Surface Area Of Typical Neuron
Di: Ava
Responses of a typical surface-orientation-selective (SOS) neuron with sensitivity to perspective cues. A: responses to 9 different orientations under the DP condition. The two-dimensional (2D The larger the dendritic surface area, the greater the amount of information the nerve cell can receive and process. Integration of Inputs: The branching structure and shape of dendrites influence how a neuron integrates multiple types of input.
Development and Evolution of Cerebral and Cerebellar Cortex
It gives off all the neuron’s processes, including all its dendrites, which make up most of the receptive surface of a neuron, and the axon, the one process that is the conducting and transmitting element of a typical neuron (Figure 8 ). For large brains, the larger number of neocortical neurons and larger cortical surface area exceeds what is needed to envelop the subcortical core, thus predicting the existence of convolutions (Van Essen, 2006), though the specific pattern of folds depends on mechanisms discussed below. An axonal terminal at the surface of a neuron from the dorsal horn of a rabbit spinal cord contains both dense-core and clear, spherical synaptic vesicles lying above the membrane thickenings.
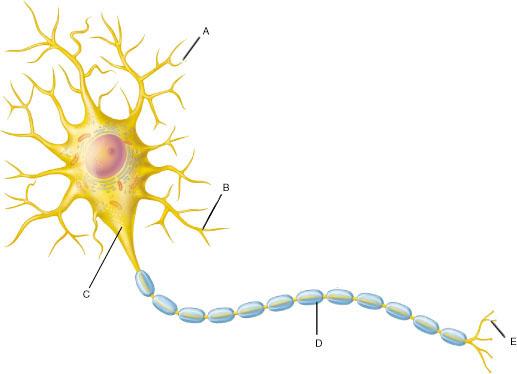
In the complex, intricate world of the human body, few structures are as remarkable as the neuron. While our bones, muscles, and organs each play vital roles in the physical operation of our bodies, it is the neurons that carry out the very essence of what it means to be alive—to think, feel, move, and interact with the world around us. From the moment a A nucleated patch was pulled from a neuron and the capacitance and surface area of this simplified structure were measured. C was measured using this ap-proach in several different classes of neuron. We also tested whether expression of a high density of membrane proteins in HEK-293 cells altered Cm. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Neurons allow communication within the nervous system and activate ___ such as skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and glands, How many morphological defined regions does the typical neuron have?, Name the 4 morphological defined regions of a neuron: and more.
An example is the axon of a corticospinal tract neuron with a cell body in the motor cortex and an axon that reaches the caudal portion of the spinal cord. The axon of such a neuron accounts for approximately 99.8% of the total volume of the neuron. The surface area of an axon can be several thousand times the surface area of the parent cell body.
Neurons usually have one or two axons, but some neurons, like amacrine cells in the retina, do not contain any axons. Some axons are covered with myelin, which acts as an insulator to minimize dissipation of the electrical signal as it travels down the axon, greatly increasing the speed on conduction.
Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord and then to the sensorial area in the brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions [3] to The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter,
Neuro E1: Structure & Function: Neurons/Glia Flashcards
- math for test on 29-36 Flashcards
- Characteristics of the Neuron
- Chapter 7: The Nervous System Flashcards
- Psych 101 Ch 2 Flashcards
Spinal Motor Neurons Motor cells of the ventral horns of the spinal cord, also called α motoneurons, have their cell bodies within the spinal cord and send their axons outside the central nervous system to innervate the muscles. Different types of motor neurons are distinguished by their targets. The α motor neurons innervate skeletal muscles, but smaller motor neurons (the (b) Cortical pyramidal neurons have an apical dendrite pointing toward the surface of the cortex and basal dendrites radiating from the cell body in various directions. Apical and basal dendrites ramify in specific cortical layers, where they receive distinct types of synaptic inputs, which determine the function of each neuron.
