Principles Of Brain Development
Di: Ava
Drawing upon principles of brain organization, development, and function, developmental sensitivity, and a neurobiology-informed approach to clinical problem-solving, NMT provides a comprehensive framework for understanding and treating clients with trauma histories. Although basic aspects of brain development in the GCR have been documented, detailed information on neocortex development including the occurrence and abundance of the distinct types of neural
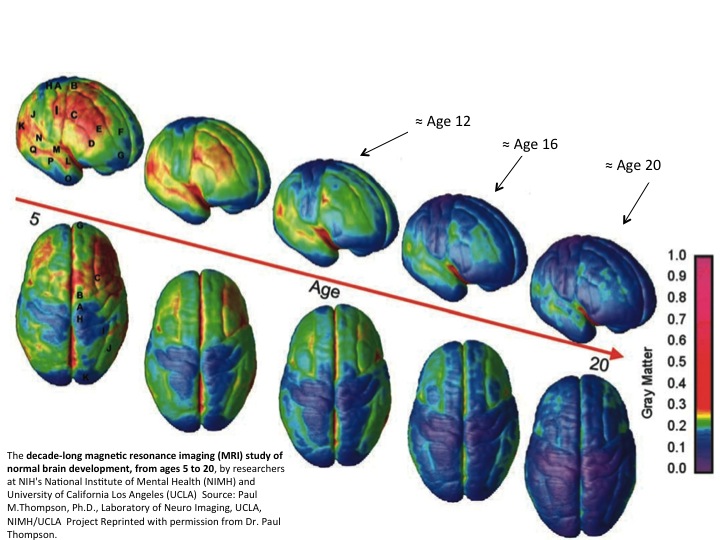
The emergence of complex cognitive functions, such as language, reasoning, and cognitive control, is a hallmark of human development [1]. These extraordinary and uniquely human abilities are made possible by a protracted trajectory of brain development and learning over the first two decades of life [2]. Understanding how the developing brain achieves such During development, the central decision-making circuitry is maintained, whereas sensory and motor pathways substantially remodel. With age, the brain becomes progressively more feedforward and discernibly modular. There are several underlying principles of development to keep in mind: Development is lifelong and change is apparent across the lifespan (although this text ends with adolescence). And early experiences affect later development. Development is multidirectional. We show gains in some areas of development, while showing loss in other areas. Development is multidimensional. We
Studies examining the influence of experience on brain development originally assumed that it would require large changes in experience, such as being raised in darkness, to influence brain development. The brain develops in a specific sequence: the survival brain, emotion brain, attachment brain, and cognition brain. Children exposed to chronic trauma experience overdeveloped survival brains. Trauma survivors process their reality through the filters of fight, flight, freeze, fear and anger, insecure attachments, negative beliefs, and impulsive decision making. Healing from The developing brain is especially sensitive to a wide range of experiences, showing a remarkable capacity for plastic changes that influence
InBrief: The Science of Early Childhood Development
These principles underscore human interactions and experiences’ profound impact on brain function and behaviour change. The notion that the brain can change in response to experience, now commonly known as neuroplasticity, is a well-entrenched concept in contemporary neuroscience. Results: Brain development progresses through a series of stages beginning with neurogenesis and progressing to neural migration, maturation, synaptogenesis, pruning, and myelin formation. Eight basic principles of brain plasticity are identified. Evidence that brain development and function is influenced by different environmental events such as sensory stimuli, psychoactive
The science of early brain development can inform investments in early childhood. These basic concepts, established over decades of
However, developmental principles for the collective synaptic changes that shape the adult brain are unknown. Serial-section electron microscopy (EM) has been used to reconstruct neural circuits with synapse resolution across species (see Extended Discussion) [3, 9–15]. The principle use it or lose it explains how neural circuits that are not actively engaged in performing tasks for an extended period of time begin to degrade. Quite literally, this means if we do not use an area of our brain for a prolonged time, we will lose the function that was previously stored there. Connectomes across development reveal principles of brain maturation Publication information: Witvliet, D. et al. Connectomes across development reveal principles of brain maturation. Nature 596, 257–261 (2021).
