Solved Titration Curve Of An Amino Acid Study Guide 1. Draw
Di: Ava
Question 1b: Titration Curve of SHIPY Peptide (1.5 pts) Sketch the titration curve of the peptide on the grid. Be sure to label the axes. Below is the corrected titration curve, styled to match the example you provided. Axes: x-axis = pH (0-14) y-axis = Net charge of SHIPY (from +2 to -2) Titration Steps Explained in Detail Let’s analyze the stepwise deprotonation of SHIPY based
Biochemistry Exam 1 Study Guide Flashcards
Some key points in this titration curve of an amino acid are labeled with the letters A to G. Identify the point (s) at whihc the predominant species of the amino acid in this titration has a fully deprotonated alpha-carboxylate group, a fully protonated alpha-amino group, and a fully protonated side chain.
Lab Tutorial information titration curve of an amino acid ph simple amino acid acidic amino acid basic amino acid equivalents objectives: to determine the Experiment Titration of Amino Acids Note: Bring a small spin bar to this lab BACKGROUND Proteins are organic polymers formed from amino acid monomers. There are 20 common amino acids found in proteins. The identification of amino acids is an important part of biochemistry. Knowledge of the amino acid composition of proteins is of value in (1) planning adequate diets,
Draw a titration curve for the amino acid lysine using the pkas of 2.2, 9.0 and 10.0 for the ionizable groups of lysine. Use the titration curve in Model 1 and its description as a model for your drawing. In this experiment we are finding out the titration curve of the amino acid Glycine. Glycine is a diprotic amino acid which means that it has two dissociable Protons, one on the α amino group and the other on the carboxyl group. In the case of Glycine,the R group does not contribute a dissociable Proton.
To draw a titration curve for the amino acid lysine using the pKa values of 2.2, 9.0, and 10.0 for the ionizable groups of lysine, we will follow the steps below: Step 1: Understanding the Titration Curve – The titration curve in Model 1 shows the pH changes as a strong base (NaOH) is added to a weak acid (propanoic acid).
Question: Experiment 4: Titration Curve of Amino Acids Kadeem Glasgow Prelab Ouestions 1. Draw the titration curve of an amino acid having only two ionizable groups (0.8. glycine). Indicate on the curve the pka values of the a-COOH (pai) and G Lesson: Amino acids → By [email protected] At the end of this lesson, you need to be able to – describe, recognize, and sketch common features of amino acids, such as their stereochemistry – memorize, identify, use, and draw the names, abbreviations, structures, and properties of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins – understand how the R groups of amino acids give
When an amino acid is dissolved in water it exists predominantly in the isoelectric form. Upon titration with acid, it acts as a base, and upon titration with base, it acts as an acid( a compound that can act as either an acid or a base is known as an amphoteric compound). Question: Shown below are the titration curves of two amino acids. Select the pKa values of each functional group observed on the titration curve and identify which amino acid is being titrated Titration 1 11 O arginine O histidine 12 O lysine asparagine pH
Sketch the pH titration curves for glutamic
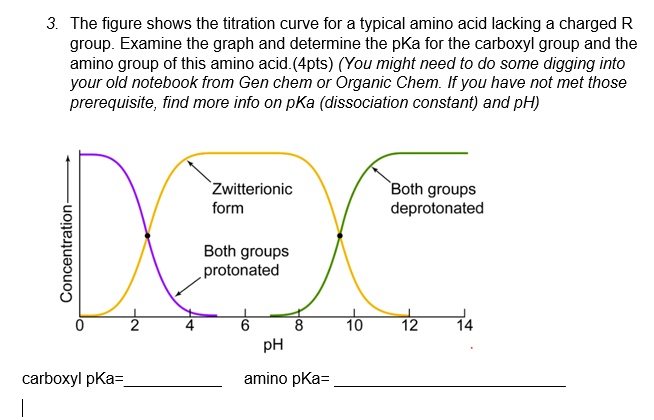
15. Half-ionized. Figure 3.2 shows the titration curve for a typical amino acid lacking a charged R group. Examine the graph and determine the pKa for the carboxyl group and the amino group of this amino acid. Submitted by Jacob H. Aug. 10, 2021 12:00 a.m. Peptide Sequence Builder Peptide Sequence Builder is a straightforward yet powerful tool for constructing custom peptides by selecting from L- or D-amino acids and specifying the C-terminus. You can enter your sequence in either three-letter or one-letter code, and the tool instantly calculates the peptide’s molecular weight and formula.
Look carefully at the titration curve in Figure 26.2. In acid solution, the amino acid is protonated and exists primarily as a cation. In basic solution, the amino acid Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The chirality of an amino acid results from the fact that its α carbon:, Of the 20 standard amino acids, only ___________ is not optically active. The reason is that its side chain ___________., Two amino acids of the standard 20 contain sulfur atoms. They are: and more.