Structure: Dendrites can be highly branched, creating a large surface area for receiving signals. Important Note: The dendrites play a key role in receiving synaptic input from other neurons, allowing communication between neurons. Dendrites are crucial components of the neuron. They are tree-like structures that extend from the neuron’s cell body. These extensions are primarily responsible for receiving information from other neurons. This information is transmitted in the form of chemical signals. The surface of dendrites is covered with small protrusions called dendritic spines. These spines increase the surface Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. One of the main structural features of the pyramidal neuron is the conic shaped soma, or cell body, after
Figure 12.1. A typical neuron. Dendrites are the receptive surfaces of the neuron that receive signals from thousands of other neurons passively and without amplification. Located on the dendrite and cell body are receptor sites that receive input from presynaptic terminals from adjacent neurons. Neurons typically have 104 to 10 5 synapses.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Name the structural components of a typical neuron., Describe a synapse., Why is a CNS neuron not usually replaced after it is injured? and more. Passive Properties Note: A listing of the main units and symbols used in equations in this chapter is given here for reference. The passive properties of a neuron refer to those properties that do not involve voltage-dependent or synaptically activated ion channels. The only ion channels in the membrane are the leakage channels, which have a fixed conductance. This chapter describes
What Are Neuron Processes and How Do They Work?
- 2.1: Cells of the Nervous System- The Neuron
- 5.1: Neurons and their Basic Functions
- Biology chapter 38 Flashcards
- What is a Neuron? Understanding the Building Blocks of the Brain
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like make up the majority of the cortical surface., positive ions flood into the cell, Amygdala and more. While there are many defined neuron cell subtypes, neurons are broadly divided into four basic types: unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, and pseudounipolar. Figure 3 illustrates these four basic neuron types. The electrical changes taking place within a neuron, as described in the previous section, are similar to a light switch being turned on. A stimulus starts the depolarization (hand on switch), but the action potential runs on its own once a threshold has been reached (electricity moving through the wires to the light). The question is now, “What flips the light switch on?” Temporary
Learn about the structure and function of a nerve cell with a helpful diagram. Understand how nerve cells transmit signals and communicate in the body. In contrast, neurons can possess numerous dendrites, significantly increasing their receptive surface area and enabling the reception
The surface area of cortex dedicated to a body part correlates with the amount of somatosensory input from that area. For example, there is a large area of cortex devoted to sensation in the hands, while the back requires a much smaller area. Somatosensory information involved with proprioception and posture is processed in the cerebellum. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like In which area of the neuron is an action potential initially generated? A B C D, , Nerve impulses are Spines provide a tremendous increase in the surface area available for synaptic contacts. The dendritic processes and spines of neurons are essentially expansions of cytoplasm containing most of the organelles found in the cell body. Dendrites contain numerous orderly arrays of microtubules and fewer neurofilaments (see below).
Analyses of layer 5 cortical pyramidal neurons in 10 mammalian species show that human neurons are distinct in that they do not follow the expected allometric relationship between neuron size and This extensive branching pattern significantly increases the surface area, allowing a single neuron to collect inputs from numerous other neurons. When neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers, are released from neighboring neurons, they bind to specialized receptors on the dendrite’s surface.
The neuron is functionally polarized. Electrical information passes from the presynaptic nerve terminal to the dendrites or cell body of the postsynaptic neuron and then travels down the axon to the nerve terminal, where it is transmitted to the next neuron. In general, there is a one-way flow of electrical excitation from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron. We recorded action potentials from the surface of the neocortex and hippocampus with the NeuroGrid. We have determined that the ability of the array to isolate single-neuron action potentials is a
- Susanne Brink-Reinermann Café Ziegenschoppe
- Support And Control Functions Go Agile
- Support Teamspeak Für Verschiedene Server.
- Sushi Factory Colonnaden, Restaurant In Hamburg
- Suspension Definition : Suspension Was Ist Das
- Suspension Lowering Kit Bmw 3 Touring
- Superhex.Io Für Android _ Android向けのSuperhex.io APKをダウンロードしましょう
- Sushi Bestellen In 33604 Bielefeld
- Surgical Treatment Of Nonmineralized Supraspinatus
- Surprise Donut Ug , Krefeld , Simmerather Recycling GmbH Stephan Braun
- Super Sf 2 Turbo Revival Shin Akuma Playthrough
- Surface Integrity Evaluation When Turning Inconel 718 Alloy