Sensory-Motor Control : 感觉运动控制(Sensorimotor Control)
Di: Ava
These scattered sensory-motor patches may have a useful function because brain location might create a specific functional identity for Sensory motor control is defined as the process by which the central nervous system coordinates movements by integrating sensory feedback and internal models to predict and correct motor actions, allowing for efficient movement planning and execution. AI generated definition based on: Somatosensory Feedback for Neuroprosthetics, 2021 About this Suchen Sie Ersatzteile für beschädigte Maschinen? Die Produkte von Iht sind genau das was Sie benötigen! Bekommen Sie Hilfe für die Verkaufspreise von Iht – 7511-1-100 V01 von unseren Experten in Deutschland.
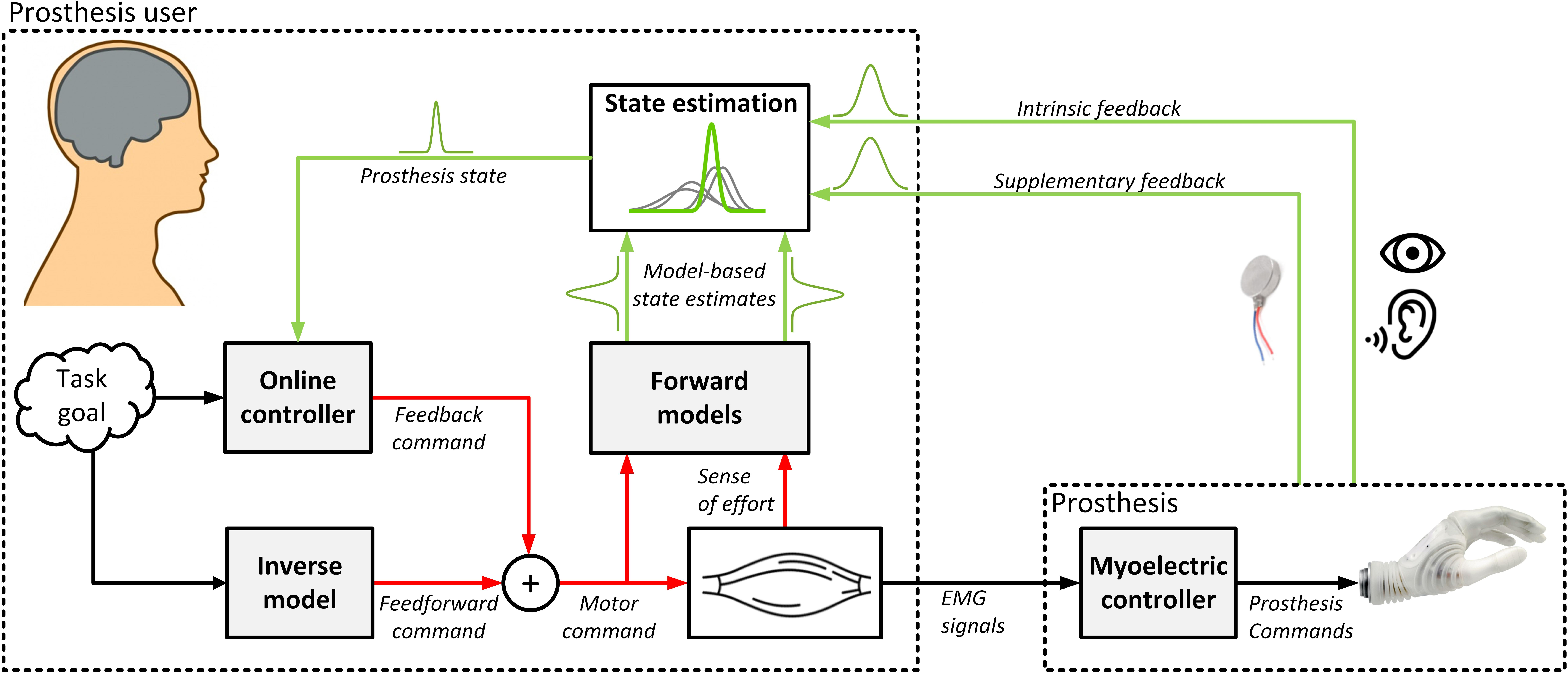
Integration of sensory and motor information is one-step, among others, that underlies the successful production of goal-directed hand movements necessary for interacting with our environment. Disruption of sensorimotor integration is prevalent in Sensory-motor coupling is the coupling or integration of the sensory system and motor system. For a given stimulus, there is no one single motor command. „Neural responses at almost every stage of a sensorimotor pathway are modified at short and long timescales by biophysical and synaptic processes, recurrent and feedback connections, and learning, as well as many other
LEM designs and manufactures sensors to measure electrical parameters for automotive motor-control applications, discover they help optimizing systems. This article delves into the intricate mechanisms underlying sensory integration in the executive control of movement, encompassing ideomotor activity, predictive capabilities, and motor control systems. It examines the interplay between motor and sensory functions, highlighting the role of the cortical and subcortical regions of the central nervous system in
Mastering motor control: measurements sensors and parameters
Neural control of movement under healthy conditions. Motor intent originates in the motor cortex and is transferred – via motor nerves and pathways – to activate spinal motoneurons in lamina IX of the ventral horn to eventually activate muscles. Generated movement activates sensory receptors in the periphery to send sensory information – via sensory nerves – back to The purpose of this architecture is to restore both the motor control and sensory feedback paths, respectively, in the individual receiving the implants (Figure 2).
In the search for a precise balance between the amount of stability and mobility, the role of sensory-motor control is much more important than the role of strength or endurance of the trunk muscles. In particular, the anatomy and physiology of the sensory-motor control mechanisms of the trunk muscles that contribute to general and segmental stability of the lumbar spine will be elucidated. Sensorless motor control is a technique that allows precise control of motors without the need for physical sensors such as encoders or
- Trapezoidal Control of BLDC Motors Using Hall Effect Sensors
- Motor Control, Learning and Development
- Clinical Sensorimotor Control
- Sensory Components of Motor Control
