The Global Positioning System: Revolutionizing Land Surveys
Di: Ava
Introduction The Global Positioning System (GPS) has become an indispensable tool in modern society, revolutionizing navigation, surveying,
Total replacement of the transit satellite and other terrestrial navaid systems. Applications and Uses of Global Positioning System : Land, Sea and Air Navigation and Tracking including onroute as well as precise navigation, collision avoidance, cargo monitoring, vehicle trucking, search and rescue operations, etc. The Global Positioning System (GPS) has revolutionized both surveying and navigation. GPS is one of the single largest breakthroughs in GIS since its inception. GPS brings the use of a locational tool, whose accuracy and precision rivals most surveying systems in use up to the present. Furthermore, the GPSs ease of use makes it an attractive technological answer to The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based hyperbolic navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission
Surveying the Future: Revolutionizing Land Survey Equipment
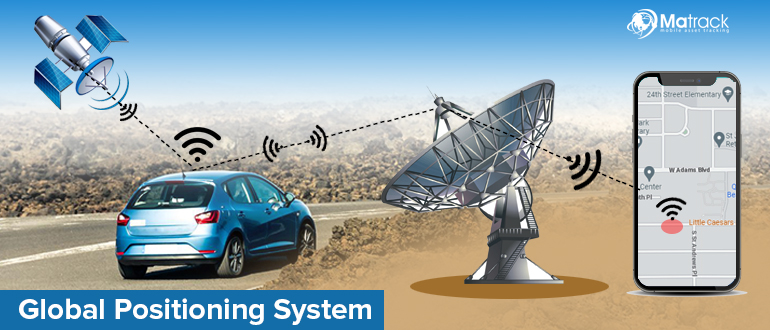
The answer lies in the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), a technology that has revolutionized navigation and positioning across the globe. In this blog, we’ll explore the basics of how GNSS works, including how receivers calculate their position by measuring the time it takes for signals to travel from satellites to the receiver. Global positioning is fundamental to navigation, communication systems, mapping and charting, and much more. The National Geodetic Survey is responsible for the development and maintenance of the National Spatial Reference System, a national coordinate system that allows surveyors and others to accurately position points of interest and ensure that their coordinates Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have drawn increased research interest in recent years, leading to a vast number of applications, such as, terrain exploration, disaster assistance and industrial inspection. Unlike UAV navigation in outdoor environments that rely on GPS (Global Positioning System) for localization, indoor navigation cannot rely on GPS due to the poor
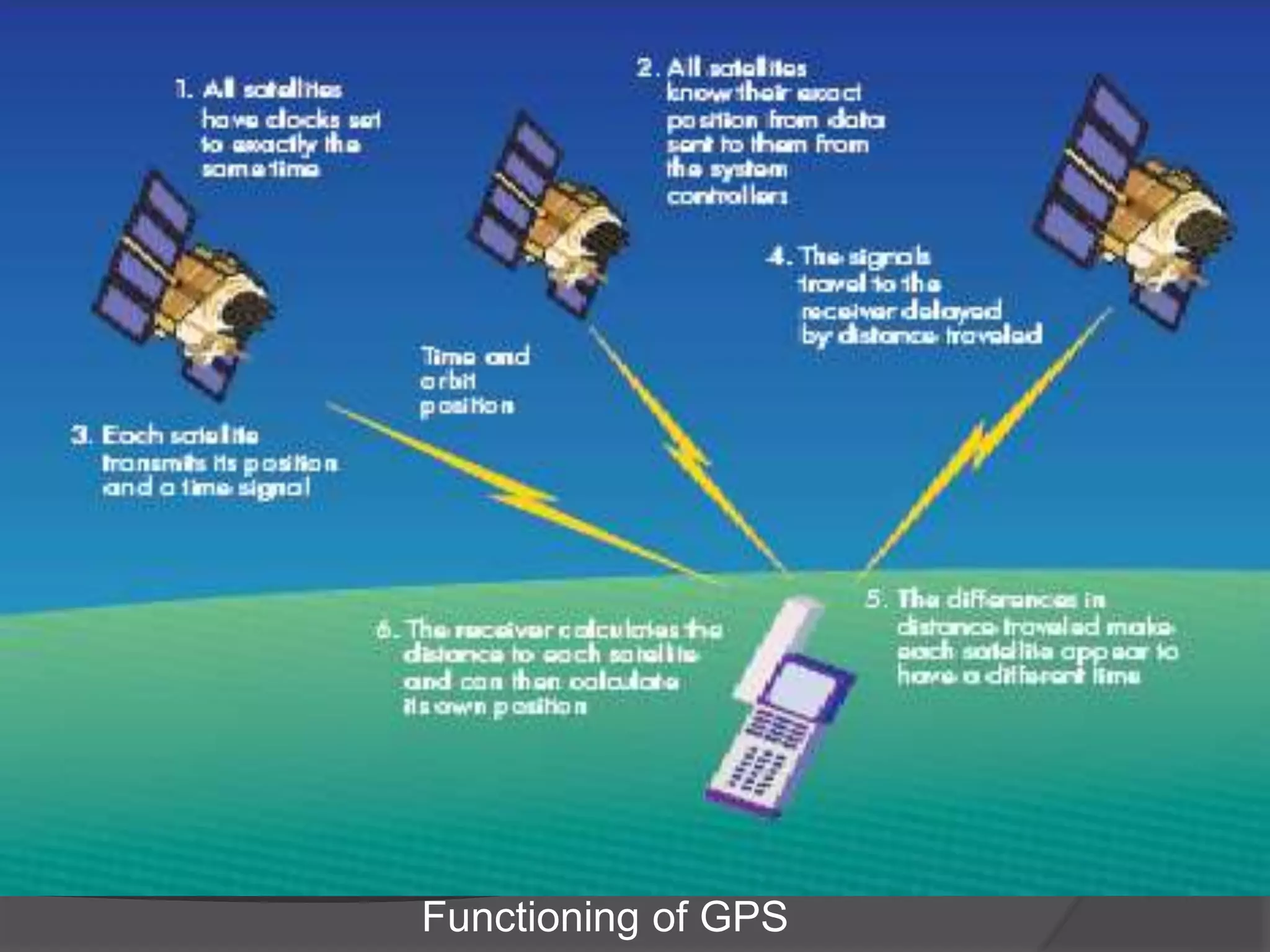
