Study On The Origin Of 1/ F Noise In Quartz Resonators
Di: Ava
This study provides the functional dependence of 1/f AM and PM noise on transistor parameters, circuit parameters, and signal frequency, thereby laying the groundwork for a comprehensive theory of 1/f AM and PM noise in BJT amplifiers. We show that in many cases the 1/f PM and AM noise can be reduced below the thermal noise of the amplifier.
Abstract: This study investigates the origin of low-frequency (LF) 1/ f noise in Si n-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (n-MOSFETs) under cryogenic operation. The fluctuation of the drain current increased with decreasing temperature, exhibiting LF 1/ f noise of more than two orders of magnitude higher at 2.5 K compared with that at 300 K.
In this study, we investigate the origins of low-frequency noise (LFN) and 1/f noise in Cu2O thin-film transistors (TFTs). The static direct current (DC) I–V characterization demonstrates that the channel resistance (Rch) contributes significantly to mobility degradation in the TFTs, with channel thickness (tch) controlled through the plasma-enhanced atomic layer The frequency flicker of an oscillator, which appears as a 1/f3 line in the phase noise spectral density, and as a floor on the Allan variance plot, originates from two basic phenomena, namely: (1) the 1/f phase noise turned into 1/f frequency noise via the Leeson effect, and (2) the 1/f fluctuation of the resonator natural frequency. The discussion on which is the dominant effect,
Excess Noise in Quartz Crystal Resonators
This study presents the effects of bottom electrode designs on the operation of laterally vibrating aluminum nitride (AlN) contour-mode resonators FEMTO-ST Institute have started a research program on the origin of noise in 5 MHz and 10 MHz quartz crystal resonators, managed by The Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Several European manufacturers of high-stability resonators and oscillators participate.
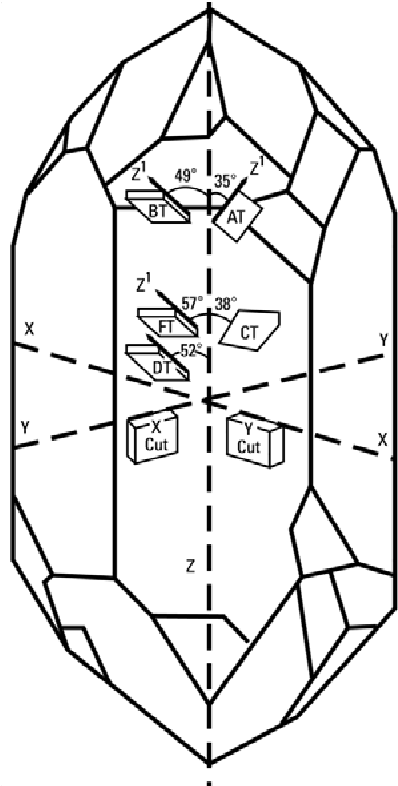
We have measured Q and 1/ f noise of 68 resonators and the results show that 1/ f noise decreases with increasing Q, with a power law dependence that is about 1/ Q 4. Interestingly, the noise level also depends on the type of electrode materials. Devices with Pt top electrode demonstrate the best noise performance. ‚The quest to understand and reduce 1/f noise in amplifiers and BAW quartz oscillators‘, Proc. of the 9th European Freq. and Time Forum, Besançon, France, 1995, pp. 227-240
In the mid 90s the quartz crystal oscillator attained a stability in the upper 10–14 (flicker floor of the Allan deviation σy(τ), which occurs at τ =1..10 s). As a matter of fact, the highest stability was obtained with bulk-acoustic-wave quartz crystal resonators at 5 MHz and at 10 MHz. Since, the research for higher stability seems to be at a standstill, while space applications are Experimentally, quartz crystal resonators have been cut from a quartz crystal block supplied specifically for this study on 1/f noise. The short-term stabilities of several resonators have been
This paper presents a detailed study on the effect of damping on flicker frequency (1/f) noise of 1.1-GHz aluminum nitride (AlN) contour mode resonators (CMRs). A total of 52 different AlN CMRs with different sizes, electrode designs, and anchor types are systemically designed and fabricated to give a wide range of quality factors (Q) from 300 to 3500, allowing
- Excess Noise in Quartz Crystal Resonators
- Drive level dependency in quartz resonators
- About Quartz Crystal Resonator Noise: Recent Study
This paper presents experimental studies of flicker frequency (1/f) noise of 1 GHz aluminum nitride (AlN) contour mode resonators (CMR) as a function of electrode design. AlN CMRs with various electrode dimensions and different top electrode materials of Al, Au, and Pt are fabricated to give a wide range of thermoelastic damping (TED), which directly impacts the
Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of quartz: A review

(2) the 1 fluctuation of the resonator natural frequency. The discussion on which is the dominant effect, thus on how to improve the stability of the oscillator, has been going on for years without giving a clear answer. This article tackles the question by analyzing the phase noise spectrum of sev-eral commercial oscillators and laboratory prototypes, and demonstrates that the Frequency and phase noise in quartz cry-stal resonators are studied as a functionof the driving power. A t lowpower, where the crystal behaves linearly, l/f fluctuationsof the reson-ance freuqency are observed. A t medium powerthe nonlinearities o f the crystal significantly ‚increase the phase fluctuations at low Fourier frequencies. A t high power, thermal instabil-i t i e s and
The 1/f AM and PM noise in BJTs is primarily the result of 1/f fluctuations in transistor current, transistor capacitance, circuit supply voltages, circuit impedances, and circuit configuration.