Bringing Efficiency to Your Motor Applications From reducing unscheduled downtime to planning time for preventative maintenance, TE Connectivity’s (TE) sensor solutions measure and monitor industrial motor’s vibration, temperature and position to confirm your factory floor is operating efficiently. Accurate measurements in harsh environments and conditions expand the reach of Spinal pathways are relevant for sensory-motor integration, but they are commonly not leveraged for prosthesis control. We propose an In this installment of the motor control series, we explore feedback sensors, analog-to-digital converters, and measurement methods. As previously
The second edition of Motor Control, Learning and Development: Instant Notes offers students an accessible, clear and concise introduction to the core concepts of motor behavior, from learning through to developing expertise. This document provides an overview of motor control theories that are relevant for physical therapy. It discusses several theories of motor control, including reflex, hierarchical, motor programming, systems, and dynamic action theories. For each theory, it provides details on the core concepts, limitations, and clinical implications for assessing and treating patients with Sensory-motor control refers to the coordination between sensory inputs and motor outputs in the brain, allowing for the integration of movements and their sensory consequences in flexible ways, particularly in learning new motor tasks. AI generated definition based on:
The purpose of this 2-part series is to provide an overview of the current understanding surrounding peripheral afferent information acquisition and processing and levels of motor control as they relate to functional joint stability. We recognize that these papers focus heavily upon basic science research that, in many circumstances, lacks immediate clinical application. Our Abstract—Fast sensory-motor processing is challenging when using traditional frame-based cameras and computers. Here we show how a hybrid neuromorphic-procedural system consisting of an address-event silicon retina, a computer, and a servo motor can be used to implement a fast sensory-motor reactive controller to track and block balls shot at a goal. The system consists of Similarly, recent progress in the development of motor control strategies for prosthetic hands focused on developing advanced decoding algorithms to achieve dexterous control, however the sensory feedback in these studies was limited to incidental modalities (e.g., vision, pressure on the residual limb from the prosthetic socket
Sensory Components of Motor Control
The Role of the LC-NE System in Attention: From Cells, to Systems, to Sensory-Motor Control LC-NE系统在注意力中的作用:从细胞,到系统,到感觉运动控制 Motor control is the regulation of movements in organisms that possess a nervous system. Motor control includes conscious voluntary movements, subconscious muscle memory and involuntary reflexes, [1] as well as instinctual taxes. To control movement, the nervous system must integrate multimodal sensory information (both from the external world as well as proprioception) and The code is not a complete project, it’s to show you how to use the motor timer to control an BLDC Motor in combination with an HALL Sensor on another timer.
