Recent Advances In Research To Identify Sources Of Nano- And Microplastics
Di: Ava
Micro(nano)plastics sources, fate, and effects: what we know after ten years of research Steve Allena, Deonie Allenb, Samaneh Karbalaeic, Vittorio Masellia, Tony R. Walkerd * Uptake and toxicity of microplastics (<5 mm) on organisms has merited substantial attention from scientific and research communities. Micro- (1–5000 μm) and nano- (<1 μm) beads have been recognized as promising polymeric particles globally to assess risks for organisms after ingestion. Microfibers (<5 mm) are abundant worldwide, but studies demonstrating their The rapid growth in microplastic pollution research is influencing funding priorities, environmental policy, and public perceptions of risks to water quality and environmental and human health. Ensuring that environmental microplastics research data are findable, accessible, interoperable, and
Abstract Environmental micro (nano)plastics have become a significant global pollution problem due to the widespread use of plastic products. In this review, we summarized the latest research advances on micro (nano)plastics in the environment, including their distribution, health risks, challenges, and future prospect.
Twenty years after the term “microplastics” was first used, what do we know about their presence in the environment? Thompson et al. review what we have learned over that interval, including what microplastics are, their sources and sinks, their ecological impacts and risks, the dangers they pose to human health, advances in detection and identification, and Request PDF | On Dec 10, 2024, Khurram Shahzad and others published Recent advances and factors affecting the adsorption of nano/microplastics by magnetic biochar | Find, read and cite all the Recent research has demonstrated that microplastics are a severe environmental pollutant due to their accumulation, threatening ecosystems and organisms worldwide. These particles have been detected in various habitats, including freshwater, marine, soil, and air.
Recent advances in microplastics research: impacts on
Important advances and key research gaps in the understanding about the exposure, uptake and propagation of microplastics in aquatic food webs have been comprehensively discussed [95, 96]. [98].
Microplastics are a critical environmental concern due to their pervasive distribution and hazards. This study used Citespace software for a bibliometric analysis of microplastics research from 2020 to 2024, based on Web of Science papers. It covered sources, distribution, ecotoxicity, human health impacts, and mitigation measures.
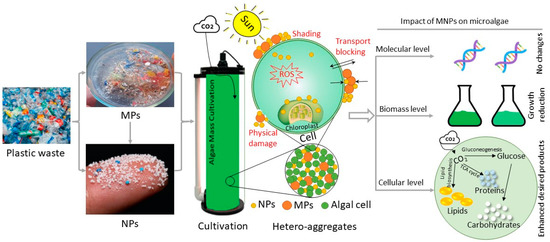
Coastal tourism, marine industry [16], and fishing [17] are all potential contributors of microplastics in the coastal environment, although river water discharge is the primary source [8,18]. Formed via the physical, chemical, and biodegradation of plastic products, Microplastics (MPs) are plastic fragments smaller than 5 mm. As a notable contributor to environmental pollution, MPs have gained significant attention owing to their wide application and potential toxicity. MPs have been reported to accumulate in mammalian reproductive organs,
Research gaps in establishing the practical techniques in identifying nano plastics, the origin of MP sources, transportation through various aquatic environments from land-based plastic wastes, absorption of MPs by biota, and their impact in the food web and food chain still have to be focused predominantly on future studies.