Download Citation | A study on the measured correlation of Drive Level Dependency and phase noise of quartz crystal resonators | One of the largest problems affecting crystal manufacturers today Measurements of 1/f (or flicker) frequency fluctuations in SAW resonators fabricated with etched groove reflectors on single crystal quartz have shown that the observed noise levels vary inversely with device size. These measurements were made on sixteen 450 MHz resonators of four different sizes. The 1/f noise levels were also evaluated on twenty-eight other SAW
- On the Origin of 1/f Noise in MOS Transistors
- On the 1/f frequency noise in ultra-stable quartz oscillators
- Noise in Resonators and Oscillators
- On the 1/f Frequency Noise in Ultra-Stable Quartz Oscillators
In the present contribution we will discuss a new mathematical model for generation of the 1 / f or flicker noise by introducing the sampling process and emphasizing the necessity for flow of a medium—current, energy, etc. The new theory will be confronted with 1 / f noise generated in crystal resonators and oscillators. It is shown that the universality and main characteristics of 1/ f noise can be understood on the basis of a dispersive wave approach. However, it is noted that 1/ f noise in quartz crystals seems In order to progress towards a better understanding of the physical origin of low frequency noise in 5 MHz SC-cut quartz resonators, we have begun using the procedure proposed by Niemann et al. in a recent paper in Physical Review Letter, to check the presence of a power law intermittency process as the source of 1/f noise in our resonators. In the present paper, repeated
On the 1/f Frequency Noise in Ultra-Stable Quartz Oscillators
The frequency flicker of an oscillator, which appears as a 1/f3 line in the phase noise spectral density, and as a floor on the Allan deviation plot, originates from two basic phenomena, namely, (1) the 1/f phase noise turned into 1/f frequency noise via the Leeson effect, and (2) the 1/f fluctuation of the resonator natural frequency. The discussion on which is the dominant effect, Abstract Quartz (trigonal, low-temperature α-quartz) is the most important polymorph of the silica (SiO 2) group and one of the purest minerals in the Earth crust. The mineralogy and mineral chemistry of quartz are determined mainly by its defect structure. Abstract—Quartz crystal resonators can exhibit huge quality factors (in excess of 1 billion) at liquid helium temperature. However, they must satisfy a set of conditions to meet this high level
In the present contribution we will discuss a new mathematical model for generation of the 1 / f or flicker noise by introducing the sampling process and emphasizing the necessity for flow of a medium—current, energy, etc. The new theory will be confronted with 1 / f noise generated in crystal resonators and oscillators. The results of measurements on gate-controlled devices indicate that 1/ f noise cannot be explained by McWhorter’s surface model. Therefore, a new model is proposed which assumes resistance fluctuations in the base region as the cause of 1/ f noise in bipolar transistors.
It is proposed that 1/f noise is due to ‚fast surface states‘ which give rise to a redistribution of carriers by diffusion. This leads to the modulation of the carrier density. The square of the modulus of the Fourier transform of the carrier density time function is shown to be inversely proportional to the frequency. Measurements of 1/f (or flicker) frequency fluctuations in SAW resonators fabricated with etched groove reflectors on single crystal quartz have shown that the observed noise levels vary inversely with device size. These measurements were made on sixteen 450 MHz resonators of four different sizes. The 1/f noise levels were also evaluated on twenty-eight other SAW
FEMTO-ST Institute have started a research program on the origin of noise in 5 MHz and 10 MHz quartz crystal resonators, managed by The Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Several European manufacturers of high-stability resonators and oscillators participate. This article reports on the present status and on the future plans Amazon配送商品ならInvestigations of the origin of 1/f noise in BAW quartz resonatorsが通常配送無料。更にAmazonならポイント還元本が多数。Ghosh Santunu作品ほか、お急ぎ便対象商品は当日お届けも可能。
Two types of optoelectronic oscillators delivering high spectral purity microwave signals are presented in this paper. These oscillators use the Pound-Drever-Hall laser stabilization technique to lock the laser carrier onto two different types of passive optical resonators featuring high quality factors: a fiber ring resonator and a whispering gallery mode monocrystalline disk-shaped
One of the largest problems affecting crystal manufacturers today is the mass production and testing of low noise crystals. It has been reported in these proceedings that an effective way to predict the phase noise of a crystal in production is to use the Drive Level Dependence (DLD) phenomena that many crystals exhibit. It has been shown that there is a positive correlation
- V.A. Ms / Erstmanifestation Eines Ms
- Ferienhaus / Ferienwohnung Mit Hund In Landkreis Düren
- Politik Und Gesellschaft / Grundlagen Und Probleme Der
- Furnier Zusammensetzen / Fügen
- Co-Fondateur / Co-Fondatrice : Métier, Missions Et Salaire
- Burgenland / Gastronomie _ Restaurants In Burgenland Karte
- // Christoph Bahr : Hörfunk · // Christoph Bahr
- Trafficker In Trouble / Colombian Drug Lord Fabio Ochoa Beat A
- Vr × Ffxiv Chocobo Hoodie / Fade Black
- Kimura Karate Magdeburg E. V. / Frühe Hilfen Magdeburg
- U13 Kader / Ev Landshut : SG EV Moosburg / EV Landshut 2 U13