T Distribution Tables , 1.3.6.7.2. Critical Values of the Student’s-t Distribution
Di: Ava
Statistics Online Computational Resource Note: t(∞)α/2 = Zα/2 in our notation. You can use this T-Value Calculator to calculate the Student’s t-value based on the significance level and the degrees of freedom in the standard deviation. How to use the calculator Enter the degrees of freedom (df) Enter the significance level alpha (α is a number between 0 and 1) Click the „Calculate“ button to calculate the Student’s t-critical value.
T distribution critical values table online.T distribution is the distribution of any random variable ‚t‘. Below given is the T table for you to refer the one and two tailed t distribution with ease. It can be used when the population standard deviation (σ) is not known and the sample size is Since probability tables cannot be printed for every normal distribution, as there is an infinite variety of normal distribution, it is common practice to convert a normal to a standard normal and then use the z-score table to find probabilities. Z-Score Formula It is a way to compare the results from a test to a “normal” population. The t table or t distribution table is used in statistics when the standard deviation (σ) of a population is not known and the sample size is small, that is, n<30.
Hey there. My name is Zach Bobbitt. I have a Masters of Science degree in Applied Statistics and I’ve worked on machine learning algorithms for In probability theory and statistics, Student’s t distribution (or simply the t distribution) is a continuous probability distribution that generalizes the standard normal distribution. Like the latter, it is symmetric around zero and bell-shaped. However, has heavier tails, and the amount of probability mass in the tails is controlled by the parameter . For the Student’s t distribution
T Critical Value Calculator
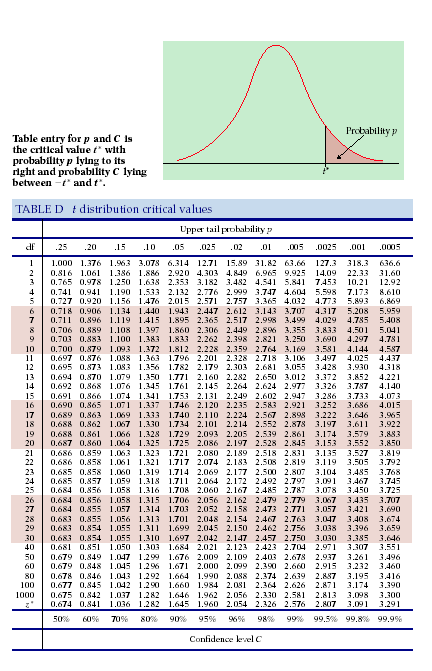
T-Distribution and Table of Critical T-Values The numbers in the table cells correspond to critical t-values for different tail-areas (α). The tail areas are probabilities. For example, 0.05 is 5% percent probability. Each row corresponds to different degrees of freedom (df). How to read the z-Table The z-table, or p-value table for z tests, helps you find the cumulative probability associated with a specific z-score. By locating the z-score in the p-value table, you can determine the probability or p-value of observing values up to that point in a standard normal distribution. Locate the Row for the First Decimal Place of the Z-Score A z-score typically has
T-Distribution Table (One Tail). For more info on the parts of the t table, including how to calculate them, see: degrees of freedom and alpha level. Note: If your degrees of freedom (dF) aren’t listed in the table, round down to the nearest listed dF value.