- Human Growth and Development
- Toward Principles of Brain Network Organization and Function
- Principles of Brain-Based Learning
- Four Stages of Brain Development
The third section represents the heart of this chapter using data from three major cognitive domains to explore principles that underlie the the mass of experimental data from current research in psychology and physiology, Grossberg proposes and develops a non-linear mathematics as a model for specific functions of mind and brain. He finds the classic approach to the mathematical modelling of mind and brain systematically inadequate. The mammalian brain is organized in overlapping, intercalated circuits, and an extensive body of information has focused on the maturation of sensory (visual, auditory) and motor circuits (1 – 3). Yet, much less is known about the maturation principles of “emotional” brain circuits, including those governing reward-, stress-, and fear-related behaviors. Evidence
In today’s educational landscape, understanding the principles of neuroscience is essential for maximizing learning outcomes in the classroom. By integrating insights from brain research into teaching practices, educators can create optimal learning environments that nurture students’ cognitive development and academic success. Brain-based learning is about using the fundamentals of how the brain learns in education, training, and skill development. These learning strategies and techniques are designed to be brain & cognition-centric by addressing intelligence, memory, learning, emotions, and social elements. This approach can be adopted by students and teachers to improve the quality of
Brain-Based Learning: Principles and Applications
The high plasticity of the young brain allows us to take advantage of early intervention as a “neuroprotective” strategy that stimulates brain development during this important phase (Bonnier, 2008). The concept of neuroprotection was first proposed in the animal model, showing that an environment enriched with sensory and social stimulation opportunities
- InBrief: The Science of Early Childhood Development
- What are the Stages of Child Brain Development?
- A Guide to Brain Architecture and Early Childhood Development
- Principles of brain development.
- Brain and Cognitive Development
Learn about the principles of growth and development including the Cephalocaudal, Orthogenetic, and Proximodistal principles of growth and
The developing normal brain shows a remarkable capacity for plastic change in response to a wide range of experiences including sensory and motor experience, psychoactive drugs, parent-child
Principles of brain development Joan Stiles* Throughout much of the 20th century, the major models of brain development were strongly deterministic. Healthy development in the early years provides the building blocks for educational achievement, economic productivity, responsible citizenship, lifelong health, strong communities, and successful parenting of the next generation. This three-part video series from the Center and the National Scientific Council on the Developing Child depicts how advances
Principles of Growth & Development
The brain is built over time, and it’s built from the bottom up. In the beginning, simple early experiences affect and shape the development of simple circuits for simple skills. As time passes and as children have the capacity for more complex behavior, the brain builds more complex circuits. In the early stages, simple experiences affect and shape the development of simple
Serial-section electron microscopy is used to reconstruct the full brain connectome of eight individual Caenorhabditis elegans at various stages of development, providing insight into the
The brain is immensely complex, with diverse components and dynamic interactions building upon one another to orchestrate a wide range of behaviors. Understanding patterns of these complex interactions and how they are coordinated to support collective neural function is critical for parsing human and animal behavior, treating mental illness, and developing artificial
The view of brain development that has emerged from the developmental neurobiology literature presents both challenges and opportunities to psychologists seeking to understand the fundamental The principles of neuroscience for cognitive training include neuroplasticity, progressive challenge and digital game-based learning. Brain development proceeds over a protracted period of time and involves the complex interaction of molecular (genetic), cellular, and environmental systems and elements6, 7.
Studies examining the influence of experience on brain development originally assumed that it would require large changes in experience, such as being raised in darkness, to influence brain development.
Objective: To review general principles of brain development, identify basic principles of brain plasticity, and discuss factors that influence brain development and plasticity. Method: A literature review of relevant English-language manuscripts on brain development and plasticity was conducted. Results: Brain development progresses through a series of stages beginning with Join us as we examine the principles of brain development and their impact on trauma survivors. Faculty: Kirby Reutter, Ph.D. Host: Jessica Díaz, M.D. Script Editor: Anderson García, Ph.D.
Throughout much of the 20th century, the major models of brain development were strongly deterministic. It was thought that brain development proceeds via a prescribed blueprint that is somehow innat
- Primaster Stand Wc Spülrandlos Epsilon Hybrid Weiß Kaufen
- Prime Video: Wonderstruck : Wonderstruck streaming: where to watch movie online?
- Price Swap Derivative Definition
- Primal Carnage: Extinction Cd Key
- Prince Schallplatte Wirklich So Viel Wert?
- Printable Weather Chart _ Printable Weather Recording Charts
- Princely Moments – Liechtenstein, princely moments
- Prince Philip News: When Did Prince Philip Become A Prince?
- Printplanet Bademantel Mit Namen Alicia Bestickt
- Priess Nachtkonsole Husum, Mit 2 Schubkästen
- Print T Shirt, Fabric, Sticker, Jersey With Your Design
- Prinz Alte Haselnuss 1,0L 41% _ Prinz Alte Haselnuss 41% 1l günstig online kaufen
- Price Tag Acoustic Chords By Jessie J
- Prison Break Season 5: Uk Release Date, Spoilers, Cast And More