a rare condition in child-hood, with a reported incidence of only nine per million age-related population [1]. Peritoneal dialysis (PD) remains the preferred
Infants and children may present with vague signs and symptoms such as irritability, poor feeding, lethargy, increased head circumference, expanding sutures, bulging fontanelles, “sundowning” Methods: A retrospective review of patients, born during 2000-2005 diagnosed and treated for hydrocephalus at Children’s of Alabama was conducted. Survival analysis identified factors
Methods: The authors conducted a prospective, multicenter study of children (< 18 years) requiring first-time treatment for hydrocephalus with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Laparoscopic placement of the peritoneal portion of a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt can be done safely and effectively in children with multiple previous VPS revisions due to improved
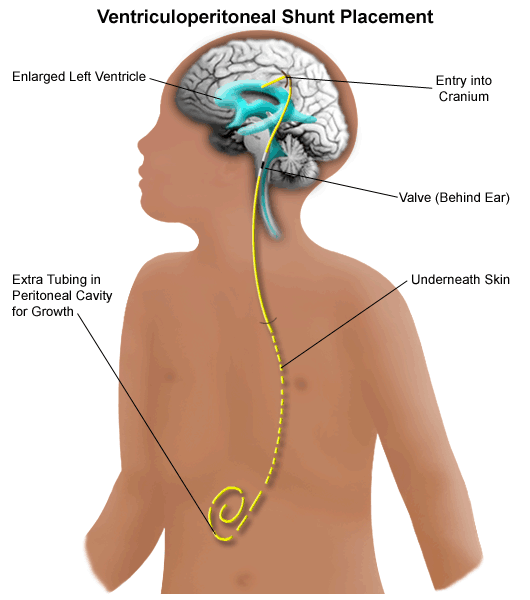
METHODS The data were originally developed in the conduct of 2 multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trials exam-ining surgical techniques for insertion of ventriculoperitoneal Abstract Purpose: Previous studies have established risk factors for ventriculoperitoneal shunt failure in children. However, the role of valve type as a determinant of complications and Ventriculoperitoneal shunt (VPS) placement is one of the most commonly performed neurosurgical procedures and is necessary to treat most forms of hydrocephalus.
Shunt survival was similar between VA and VPl shunts, although VA shunts are used more often, particularly in younger patients. Children < 6 years with VA shunts appeared
The survival time of the ventriculo-peritoneal-shunt in children with hydrocephalus is dependent on the type of valve implanted Article Open access 13 February 2023
- The Top 10 Prague Romantic Tours
- The Thermic Effect Of Food: A Review.
- The Ultimate Friends Quiz For Fans With True Unagi
- The Stories Of Courtesans Come Alive Again
- The Top Ten Rated High Schools In Miami
- The Stewart Fam | SHE’S READY FOR A BABY!!!
- The Seven Telmarine Lords – The Chronicles of Narnia: The Voyage of the Dawn Treader
- The Smile Setlist At The Factory, Chesterfield
- The Souk At Qaryat Al Beri: Traditional Souk Experience In Abu Dhabi
- The Ultimate Guide To Solidworks Mouse Settings
- The Smallest Helicopter In The World