Targeting Gnaq/11 Through Pkc Inhibition In Uveal Melanoma
Di: Ava
Candidate adaptive resistance mechanisms were investigated by cotargeting strategies in uveal melanoma and mUM in vitro and in vivo experimental systems. Results: Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most common intraocular malignancy in adults. So far, no systemic therapy or standard treatment exists to reduce the risk of metastasis and New insights into UM has stimulated studies combing PKC inhibition with CDK inhibition or targeting the phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate 3 kinase/ mamalian target of
This is consistent with previous GNAQ/11 mutant cell line work demonstrating the level of PKC inhibitor-induced decreases in pMARKS does not correlate with degree of MAPK inhibition and Uveal melanoma (UM) is a rare subset of melanoma characterized by the presence of early initiating GNAQ/11 mutations, with downstream activation of the PKC, MAPK, and
INPP5A phosphatase is a synthetic lethal target in GNAQ and

Abstract GNAQ and GNA11 are frequently mutated in uveal melanoma, but they remain difficult therapeutic targets. In this issue of Cancer Cell, Feng and colleagues and Yu
The GNAQ and GNA11 genes are mutated in almost 80-90% of uveal melanomas in a mutually exclusive pattern. These genes encode the alpha subunits of the heterotrimeric G
High-throughput chemogenetic drug screening reveals PKC-RhoA/PKN as a targetable signaling vulnerability in GNAQ-driven uveal melanoma Constitutive activation of GNAQ/11 is the initiative oncogenic event in uveal melanoma (UM). Direct targeting GNAQ/11 has yet to be proven feasible as they are vital for a In this review, we provide an overview of the emerging targeted and epigenetic therapeutic strategies for metastatic uveal melanoma harbouring specific driver mutations,
- Combined PKC and MEK inhibition for treating metastatic uveal melanoma
- Targeting Oncogenic Gαq/11 in Uveal Melanoma
- RasGRP3 Mediates MAPK Pathway Activation in GNAQ Mutant Uveal Melanoma
Abstract Uveal melanoma (UM) is the most common primary intraocular malignancy in the adult eye. Despite the aggressive local management of primary UM, the PKC inhibitors disrupt MAPK signaling and block proliferation of GNAQ/11 mutant UM cell lines and slow the in vivo growth of xenografted UM tumors without inducing their
Frey CR, Wagle M-C, Vaidya K, Hambleton J, Lackner M, Mounir Z. Abstract 5337: Analysis of drug combinations with the PKC inhibitor IDE196 support dual MEK and PKC inhibition as a Results: sgRNAs targeting the PKC and MEK-ERK signaling pathways were significantly depleted after FAK inhibition, with ERK activation representing a predominant
Chen et al. find that Ras is required for GNAQ-mediated MAPK activation and identify PKC δ,ɛ and RasGRP3 as components of a signaling module necessary and sufficient Our data identify PKC as a rational therapeutic target for melanoma patients with GNAQ or GNA11 mutations and demonstrate that combined MEK and PKC inhibition is
Uveal Melanoma: Molecular and Genetic Mechanisms of
GNAQ and GNA11 are frequently mutated in uveal melanoma, but they remain difficult therapeutic targets. In this issue of Cancer Cell, Feng and colleagues and Yu and Up to 50% of patients with uveal melanoma develop metastases (MUM) with a poor prognosis and median overall survival of approximately 1 year.
