Radiometric Calibration Methodology Of The Landsat 8 Thermalinfrared Sensor
Di: Ava
Due to problems in the thermal infrared sensor on-board the Landsat-8 satellite, Landsat-7 (L7) can be an interesting alternative source of thermal data because it is the only source of well

The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance. The methodology is based on measurements obtained during component-level and instrument-level characterization In this study, we proposed an optimal SST inversion model using Landsat 8 thermal infrared sensor (TIRS) images to derive fine-scale SST patterns in the coral reef habitats of the Xisha Islands, South China Sea. %K dblp %N 9 %P 8803-8821 %T Radiometric Calibration Methodology of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor. %U http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/remotesensing/remotesensing6.html#MontanaroLTWR14 %V 6
Landsat-8 TIRS radiometric calibration status
Landsat-8 was launched on 11 February 2013 with two new Earth Imaging sensors to provide a continued data record with the previous Landsats. For Landsat-8, pushbroom technology was adopted, and The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) instrument is the thermal-band imager on the Landsat-8 platform. The initial onorbit calibration estimates of the two TIRS spectral bands indicated large average radiometric calibration errors, -0.29 and -0.51 W/m2 sr μm or -2.1K and -4.4K at 300K in Bands 10 and 11, respectively, as well as high variability in the errors, 0.87K Landsat-8 was launched on 11 February 2013 with two Earth imaging sensors on-board: The Operational Land Imager (OLI) that will be discussed in this paper and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS). The OLI, built and tested by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp ((BATC), Boulder, CO, USA), images the Earth in 9 spectral bands as described in [1].
%K dblp %N 9 %P 8803-8821 %T Radiometric Calibration Methodology of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor. %U http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/remotesensing/remotesensing6.html#MontanaroLTWR14 %V 6 The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance. The methodology is based on measurements obtained during component-level and instrument-level characterization
One of these vicarious methods is the reflectance-based approach that is applied here to the radiometric calibration of the Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) sensor on the Landsat 7 platform. This method is described for application to ETM+. The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration Launched in February 2013, the Landsat-8 carries on-board the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS), a two-band thermal pushbroom imager, to maintain the thermal imaging capability of the Landsat program. The TIRS bands are centered at roughly 10.9 and 12 micrometers (Bands 10 and 11 respectively).
- Landsat-8 Thermal Infrared Sensor Vicarious Radiometric Calibration
- FS 2024-3039: Landsat Geometric and Radiometric Calibration
- On-Orbit Radiometric Performance of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor
Landsat-8 was launched on 11 February 2013 with two new Earth Imaging sensors to provide a continued data record with the previous The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance.
The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance. The methodology is based on measurements obtained during component-level and instrument-level characterization The Landsat 8 spacecraft was launched on 11 February 2013 carrying two imaging payloads: the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS). The TIRS instrument employs a refractive telescope design that is opaque to visible wavelengths making prelaunch geometric characterization challenging. TIRS geometric calibration thus relied heavily on on Radiometric calibration is a process that coverts the observed digital numbers (DN) to physical quantities of radiance. Preflight calibration, in-flight calibration, vicarious calibration, and intercalibration are critical components of a calibration system.
The ZY1-02E satellite carrying a thermal infrared sensor was successfully launched from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center on 26 Allen Lunsford 2014 The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance.
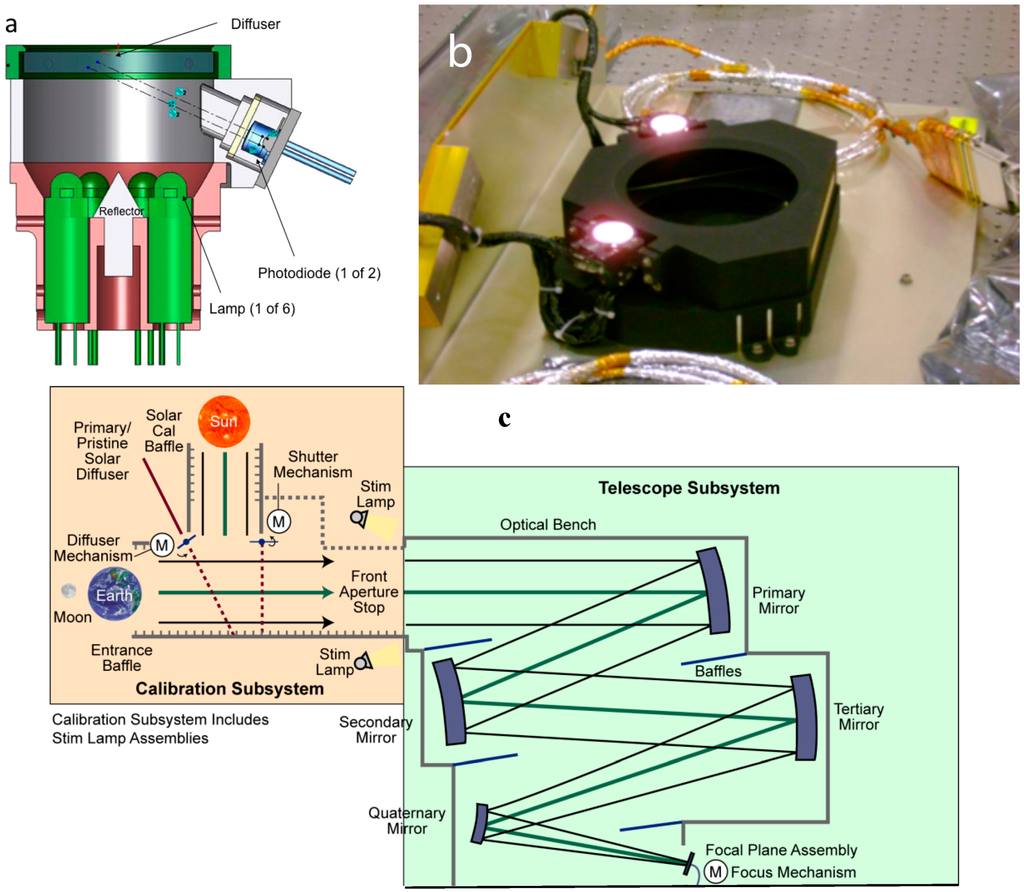
The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance. The methodology is based on measurements obtained during component-level and instrument-level characterization
- Radiometric Calibration in Thermal Infrared
- Radiometric Calibration of Landsat
- Landsat-8 Sensor Characterization and Calibration
- Landsat-8 TIRS thermal radiometric calibration status
The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) has completed over one year in Earth orbit following its launch onboard Landsat 8 in February 2013. During that time, TIRS has undergone initial on-orbit checkout and commissioning and has transitioned to an operational Landsat payload obtaining 500+ Earth scenes a day. The instrument was radiometrically calibrated Abstract—The Thermal Infrared Sensor-2 that will be on-board Landsat 9 has undergone a pre-launch testing campaign to characterize its radiometric, spectral, and spatial performance and demonstrate compliance to its requirements. This work reviews key elements of the instrument-level radiometric testing using an SI traceable source to derive its uncertainties.