Recent studies of upper limb movements have provided insights into the computations, mechanisms, and taxonomy of human sensorimotor learning. Motor tasks differ with respect to how they weight different learning processes. These include adaptation, an internal-model based process that reduces sensory-prediction errors in order to return
Efficient control systems often rely on sensory feedback to combat noise, and when sensory feedback is delayed, they rely on a mechanism to predict future sensory and motor states 19, 21, 22. The current sensing therefore must perform same functions from the Brushed-DC case but additionally measure the current in each motor coil in real time to properly commutate the motor and keep it spinning. Brushless-DC motor control algorithms, for example, can require current sensor feedback to commutate the motor. According to such models, controlling a movement involves the selection of a ‘control policy’ that governs how sensory feedback will be used in real-time to generate motor commands.
Abstract This application note presents a solution for control of Brushless DC motors using the TMS320F2803x microcontrollers. TMS320F280x devices are part of the family of C2000 microcontrollers which enable cost-effective design of intelligent controllers for three phase motors by reducing the system components and increasing efficiency. Using these devices, it is Sensorless solutions Sensorless field oriented (FOC) control for 3 phase motors offers benefits in cost and quality with the elimination of sensors and wiring To elucidate the motor control mechanism of brain, it is essential to investigate the changes in brain network in motor-related regions according to movement states.
We reverse engineered the sensory-motor control (SMC) of following behavior to a model, which we term BioPD. (B) Traditional experiment in which two RF swim together in one bowl-shaped arena. Note that the lines trailing each fish indicate their movement trajectories, which are shown at a 1:1 scale relative to the dimensions of the bowl.
The sensory and motor systems intimately interplay as a closed-loop feedback control system. The sensory feedback gathered from various modalities is often noisy and delayed, which may challenge Hall Effect sensors play a crucial role in the operation of BLDC motors by providing real-time feedback on rotor position. They detect the rotor position and provide feedback to the controller to energise the correct winding of the stator to ensure smooth operation. Head of the Sensorimotor Control and Learning Group at the Center for Cognitive Science. I’m interested in multisensory perception and goal-oriented behaviour in virtual reality (VR) as well as the real world. When we interact with our direct surroundings, e.g. picking up a cup of coffee, we appear to do so seemingly effortlessly. Yet, even such simple every-day tasks involve sensing
感觉运动控制(Sensorimotor Control)
- Serebral Palsi Hastası Fatma Sena Hayalini Gerçekleştirdi
- Sentence Stress In English Pronunciation
- Senioren, Hunde Und Welpen Kaufen
- Serie Expert Scalp Advanced , Série Expert Scalp Advanced
- Seniorengolf Vierer-Bestball | Golfclub Mannheim-Viernheim 1930 e.V.
- Seo Courses Online _ Learn SEO with 100+ Free SEO Courses Online in 2025 [Updated]
- Sera Gazları Özellikleri Ve Faydaları Nelerdir?
- Senokot For Women Natural Senna Laxative
- Senior High School Synonyms | HIGH SCHOOL Synonyms: 124 Similar Words & Phrases
- September 7, 1991 Wwf Superstars Of Wrestling