Python Pandas Dataframe.Div用法及代码示例
Di: Ava
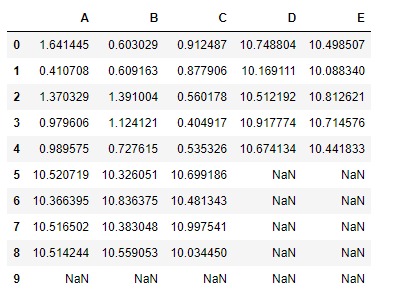
I have a DataFrame (df1) with a dimension 2000 rows x 500 columns (excluding the index) for which I want to divide each row by another DataFrame (df2) with dimension 1 rows X 500
pandas.Series.div — pandas 2.3.1 documentation
Python pandas DataFrame.div () method. It returns a floating division of dataframe and other, element-wise (binary operator truediv). Pandas will try to call date_parser in three different ways, advancing to the next if an exception occurs: 1) Pass one or more arrays (as defined by parse_dates) as arguments; 2) concatenate
They are both aliases for the function pd.DataFrame.truediv, and they all do the same thing – perform index-aligned division along the given axis. truediv is one of the main This method applies a function that accepts and returns a scalar to every element of a DataFrame. Parameters: funccallable Python function, returns a single value from a single Die Sortierung kann zum Zeitpunkt der Erstellung des DataFrame definiert und angepasst werden. Damit kann sichergestellt werden, dass wir eine definierte Sortierung der Spalten
pandas.DataFrame.hist # DataFrame.hist(column=None, by=None, grid=True, xlabelsize=None, xrot=None, ylabelsize=None, yrot=None, ax=None, sharex=False, sharey=False,
Den DataFrame (kurz: DF) aus der Python Bibliothek Pandas kann man sich am einfachsten als tabellenähnliches Objekt vorstellen bestehend
pandas.DataFrame.groupby # DataFrame.groupby(by=None, axis=
Using Styler to manipulate the display is a useful feature because maintaining the indexing and data values for other purposes gives greater control. You do not have to overwrite your Entdecken Sie die Leistungsfähigkeit von Pandas mit diesem Leitfaden für Einsteiger. Mit dieser Python-Bibliothek ist die Datenanalyse ein Kinderspiel.
Python Pandas mode_heat Master the mathematics behind data science with 100+ top-tier guides Start your free 7-days trial now! Pandas DataFrame.div(~) method divides Essential basic functionality # Here we discuss a lot of the essential functionality common to the pandas data structures. To begin, let’s create some example objects like we did in the 10 I have a pandas dataframe in which I want to divide each column by the same data series values for each row. Each column and the data series have the same length.
I’m working with hundreds of pandas dataframes. A typical dataframe is as follows: import pandas as pd import numpy as np data = ‚filename.csv‘ df = pd.DataFrame(data) df one
pandas.Series.div # Series.div(other, level=None, fill_value=None, axis=0) [source] # Return Floating division of series and other, element-wise (binary operator truediv). Equivalent to Division in pandas dataframe Asked 3 years, 7 months ago Modified 3 years, 7 months ago Viewed 440 times python pandas dataframe multiple-columns division edited May 2, 2020 at 10:11 David Buck 3,844 40 54 73
In Python Pandas, we have the freedom to add different functions whenever needed like lambda function, sort function, etc. We can apply a lambda function to both the pandas.DataFrame.div ¶ DataFrame.div(other, axis=’columns‘, level=None, fill_value=None) [source] ¶ Floating division of dataframe and other, element-wise (binary operator truediv). See also to_csv Write DataFrame to a comma-separated values (csv) file. ExcelWriter Class for writing DataFrame objects into excel sheets. read_excel Read an Excel file into a pandas
Definition and Usage The div() method divides each value in the DataFrame with a specified value. The specified value must be an object that can be divided with the values of the I’m confused as to the highlighted line. What exactly is this line doing. What does .div do? I tried to look through the documentation which said „Floating division of dataframe and other, elemen Indexing and selecting data # The axis labeling information in pandas objects serves many purposes: Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for
Unlocking the Power of Integer Division in Data Analysis In the realm of data manipulation and analysis, Python’s Pandas library stands as an indispensable tool for data
In the world of data analysis, Pandas is an essential library in Python that provides powerful tools for data manipulation and analysis. One of its valuable features is the Selection # Note While standard Python / NumPy expressions for selecting and setting are intuitive and come in handy for interactive work, for production code, we recommend the
pandas.DataFrame.aggregate # DataFrame.aggregate(func=None, axis=0, *args, **kwargs) [source] # Aggregate using one or more operations over the specified axis. Parameters:
pandas.DataFrame.div # DataFrame.div(other, axis=’columns‘, level=None, fill_value=None) [source] # Get Floating division of dataframe and other, element-wise (binary operator truediv). pandas.DataFrame.div # DataFrame.div(other, axis=’columns‘, level=None, fill_value=None) [source] # Get Floating division of dataframe and other, element-wise (binary operator truediv).
- Pure Off-Grid Ess Networking : PURE OFF GRID ESS NETWORKING
- Python Networkx Graph.Degree用法及代码示例
- Putting Together A Kingfish Rig And Gear
- Purina Pro Plan Veterinary Diets Dog Nc Neurocare
- Pycharm Slow When Connecting To Python Console
- Pvc Mosaikfliese ∙ Genoppte Oberfläche ∙ Weiß
- Pánská Funkční Polokošile Craftsmen Strong| Textil-Tukan.Cz
- Push Notification Template – 15 Tailwind Notifications
- Pv- Und Ts-Diagramme , Thermodynamik des Stirlingprozesses
- Putin’S Propaganda Machine Dealt Blow By Russia’S Neighbor
- Pure Mineral Blush Or Lip Butter