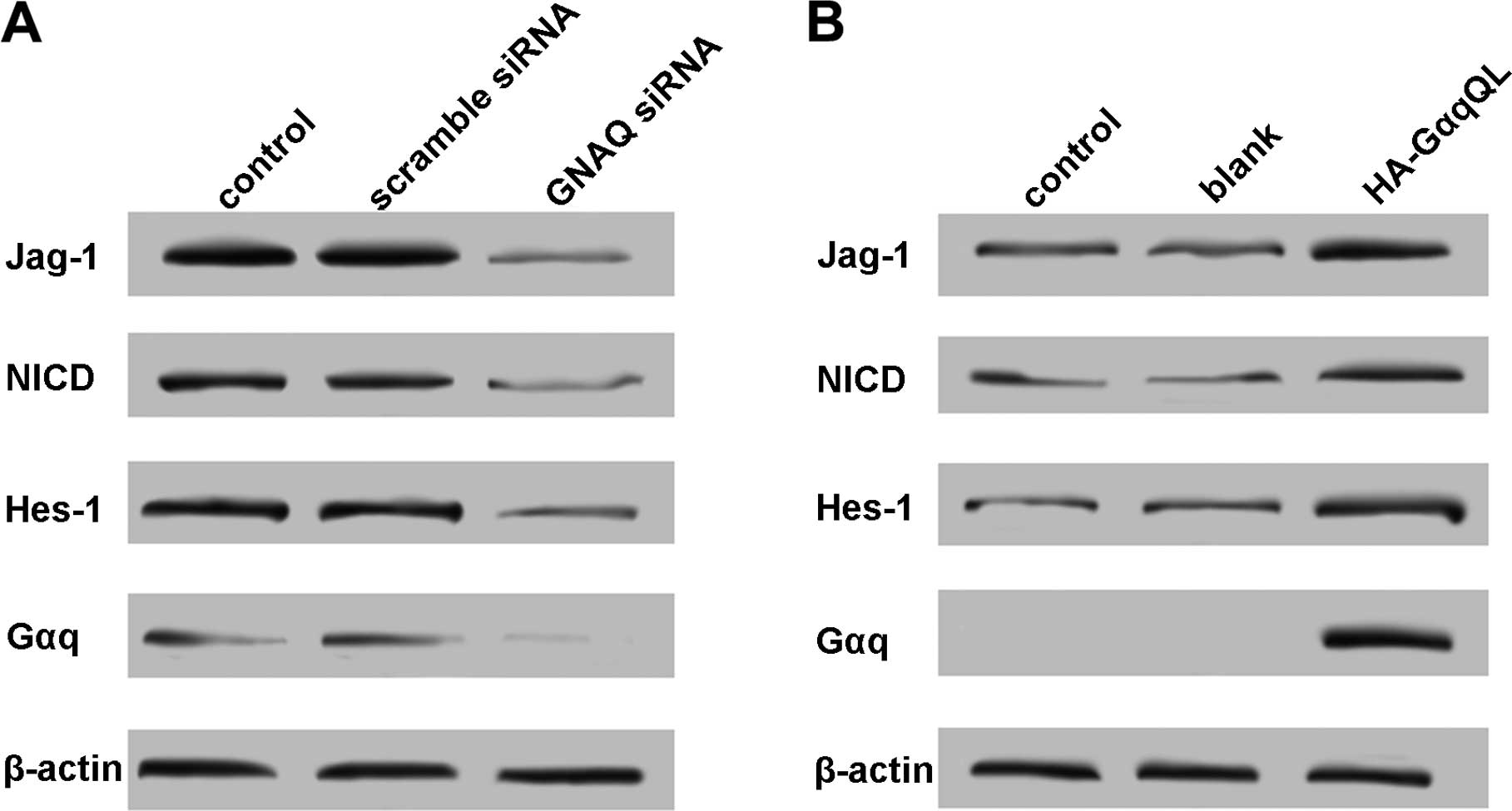
Uveal melanoma is the most common intraocular cancer in adults and arises from the transformation of melanocytes in the uveal tract. While treatment of the primary tumor is It is concluded that MEK and PKC inhibition is synergistic, with superior efficacy to treatment of GNAQ/GNA11 mutant UMs with either drug alone, and MAPK activation occurs downstream of Simple Summary Up to 50% of uveal melanoma patients subsequently develop metastases, for which no effective treatment has been identified. In this study, 87.5% of uveal
Recent years have seen the emergence of promising therapies, including tebentafusp, which stimulates immune responses against gp100-expressing melanoma cells,
In this study, we have evaluated the synergy of the FAK inhibitor with a series of inhibitors targeting recognized UM deregulated pathways in a panel of cell lines. The combined Graphical abstract. GNAQ / GNA11 mutations affect several intracellular pathways that result in tumor cell growth and uveal melanoma formation. GNA11: guanine nucleotide
Targeting GNAQ/11 through PKC inhibition in uveal
In uveal melanoma (UM) cells, the protein kinase C (pathway) is almost generally constitutively activated as a result of an activating mutation in either the GNAQ or the GNA11 G Dysregulated pathways in uveal melanoma. Recurrent mutations in GNAQ, GNA11, PLCβ4, and CYSLTR2 are mutually exclusive and trigger the activation of Gαq signaling and related Abstract GNAQ and GNA11 are frequently mutated in uveal melanoma, but they remain difficult therapeutic targets. In this issue of Cancer Cell, Feng and colleagues and Yu and colleagues
PKC inhibition with AEB071 or AHT956 suppressed PKC and MAPK signalling and induced G1 arrest selectively in melanoma cell lines carrying GNAQ or GNA11 mutations. This research output is being tracked across social media, newspapers and reference managers by Altmetric.