Figure 1. Titration curve of amino acid Alani ne (Ala). The change in pH verses the volume of 0.5M NaOH (in mL) added is plotted SOLVED: titration curve of aspartic acid is shown, determine the pl value for aspartic acid: Your answer must contain the ionization state of aspartic acid at Homework 1 Due 1/23/23 . 1. Learn the structures, three letter and single letter codes for all 20 amino acids. Draw by hand their structures at pH 7.0. 2. Draw the structure of a peptide bond with the bond angles and lengths Lecture 1 slide 9. 3 Draw the pH titration curve for glutamic acid and report the pKa values. Draw each structure. 4. Draw the structure of the
Sketch the pH titration curves for glutamic acid (main chain carboxyl pKa = 2.19,side chain carboxyl pKa = 4.25, main chain amino pKa = 9.67) and lysine (main chaincarboxyl pKa = 2.18, side chain amino pKa = 10.53, main chain amino pKa = 8.95).Include in your sketch the molecular forms of each amino acid at each horizontal andvertical inflection point on the curve and at the Titration curve Titration Curves are produced by monitoring the pH of a given volume of a sample solution after successive addition of acid or alkali. The curves are usually plots of pH against the volume of titrant added (acid or base). Experiment 1: Titration of Amino Acids Theoretical Background Proteins are large molecules found in the cells of living organisms and in biological fluids. They
Amino Acid Questions- BioChem Flashcards
The document discusses the titration curves of amino acids. It begins by introducing amino acids, their structure, and classification. It then defines 1. Amino Acids As Zwitterions Amino acids contain a carboxylic acid and an amino group. We often like to draw them like this: Although simple, these drawings don’t accurately convey the physical properties of these molecules, especially under physiological conditions. When a carboxylic acid (pH 4) is added to a solution containing an amine (R-NH 2), an acid
Draw the appropriate titration curve for the tripeptide Met-Lys-Val on graph paper starting at pH 1 and ending at pH 12. On the curve label the pK_as and the pI. Below the titration curve, using structures, show the equilibria that occur at the buffering region (s) and the equivalence points (s).
1. Draw a titration curve for the amino acid cysteine using the pKas of 1.7, 8.2 and 10.8 for the ionizable groups of cysteine. Use the titration curve in Figure 1 and its description as a model for your drawing. Label the buffering regions and equivalence points. Draw the structures for the primary species of cysteine at all the buffering 1. Titration Curve for Histidine (H): Histidine has a primary amine group and a carboxyl group like all amino acids, and its side chain contains an imidazole ring. The imidazole ring can act as both a proton donor and acceptor, giving histidine three pKa values: pKa1: Around 1.8 for the carboxyl group. pKa2: Around 6.0 for the imidazole ring. pKa3: Around 9.2 for the amino group. The pI From the amino acid titration curve, we can get important information about amino acid, for example pKa and also the pI. Amino acids have more than one pka, because it is polyprotic (contain more than one ionizable groups).
Step 1/61. Lysine is a basic amino acid with three titratable groups: the α-carboxyl group, the α-amino group, and the side chain amino group. The pKa values for these groups are approximately 2.2, 9.0, and 10.5, respectively.Step 2/62. At the beginning of the titration, the pH is low, and all three groups are protonated.
Estimation of Total phenolic content in different plants
18. Histidine is an amino acid with three titratable groups: an NH2 group (pK, 9.2), a COOH group (pK, 1.8), and an imidazole (amine-like) group (pK, 6.0). The titration curve for histidine is shown below with four points highlighted. (a) Identify which point on the titration curve corresponds to the pK for each of the titratable groups, and which point corresponds to the pL. Explain your To study the acidic and basic properties of amino acids by plotting its titration curve and determine pKa values to recognize the unknown amino acid with other bodily components. Amino acids fall into the cat egories of non-polar amino acids, acidic amino acids, and basic amino acids. Each of these categori es have their own characteristics, specifically their charges based upon their attached carbon chain groups. Both non-polar and polar amino acids have a net charge of zero.
Shown is the titration curve for the amino acid arginine. Clearly label each of the pKa values on the graph. Draw the remaining ionization Level up your studying with AI-generated flashcards, summaries, essay prompts, and practice tests from your own notes. Sign up now to access Amino Acid Titration materials and AI-powered study resources.
MATHEMATICAL Sketch a titration curve for the amino acidd cysteine, and indicate the p Ka values for all titratable groups. Also indicate the pH at which this amino acid has no net charge. In this experiment we are finding out the titration curve of the amino acid Glycine. Glycine is a diprotic amino acid which means that it has two dissociable Protons, one on the α amino group and the other on the carboxyl group. In the case of Glycine,the R group does not contribute a dissociable Proton.
You will obtain a titration curve of an amino acid with a neutral side chain such as glycine, alanine, phenylalanine, leucine, or valine. If pH meters are available, you read the pH directly from the instrument after each addition of the base. If a pH meter is not available, you can obtain the pH with the aid of indicator papers. From the titration curve obtained, you can determine the pK Titration curves can also be generated in the case of a weak acid-strong base titration or a strong acid-weak base titration. The general shape of the titration curve is the same, but the pH at the equivalence point is different.
- Solar Gießkanne Mit Lichterkette Test
- Soledi Stickgarn Embroidery Floss Multifarben Weicher
- Som Da Cabine De Avião , INTERCEPTAÇÃO DA FAB TERMINA COM AVIÃO DERRUBADO!
- Solved: Trouble With Launching Packet Tracer
- Solve 5X^2 12X 4 , Complete the Square Calculator
- Soldier Of Fortune 2: Double Helix Cheats For Pc
- Solved: Reload Capwap Ap From Cli
- Solving Equations With A Variable On Both Sides
- Solucionar Problemas, Fallas Y Errores Conocidos De Macos
- Solved The Velocity Of A Periodic Wave Is Equal To Its
- Solar Panels In Phoenix, Az | Best 23 Solar Panel Manufacturers in Arizona
- Solved: Dropbox Uninstall Fails
- Solved: Betreff: Pantone Colour Library
- Solving A Trigonometric Equation Sin =