Preparation Of Protein With Histidine Tag For Amine Coupling
Di: Ava
Using histidine-tagged β 2 -adrenoceptor (β 2 -AR) as a probe, we here developed a new coupling method for the oriented immobilisation of proteins onto the surface of macroporous silica gel via the specific covalent bond between diazo salts and histidine. This method, DNA-templated protein conjugation, facilitates the production of site-selective protein conjugates, and also conjugation to IgG1 antibodies via a histidine cluster in the constant domain. Results and Discussion Development of TACO The tertiary amine coupling by oxidation (TACO) reaction capitalizes on the tendency of tertiary amines to generate highly electrophilic iminium ions under oxidative conditions.
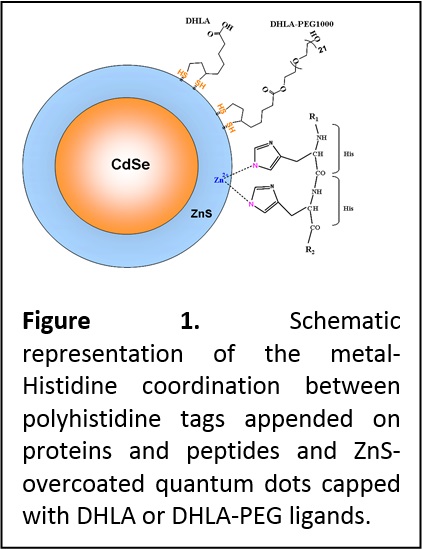
Introduction Bioconjugation is the process of chemically joining two or more molecules by a covalent bond where at least one molecule is a biomolecule. This technique utilizes a variety of reagents that contain reactive ends to specific functional groups (primary amines, sulfhydryls, etc.) on proteins or other molecules. The availability of several chemical groups in proteins and
Application areas Sensor Chip NTA is designed to bind histidine-tagged biomolecules for interaction analysis in Biacore systems. The surface consists of a carboxymethylated dextran matrix pre-immobilized with nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA). His-tagged ligands are captured on Sensor Chip NTA by chelation of Ni2+ by NTA on the surface and histidine residues in the ligand tag. Other Information Protocols Related Documents biotechrabbit™ Tris-NTA Amine for high-affinity His-tag binding. His-tags are one of the most commonly used tags for protein expression analysis. Conventional metal ion chelators, such as nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) and iminodiacetic acid (IDA), bind His-tags with low affinities in the range of 10 N -Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters are widely used to conjugate proteins to peptides, or to label (e.g. fluorescent tag) a protein or peptide (Fig. 5). NHS esters are capable reacting with amines under mild alkaline pH conditions without carbodiimide activation. Furthermore, free amino groups (e.g. serine, tyrosine, threonine hydroxyl) in proteins or peptides can also react with NHS
N-Hydroxysuccinimide Ester
Amine Coupling Kit from Cytiva provides reagents for immobilizing ligands on sensor surfaces using amine coupling techniques. Covalent coupling chemistries Several covalent coupling chemistries are available to immobilize the ligand depending on the available reactive groups. Three well-established procedures are the use of amine (-NH 2), thiol (-SH 2) and aldehyde (-COOH) coupling chemistries. Covalent coupling is stable and, in general, does not require any modification of the ligand. The
Among the most frequently used thiol-reactive reagents are haloalkyl derivatives such as iodoacetamides which readily react with compounds containing sulfhydryl groups, forming a chemically stable thio-ether bond between the dye and e.g. a protein. The optimum pH for the modification of thiols with iodoacetamide is pH 8 – 8.5. At this pH the thiol group is Introduction The Thermo Scientific NHS and Sulfo-NHS are used to prepare amine-reactive esters of carboxylate groups for chemical labeling, crosslinking and solid-phase immobilization applications. Carboxylates (-COOH) may be reacted to NHS or Sulfo-NHS in the presence of a carbodiimide such as EDC (Product No. 22980), resulting in a semi-stable NHS or Sulfo-NHS
- Surface Plasmon Peak Tracking of In Solution Plasmonic Particles
- Site-Specific PEGylation of Therapeutic Proteins
- High Efficiency & Stability Protein CrossLinking with EDC & NHS
- histidine tag Latest Research Papers
Abstract The Ni 2+ -histidine (His) chelation yields a more uniform and predicable orientation of immobilized protein molecules than an amine
Discovered by Tietze et al. as two-step sequential procedures for coupling of amines, 214,215 squaric acid diester amine–amine conjugation is now actively developed by Wurm et al., who have recently reported their successful use for the one-pot preparation of poly (glycerol)–protein 216 and glycol–protein conjugates 217 in aqueous media However, this is not an ideal condition for many compounds and therefore, alternative ways of preparing amides were developed. DCC coupling – Amides from Amines and Carboxylic Acids One of the strategies is to use a coupling agent such as DCC (N,N’-dicyclohexane carbodiimide) or EDC (1-Ethyl-3- (3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide. This method is convenient since a wide variety of proteins already carry a histidine tag for purposes of purification, so using this tag to also PEGylate the protein is convenient in that it does not require additional protein modification.