Satellite navigation is a system of satellites that provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning with global coverage and allow small electronic receivers to determine location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) using time signals transmitted from satellites. Often times the terms „GNSS“ and „GPS“ are used interchangeably but there are key differences between the two:
Introduction The Global Positioning System (GPS) has led to a revolution in the land surveying profession. The GPS technology is being employed in a variety of surveying applications while the technology is still evolving. At present there are only nationally accepted procedures/methodologies for performing static GPS surveys. Newer methodologies have Official U.S. government information about the Global Positioning System (GPS) and related topics
The Global Positioning System (and to a potentially greater extent, the emerging Global Navigation Satellite System) enables both surveyors and ordinary citizens to determine positions by measuring distances to three or more Earth-orbiting satellites.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is the oldest and most widely used GNSS system, and as such will be extensively discussed in the first part of this book. The development of GPS satellites dates from the 1960s [1, 2]. By 1973, the US military had embarked on Georeferencing technologies, such as the Global Positioning System (GPS), utilize satellite constellations to accurately determine locations on Earth, revolutionizing precision agriculture. GPS plays a crucial role in enabling variable rate technology in agricultural practices by providing precise positioning [16]. Space The Global Positioning System (GPS) is revolutionizing and revitalizing the way nations operate in space, from guidance systems for crewed vehicles to the management, tracking, and control of communication satellite constellations, to monitoring the Earth from space.
Precision agriculture (PA) and its suite of information technologies—such as soil and yield mapping using a global positioning system (GPS), GPS tractor guidance systems, and variable-rate input
Aerial survey and mapping
In short, GPS, or the global positioning system, is a satellite-based navigation system. GPS was first developed for military use starting in the 1970s and became fully operational in 1993. Since then, it has expanded its use to consumer and commercial
Gain an in-depth understanding of RTK Survey, a pivotal technology that significantly enhances positioning data accuracy.