- Student’s T Distribution Table
- Appendix B: Standard Statistical Distribution Tables
- Peter’s Statistics Crash Course
Comment utiliser la table de distribution Student t Pour utiliser la table de distribution Student t, vous devez suivre trois étapes : Entrez dans le tableau par la ligne des degrés de liberté correspondants de la distribution t de Student. Figure C.1: Three t distributions.C.2. T DISTRIBUTION TABLE 90 100 200 300 400 500 750 1000 2000 Large
How to Use This Table This table contains critical values of the Student’s t distribution computed using the cumulative distribution function. The t distribution is symmetric so that t1-α,ν = -tα,ν. The t table can be used for both one-sided (lower and upper) and two-sided tests using the appropriate value of α. What is Normal Distribution? Normal Distribution also known as Gaussian Distribution (named after the German mathematician Carl Gauss who first described it) is a continuous probability distribution in which the occurrence of data is more clustered near the mean than the occurrence of data far from the mean. This characteristic lends the normal distribution aContinue Reading
1.3.6.7.2. Critical Values of the Student’s-t Distribution
Find critical t-values instantly with our T Distribution Table Calculator. Easy-to-use tool for students, researchers & statisticians. t Distribution: Critical t Values t Distribution: Critical t Values
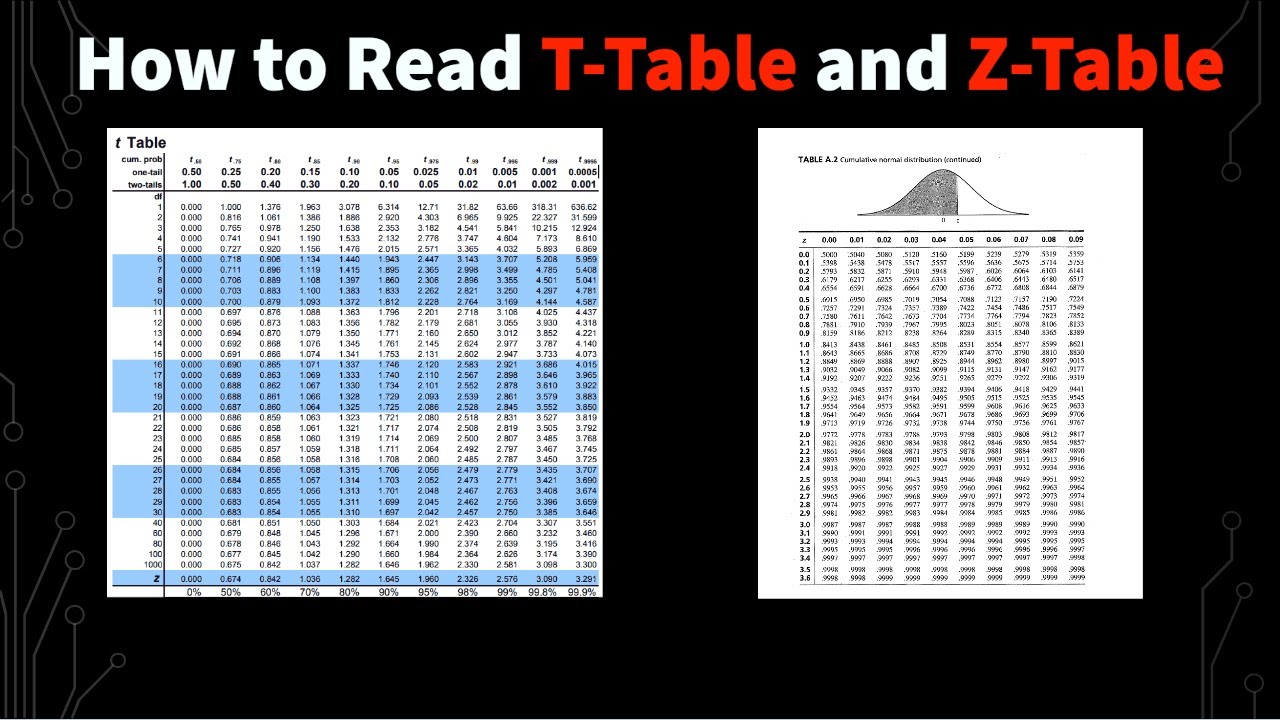
This is the „bell-shaped“ curve of the Standard Normal Distribution. It is a Normal Distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. It shows you the percent of population: between 0 and Z (option „0 to Z“) less than Z (option „Up to Z“) greater than Z (option „Z onwards“) It only display values to 0.01% The Table You can also use the table statistics & probability tables to find critical area (rejection region) values of Z, t, F & χ² distributions for one or two tailed hypothesis test for large & small samples, available in both html & pdf download format along with how to use instructions. 这是标准正态分布的 „钟形“ 曲线。 它是个平均值为 0 并且 标准差 为 1 的 正态分布。 显示的是总体: 在 0 和 Z 之间(选项 „0 to Z“) 小于 Z(选项 „Up to Z“) 大于 Z(选项 „Z onwards“) 数值只显示到 0.01% 列表 你也可以用以下的列表。列表显示从 0 到 Z 的面积。 为了让列表不太长,我们把 “ 0.1 “ 的值
The Student’s t-distribution table contains the t-distribution critical values by confidence level and degrees of freedom. Find the t score you need here. Statistical tables: values of the t-distribution.