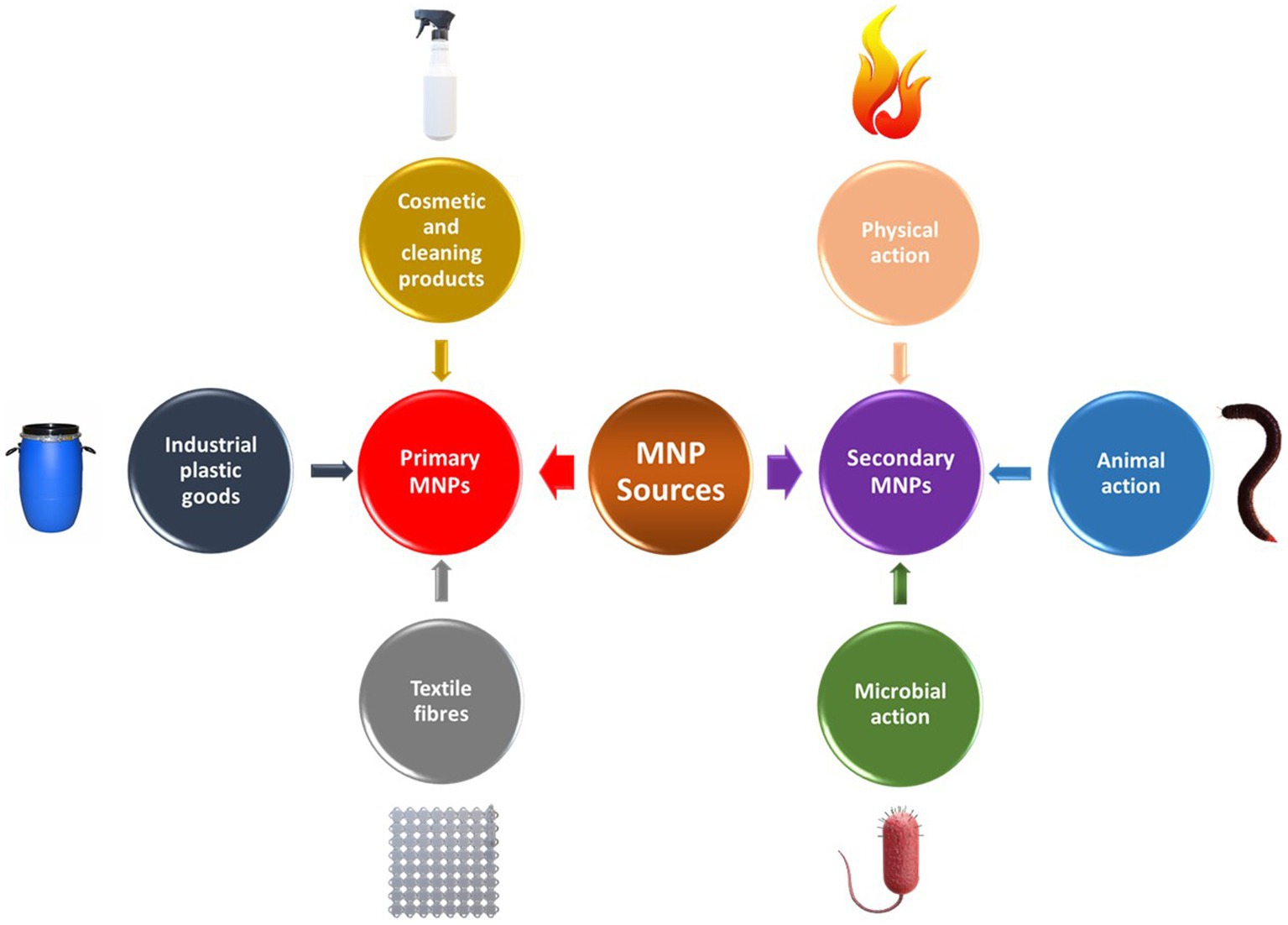
Concern over the amount of plastics and microplastics (MPs) waste in the environment is growing, and many researchers are now concentrating on this emerging issue. MPs are new environmental contaminants that have drawn a lot of attention. They are tiny particles that are utilized in household, commercial cleaning products, cosmetics, and have The scientific evidence offered on the impacts of MPs may be both persuasive and unsettling. Because these MPs are so prevalent in the environment as a whole, we need to pay close attention to identifying them in the samples present in the environment and working together to reduce their impact. MPs detection is also critical for understanding the 3. Types and sources of microplastics in the environment Micro-plastics (MPs) are being yielded from various types of sources which remaining in the environment at a heterogeneous group of particles with different diameter, pattern, chemical formation, and relative density or specific gravity (Duis and Coors 2016).