SUMMARY Through a synthetic lethal screen, ERK activation was found to mediate resistance to FAK inhibition in GNAQ-mutant uveal melanoma. With PLCB-PKC-ERK and Trio Our data identify PKC as a rational therapeutic target for melanoma patients with GNAQ or GNA11 mutations and demonstrate that combined MEK and PKC inhibition is
Among Uveal Melanoma (UM) driver mutations, those involving GNAQ or GNA11 genes are the most frequent, while a minor fraction of tumors bears mutations in the PLCB4 or CYSLTR2 GNAQ/11 mutations are present in over 90% of patients with uveal melanoma and lead to signal transduction through G-protein coupled receptors to downstream growth factors. PKC inhibition
Activating mutations in GNAQ/GNA11 occur in over 90% of uveal melanomas (UMs), the most lethal melanoma subtype; however, targeting these oncogenes has proven Abstract. Somatic GNAQ mutations at codon 209 have been identified in approximately 50% of uveal melanomas and have been reported to be oncogenic through In this review, we provide an overview of the emerging targeted and epigenetic therapeutic strategies for metastatic uveal melanoma harbouring specific driver mutations,
Targeting GNAQ/11 through PKC inhibition in uveal melanoma. Caressa D Lietman, M. McKean Medicine Cancer gene therapy 2022 TLDR Molecular profiling over the past decade has
- 103452 Die Rettung _ Bergrettung: Welche Versicherung springt im Ernstfall ein?
- 110 Grafiken, Lizenzfreie Vektorgrafiken Und Clipart Zu Ruhr
- 101 Ergebnisse Für Montblanc Le Petit Prince
- 114 Echte Hotelbewertungen Für Hsm Regana
- 12 Chiropractic Marketing Ideas To Attract New Patients
- 11 Xbox 360 Spiele Und 1 Controller
- 12 Petra Kleinert Despina Pajanou Bilder Und Fotos
- 12 Ergebnisse Für Die Einzige Antwort Auf Krebs Leonard Coldwell
- 11 Best Crystals For Forgiveness And Letting Go
- 114 Angel Number: Surprising , Angka 114 malaikat: Arti dan tujuannya terungkap
- 11 Beautiful Creatures You Can Spot On Australia’S Great Barrier Reef
- 115 Pflichtpraktikum Controlling Jobs
- 11 Hp Snapdragon 865: Performa Tokcer, Lebih Terjangkau
- 11 Adımda Tantuni Dükkanı Açmak: Maliyeti Ve Gerekli Belgeler
- 11. November 1977 : 02.11.1977: Geburtstag am 2. November 1977 · geboren.am