The Global Positioning System Jules G. McNeff Invited Paper Abstract— The paper provides a top-level perspective on how the global positioning system works, how its services are used, and delves into the most important technical and geo-political factors affecting its long-term availability in an international setting.
GPS or GNSS GPS or Global Positioning System was developed and is maintained by the US Department of Defense. Since the introduction of GPS many other countries have developed similar satellite based navigation systems, such as the Russian Glonass, Chinese BeiDou and European Galelio. Modern surveying GPS equipment, and recent smart phones, are now able Tutorial Contents What is DGPS? A DGPS stands for Differential Global Positioning System. It is an enhancement to the Global Positioning System (GPS) which provides improved location accuracy, in the range of operations of each system, from the 15-meter nominal GPS accuracy to about 1–3 centimeters. Overview of class Aim: To introduce the principles of the operation of the GPS system and its applications
Surveying Using GPS and Conclusion
In the agrifood system, data can be captured from various sources, such as satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and diferent sensors like the global positioning system (GPS) or cameras. Each of these data sources has its own properties that Don D’Onofrio National Geodetic Survey Introduction The Global Positioning System (GPS) has led to a revolution in the land
In the agrifood system, data can be captured from various sources, such as satellites, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and diferent sensors like the global positioning system (GPS) or cameras. Each of these data sources has its own properties that The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a constellation of navigation satellites called Navigation Satellite Timing And Ranging (NAVSTAR), maintained by the U.S. Department of Defense. Many outdoor enthusiasts recognize that a handheld GPS receiver can be an accurate tool for determining their location on the terrain. The GPS receiver helps determine DGPS or Differential GPS is a technique used to improve and enhance the accuracy of the Global Positioning System ( GPS ). The nominal accuracy of a GPS system is around ± 15 meters and the DGPS technique can increase the accuracy of the data to ± 3 cm ( centimeters ).
This document summarizes the third edition of the book „GPS for Land Surveyors“ by Jan Van Sickle. The third edition has been updated with new information on real-time network services, GPS codes such as M-code and L2C, and an entire chapter dedicated to GNSS systems beyond GPS. The book covers fundamental GPS theory, practical applications, advanced
Background The Global Positioning System (GPS), which is the world’s most accurate method of navigation, was conceived to enhance navigation accuracy for U.S. military forces during the early 1970s. Since 1984, the GPS has found application in a myriad of systems–from automotive monitors advising drivers of the locations of hotels and restaurants to guidance systems which
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation and surveying system used for the determination of precise position and time of a point using radio signals from the satellites. It works based on the principle of trilateration. Hence, it is primarily a navigation system for real-time positioning. No Time to Read?? Watch the Video : What is GPS Explore the dGPS (Differential Global Positioning System), its working principles, advantages, disadvantages, and differences compared to standard GPS for precise location accuracy.
Principles of the Global Positioning System, Lecture 1
In recent years, the integration of GPS (Global Positioning System) technology into farming practices has sparked a profound revolution in agriculture, reshaping traditional methods and offering a myriad of opportunities for increased efficiency, productivity, and
- The Headbangers – The Headbangers Return WWE SMACKDOWN 30 August 2016
- The History Of Dacia _ Dacia: The brand that thinks big
- The Fall: The 1970S, 12Cd Box Set
- The Hidden Treasures Of New World: A Guide To New World’S
- The Iaslc Atlas Of Alk And Ros1 Testing In Lung Cancer
- The Future Of High Energy Density Batteries
- The Golden Notebook: Doris Lessing
- The Fs Group Around The World _ War/No More Trouble feat. Bono
- The Garden Of Sinners Watch Order 2024
- The Ethical Life Of Euphemisms
- The Home Depot Stock Price _ The Home Depot Stock Forecast & Analyst Price Targets
- The Gift Further Reading , Further Reading Podcast — Apple Podcasts