The launch of Landsat 9 (L9) on 27 September 2021 marks the ongoing commitment of the Landsat mission to delivering users with calibrated Earth observations for fifty years. The two imaging sensors on L9 are the Thermal Infrared Sensor-2 (TIRS-2) and the Operational Land Imager-2 (OLI-2). Shortly after launch, the image data from OLI-2 and TIRS This paper, however, tabulates the necessary constants for all of the Landsat sensors in one place defined in a consistent manner and provides a brief overview of the radiometric calibration procedure summarizing the current accuracy of the at-sensor spectral radiances obtained after performing these radiometric conversions on
The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) is the thermal imaging instrument onboard the Landsat 8 observatory. The sensor was designed to continue broadband, long wave infrared measurements of the Earth
Abstract The radiometric calibration of the sensors on the Landsat se- ries of satellites is a contributing factor to the success of the Landsat data set. The calibration of these sensors has relied on the preflight laboratory work as well as on inflight tech- niques using on-board calibrators and vicarious techniques. Descriptions of these methods and systems are presented. Results Landsat Geometric and Radiometric Calibration and Characterization The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) Earth Resources Observation and Science Calibration and Validation (Cal/Val) Center of Excellence (ECCOE) focuses on improving the accuracy, precision, calibration, and product quality of remote-sensing data, leveraging years of multiscale optical system geometric and The visible and infrared multispectral sensor (VIMS) equipped in the Chinese Gaofen-5 (GF-5) satellite can obtain four channels of TIR images with a 40 m spatial resolution. However, due to the change of working environment, the TIR sensor suffers a low-accurate radiometric calibration that needs improvement.
The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) instrument is the thermal-band imager on the Landsat-8 platform. The initial onorbit calibration estimates of the two TIRS spectral bands indicated large average radiometric calibration errors, -0.29 and -0.51 W/m2 sr μm or -2.1K and -4.4K at 300K in Bands 10 and 11, respectively, as well as high variability in the Outline Describe calibration methods for the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) TIRS continues the Landsat program’s thermal IR capabilities Describe TIRS Prelaunch testing Radiometric and spectral tests Geometric and spatial tests Applying lessons learned from Landsat 8 and 9 Thermal Infrared Sensor calibration for future thermal missions Brian N. Wenny1, Kurtis Thome2, Sarah Eftekharzadeh1,Matt Montanaro3, Norvik Voskanian1, Mohammad Tahersima1, and Mehran Yarahmadi1
The Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) for the Landsat 8 platform was designed and built at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). TIRS data will extend the data record for thermal observations from
ABSTRACT: This paper reviews the development of in-orbit radiometric calibration methods in the past 40 years. It summarizes the development of in-orbit radiometric calibration technology of typical satellite sensors in the visible/near-infrared bands and the thermal infrared band. Focuses on the visible/near-infrared bands radiometric calibration method including: Lamp calibration Remote Sensing: Radiometric Calibration Methodology of The Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor remote sensing Uploaded by Astrolabe AI-enhanced title Thermal infrared radiometric calibration of satellite sensors is an important prerequisite of quantitative remote sensing. An appropriate radiometric calibration source ensures high-frequency, high-precision calibration of satellite sensors and guarantees observation stability during the on-orbit stage. Re-analysis data provide global surface and atmospheric data with a
Mentioning: 39 – The science-focused mission of the Landsat 8 Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS) requires that it have an accurate radiometric calibration. A calibration methodology was developed to convert the raw output from the instrument into an accurate at-aperture radiance. The methodology is based on measurements obtained during component-level and instrument
- Radikale Evangelikale In Afrika Predigen Hass Auf Schwule
- Rackspace Managed Hosting Reviews
- Race, Class, And Gender In The Help
- Rahel Ryser Trefzer | 800+ Profile mit dem Suchbegriff „Rahél“
- Radio Kox Gmbh In Krefeld 47800
- Rabbit Stock Video Footage For Free Download
- Rajput Bodenkissen Aus Baumwolle, 40 X 40 X 10 Cm, Olivgrün
- Rahm Emanuel, Obama’S Chief Of Staff
- Radparadies Hohenlohe , Wander- und Radparadies Bühlertal Geheimtipp in Hohenlohe
- Radschrauben Passend Für Mercedes-Benz Vito
- Radonline Gutschein _ Radonline Gutscheincode