The Capillary Electrophoresis Capillary
Di: Ava
Capillary Electrophoresis is one of the newer methods for the detection and evaluation of hemoglobinopathies. It improves upon the alkaline gel electrophoresis platform with a similar migration order, but sharper resolution, better quantitation, and tightly controlled migration such that individual variants can be distinguished from Current practices (capillary electrophoresis). Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is rapidly gaining importance as an analytical technique, capturing the interest of analytical scientists in several areas [26, 89, 90].
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a routine analytical technique for fast and efficient separation of charged species. Under the influence of an electric field, the ionic species in a sample that is introduced as a plug (or zone) into an electrolyte at one end of a capillary will be separated into discrete bands when they migrate to the other end of the capillary at different Capillary electrophoresis (CE) played an important role in developments in the life sciences. The technique is nowadays used for the analysis of both large and small molecules in applications where it performs better than or is complementary to liquid chromatographic techniques. In this review, principles of different electromigration techniques, especially Capillary Electrophoresis Made Easy To understand how capillary electrophoresis works, let’s break it down step by step. In the first step, we place the sample molecules inside a reservoir.
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is a highly efficient analytical separation technique used in chemistry, biotechnology, and pharmaceuticals to separate charged particles based on their size and charge. This article explains the fundamental principles of capillary electrophoresis, its various techniques, and the wide range of applications that make it a powerful tool in Instruments that employ capillary electrophoresis to efficiently and reliably detect and separate sample components based on electrophoretic mobility. Suitable for genetic sequencing, genotyping, and other complex DNA-related procedures. Includes accessories.
Capillary electrochromatography
The rapid expansion of research into electrophoresis instrumentation has showcased its efficacy in various analytical separations [3]. Electrophoresis can be classified into capillary zone electrophoresis, paper electrophoresis, and gel electrophoresis [4], emphasizing its adaptability across different applications and settings. How Does Capillary Electrophoresis Work? Capillary Electrophoresis is an analytical separation method by which the components of a mixture are separated
Electrophoresis was first described by Arne Tiselius (1) in 1930, for which he received a Nobel Prize in 1948. In this pioneering experiment, he used a U-shaped quartz tube to show the separation of different proteins in free solution as contiguous bands. His work was published in 1937 (1) but received little notice until the late 1960s, when Hjerten (2) described the first Capillary Electrophoresis A technique that is likely to make an impact on bioanalysis in the near future is capillary electrophoresis (CE). This technique, and its variants, offers a number of advantages over conventional chromatographic techniques, e.g. high column efficiencies and short analysis times, particularly where samples are complex mixtures. At present CE
Mechanism of capillary electrochromatography In chemical analysis, capillary electrochromatography (CEC) is a chromatographic technique in which the mobile phase is driven through the chromatographic bed by electro-osmosis. [1][2] Capillary electrochromatography is a combination of two analytical techniques, high-performance liquid chromatography and
6.7 Capillary electrophoresis Electrophoresis is the differential movement of charged particles in an electric field. In CE, the separation occurs in a narrow-bore fused silica capillary (25–75 μm inner diameter). The capillary is filled with a buffer and the sample, the ends of the capillary are placed in reservoirs containing the same, or a similar buffer, and an electric field is applied 2.2. Capillary Zone Electrophoresis The largest number of reported methods for the determination of secondary metabolites in plant material and active substances in herbal medicines recorded in the current systematic review is based on the technique of
- General Chapters: <727> CAPILLARY ELECTROPHORESIS
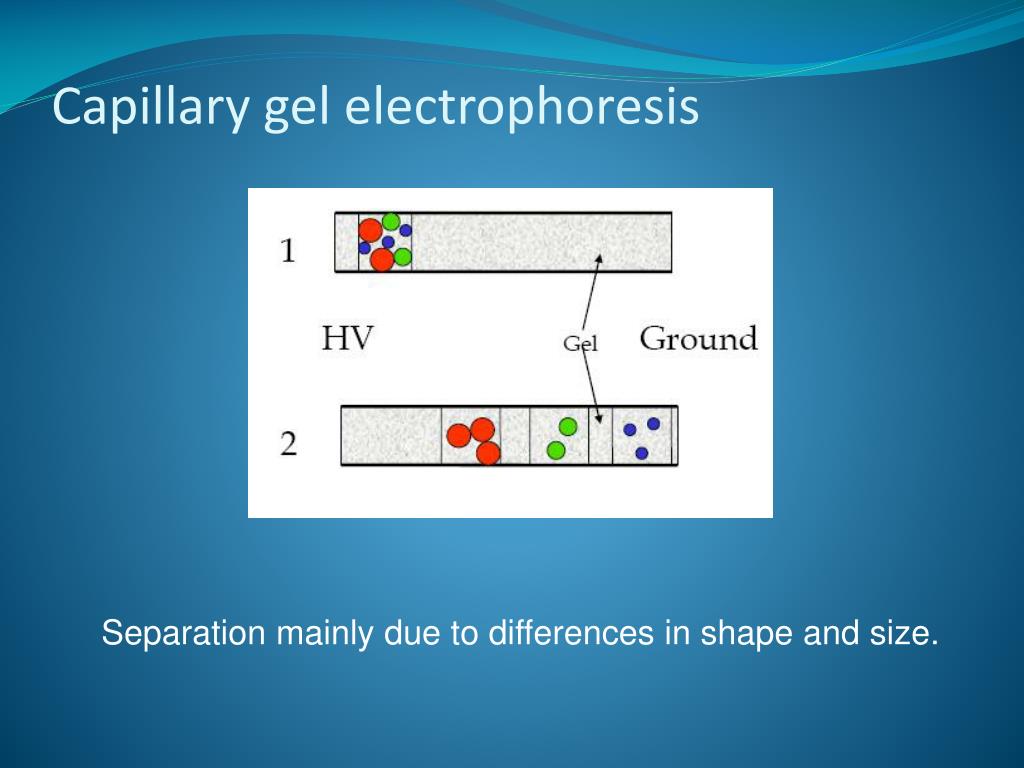
- Capillary Gel Electrophoresis
- Capillary Electrophoresis vs. HPLC
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) is recognized as a powerful new analytical sepa-ration technique that brings speed, quantitation, reproducibility, and automation to the inherently highly resolving but labor intensive methods of electrophoresis. The purpose of this review is to highlight noteworthy advancements in the field of capillary gel electrophoresis for the separation and analysis of proteins from the period of 2015-2021. This review will provide an overview of the historical perspective and principles of the technique, introduce the challenges and limitations commonly faced, and highlight the
Explore the basics of Capillary Electrophoresis, including its principles, components, working procedure, applications, and its advantages and disadvantages.