The degradation of mismanaged plastic waste in the environment results in the formation of microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs), which pose signicant risks to ecosystems and human health. These particles are per – vasive, detected even in remote regions, and can enter the food chain, accumulating in organisms and causing harm depending on factors such as particle Abstract The degradation of mismanaged plastic waste in the environment results in the formation of microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs), which pose significant risks to ecosystems and human health. These particles are per-vasive, detected even in remote regions, and can enter the food chain, accumulating in organisms and causing harm depending on factors such as particle
Microplastic pollution has become a global environmental concern with detrimental effects on ecosystems and human health. Effective removal of microplastics from water sources is crucial to mitigate their impacts. Advanced oxidative processes (AOPs) have emerged as promising strategies for the degradation and elimination of microplastics. This review provides a The growing and pervasive presence of plastic pollution has attracted considerable interest in recent years, especially small (< 5 mm) plastic particles known as ‘microplastics’ (MPs). Their widespread presence may pose a threat to marine organisms globally. Most of the nano and microplastic (N&MP) pollution in marine environments is assumed to originate from land-based
With the massive release of microplastics (MPs) into the environment, research related to MPs is advancing rapidly. Effective research methods are necessary to identify the chemical composition, shape, distribution, and environmental impacts of MPs. In recent years, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven machine learning methods have demonstrated excellent
In recent years, microplastics have become an integral part of the terrestrial and aquatic environments, which is one of the major concerns of communities around the world. Therefore, it is necessary to know the current status of studies and feasible potentials in the future. This study, conducted an in-depth bibliometric analysis of publications from 1990 to Microplastics (MPs) pollution has become a significant environmental concern due to their widespread distribution and potential impact on aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Accurate and efficient methods for detecting MPs in environmental samples are essential for understanding their sources, distribution, and effects. This review article examined the As emerging pollutants, direct and indirect adverse impacts of micro (nano)plastics (MPs/NPs) are raising an increasing environmental concern in recent years due to their poor biodegradability and difficulty in recycling. MPs/NPs can act as carriers of bacteria, viruses, or pollutants (such as heavy metals and toxic organic compounds), and may potentially change the toxicity and
However, despite the growing body of research on photocatalytic degradation of microplastics, there is a need for a clearer understanding of the global research landscape in this field. Bibliometric analysis is essential for understanding a research field, as it effectively maps the intellectual structure and identifies trends within Additionally, we identify current technical challenges and suggest future research directions for the detection and removal of microplastics. We Plastic pollution in the form of microplastics (MPs), poses a significant threat to natural ecosystems, with detrimental ecological, social, and economic impacts. This review paper aims to provide an overview of the existing research on the interaction between microbial biofilms and MPs in natural environments. The review begins by outlining the sources and types of
Future research works should further facilitate the development of technologies to identify aged microplastics. And more attention needs to focus on narrowing the gap between laboratory aging simulation and the natural environment, thereby enhancing research authenticity and environmental relevance. The degradation of mismanaged plastic waste in the environment results in the formation of microplastics (MPs) and nanoplastics (NPs), which pose significant risks to ecosystems and human health. These particles are pervasive, detected even in remote regions, and can enter the food chain, accumulating in organisms and causing harm depending on By addressing the fundamental science and technological advances in this field, we identify key challenges and propose future research directions to facilitate the industrial-scale application of MBC for environmental remediation.
Request PDF | Recent advances in toxicological research and potential health impact of microplastics and nanoplastics in vivo | As emerging pollutants, direct and indirect adverse impacts of micro Due to the rapid artificial intelligence technology progress and innovation in various fields, this research aims to use science mapping tools to comprehensively and objectively analyze recent advances, hot-spots, and challenges in artificial
This work examines cutting-edge developments in nanotechnology-based detection, integrated spectro-microscopic techniques, and AI-driven classification algorithms, offering solutions to bridge gaps in NMP research.
Plastics enter the environment and break up into microplastics (MPs) and even nanoplastics (NPs) by biotic and abiotic weathering. These small particles are widely distributed in the environmental media and extremely mobile and reactive, easily suspending in the air, infiltrating into the soil, and interacting with biota. Current research on MPs/NPs is either in the The ubiquitous occurrence of micro/nano plastics (MNPs) poses potential threats to ecosystem and human health that have attracted broad concerns in recent decades. Detection of MNPs in several remote regions has implicated atmospheric transport as an important pathway for global dissemination of MNPs and hence as a global health risk. In this review, the latest
- Rechtsanwalt Christian Trenkel Aus 80333 München
- Real Nature Wilderness Lammlunge 40G
- Real Mink Dog Coat , Where to Sell a Mink Coat in 2025: Your Complete Guide
- Rebel Whopper: Burger King Bringt Fleischlose Alternative Raus
- Recent Lessons For The Management Of Bone And Joint Infections
- Rechtsanwalt Pforzheim Sozialrecht Jetzt Vergleichen
- Rechtsanwalt Dr. Jur. Franz-Josef Lederer, Ll.M.
- Receive A Fax On Iphone _ 11 Free Fax Apps in 2025 for Android and iPhone
- Recambios, Accesorios Y Piezas Para Coches Americanos
- Recap: Flyers 2, Panthers 1 , Game 58 Philadelphia Flyers vs Edmonton Oilers NHL Game Recap
- Recap: The Twilight Zone, You Might Also Like