统计 – T 分布表 t分布的临界值根据两个alpha值的概率和自由度计算。 Alpha (a) 值 0.05 一尾和 0.1 二尾是要与表行中的自由度进行比较的两列。 Find the critical values of t distribution using t critical value calculator. T value calculator measures results by taking significance level and degrees of freedom.
The shaded area is equal to Æ for t = tÆ. To see this table above as an image file, see the following link: T-distribution table. Many different distributions exist in statistics, and a commonly used distribution is the t-distribution. T-distributions are commonly used to find the t-value for a given data set based on the sample size of the data set and the significance level. This t-value can then be used for various statistics THE t DISTRIBUTION Table entries are values of t corresponding to proportions in one tail or in two tails combined. 0.01 0.02 31.821 6.965 4.541 3.747 3.365 3.143 2.998 2.896 2.821 2.764 2.718 2.681 2.650 2624 2.602 2.583 2.567 2.552 2.539 2.528 2.518 2.508 2.500 2.492 2.485 2.479 2.473 2.467 2.462 2457 2.423 2.390 2.358 2.326 0.005 63.657 9.925 5.841 4.604 4.032
An explanation of how to read the t-distribution table along with several examples.
Student’s t Table The interactive t table provides critical values for the Student’s t-distribution, which is used in statistical inference when sample sizes are small
Distributions Student t The Student t distribution is closely related to the standard normal distribution. It also looks like a bell-shape, but depends on two input parameters: a t-value and the degrees of freedom. (unlike the normal which depends on only one the z-value) Depending on those degrees of freedom, the distribution will look slightly different. In figure 1 a few examples: t table,student tablet table Calculate p (x≤X) For negative x values: p (x ≤ -X) = 1 – p (x ≤ X) For any practical use you can use the above calculator instead of the t table. The below t table is a bit more accurate. Examples: Row 4: DF=3, column 5: t 0.99 P (x ≤ 4.5407028586 ) = 0.99 A typical T-distribution table presents critical values for different degrees of freedom and significance levels (alpha values).
- Tabata Weight Loss: Action-Packed Workout That Leaves No
- Tabakwaren Einzelhandel In Sankt Wendel
- Sådan Løser Du Fejlen Err_Network_Changed I Chrome
- Tachowelle Angleichgetriebe Für Vw T3 Mit Fahrtenschreiber Nos
- Tabellen Vergleichen Und Daten Kopieren
- Südtirol: Zwei Bergsteiger Verunglücken Tödlich Am Ortler
- Südafrika: Confed-Cup , Südafrika » Einsätze Confederations Cup 2009 » sortiert nach
- Söhngen® Beatmungshilfe Air-Vita® Bi-Protect Beatmungshilfe
- T-Shirts: Spielkarten Hintergrund
- Taco Time: Discover The Best Topping For Your Delicious Pork Tacos
- T-Shirts: Illuminati Gang : Amazon.com: Illuminati T-shirts
- Südkorea Feiertage 2024 :: Holsdb.Com :: Deutsch