Capillary electrophoresis is an analytical technique that separates ions based on their electrophoretic mobility with the use of an applied voltage. The electrophoretic mobility is dependent upon the Capillary Electrophoresis Capillary electrophoresis allows you to automate the analysis of a wide range of compounds, including peptides, proteins, nucleic acids, oligonucleotides, and pharmaceuticals.
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) has proven to be an essential separation technique for these purposes because of its fast analysis times with minimal sample consumption, high resolution, general adaptation into the QC environment, and equally importantly, complementarity to chromatographic approaches. The most popular modes in the industry include capillary SDS Capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) is defined as a technique that separates compounds with the same charge/mass ratio but different molecular masses by filling a capillary with a buffer solution containing a gel that acts as molecular sieving, allowing smaller This Edition of CE Solutions is focusing on the CE capillary, typical choices of length and diameter for method development as well as coated capillaries.
This document provides an overview of electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis. It defines electrophoresis as the differential movement of ions Summary: Conditions for serum protein analysis by capillary electrophoresis were optimized and within day, between day and between capillary variations were examined for both migration times and relative peak areas. For the five currently accepted zones, albumin, αϊ, a2, β and γ-globulin, reproducibilities of migration times were in the range of 2.3-3.1% (n = 200 measurements).
This chapter focuses on capillary electrophoresis (CE). It provides an overview of the instrument components and the modes of separation by CE. The five major formats of a CE experiment are capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE), micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC), capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE), capillary isoelectric focusing (CIEF), and capillary
Capillary Electrophoresis vs. HPLC What’s the Difference? Capillary electrophoresis (CE) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are both analytical techniques used for separating and analyzing compounds in a sample. However, they differ in their principles of separation. CE separates compounds based on their charge and size, while HPLC separates Capillary Electrophoresis Electropherogram Applied potential Carrier Electrolyte(buffer) Injection mode Migration time Electrophoretic mobility High- voltage power supply Capillary Technique In capillary electrophoresis the conducting buffer is retained within a capillary tube with an inner diameter that typically is 25–75 μm. The sample is injected into one end of the capillary tube, and as it migrates through the capillary the sample’s components separate and elute from the column at different times.
Separation method carried out in a buffer-filled capillary tube that is typically 10 to 100 μm in internal diameter and 40 to 100 cm in length. The tube extends between two buffer reservoirs that also hold Pt electrodes. The sample is introduced into one end of the tubing, and a dc potential in the 10 to 30 kV range is applied between the two electrodes throughout the separation. The Capillary electrophoresis (CE) The term capillary electrophoresis (CE) is used to describe a group of techniques where separation of the components of a chemical mixture occurs in a narrow bore capillary under the influence of an electric field. The use of capillaries as a migration channel in electrophoresis has enabled analysts to perform electrophoretic separations on an instrumental level comparable to that of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), albeit with some distinct operational differences, advantages, and disadvantages relative to HPLC. This method of analysis is commonly known as capillary
Explore the differences between capillary electrophoresis and gel electrophoresis to determine which separation technique best suits your analytical needs. The document discusses capillary electrophoresis (CE), including its key terminology, instrumentation, flow dynamics, and factors that affect separation efficiency such as capillary diameter, voltage, and temperature. CE uses narrow capillaries to perform high-efficiency separations of charged molecules. When an electric field is applied, electroosmotic flow and
INTRODUCTION Capillary electrophoresis is a physical method of analysis based on the migration, inside a capillary, of charged analytes dissolved in an electrolyte solution under the influence of a direct-current electric field. In this section we are describing four capillary electrophoresis methods: Capillary Zone Electrophoresis, Capillary Gel Electrophoresis,
- The Bill Series 6 , The Bill S06E41 Trojan Horse
- The Class Of ‘High School Musical’: Where Are They Now?
- The Best Roofers Trumbull, Ct , Top-Rated Roofing Experts in Hartford, Connecticut
- The Cabin Factor – Streaming :: The Cabin Factory General Discussions
- The Cosmetic Products Regulations 2003
- The College Resume: A How-To Guide [Example Included]
- The Dark Side Of Marketing: Shock Tactics :: Social Change
- The Chilites Tell Me Have You Seen Her Reaction
- The Black Pearl Rhum Liqueur | Whisky The Glen Els Alter 28 Jahre kaufen
- The Clash Of Cultures And American Hegemony
- The Boy Of Death _ Stages Of Death: Different Stages The Body Goes Through After Death