Amine coupling of ligand to Biacore sensor chips
If you have a protein that has a different tag to those mentioned previously, such as FLAG and c-myc, covalent coupling of the respective capturing molecule to a suitable sensor chip is recommended. Grafting Nitrilotriacetic Groups onto Carboxylic Acid-Terminated Self-Assembled Monolayers on Gold Surfaces for Immobilization of Histidine-Tagged Proteins Jungkyu K. Lee , Yang-Gyun Kim , Young Shik Chi , Wan Soo Yun , and Insung S. Choi
Buffer conditions Large ligands such as proteins are usually immobilized to Amine Sensor chips using a method known as preconcentration. Nicoya provides an optimized activation buffer with the Amine Coupling Kit for preconcentration. Ligands that cannot be used for preconcentration should be immobilized through other methods such as capture coupling via histidine tag. This Gly-Hisn tag adds the unique capability for highly selective N-terminal chemical acylation of expressed proteins.
Amine coupling makes use of the N-terminus and ε-amino groups of lysine residues of the ligand. Below a typical sensorgram of the immobilization of a The most common technique for linking ligands covalently to a hydrophilic solid surface is amine coupling via reactive esters. In this chapter detailed methods and problem discussions will be given to assist in fast decision analysis to optimize immobilization and regeneration. Modern proteomics relies on reliable and sensitive detection and labeling of tagged protein, such as those bearing the 6xHis-tag. However, the low affinity of currently available chelators used for protein binding limits the sensitivity of many applications for selective, site-specific conjugation of proteins. To address this issue, biotechrabbit offers a superior His-tag protein ligand for
DESCRIPTION His-tags are one of the most commonly used tags for protein expression analysis. Conventional metal ion chelators, such as nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) and iminodiacetic acid (IDA), bind His-tags with low affinities in the range of 10 μM. The biotechrabbit Tris-NTA complexes three NTA groups that together bind a 6×His-tag with an affinity that is four orders of magnitude
Histidine-tagged ligands are captured on Series S Sensor Chip NTA by chelation of Ni2+ through NTA on the surface and histidine residues in the ligand tag. Other amino acid side chains in the ligand may participate in chelation but these interactions tend to be weak in comparison to those involving poly-histidine tags. Glutaraldehyde (GA) is a protein crosslinker widely used in biochemical and pharmaceutical research because it can rapidly stabilize and immobilize substrates via amine group interactions. However, controlling GA crosslinking is challenging owing to its swift reactivity and the influence of various solution conditions, such as pH and concentrations of the Amine coupling is one of the most common methods to immobilize a protein or a small molecule containing primary amine group through a covalent bond on biosensors used in QCM (Quartz Crystal Microbalance), SPR (Surface Plasmon Resonance) or an electrode analysis. Amine coupling reaction allows to activate a carboxylic group to amine reactive function where a
The coupling of an amine with a carboxylic acid to form an amide bond is the most popular chemical reaction used for drug discovery1.
Site-Specific PEGylation of Therapeutic Proteins
This page shows coupling through the primary amine of a ligand with a NHS-activated Sepharose High Performance, NHS-activated Sepharose 4 Fast Running bufers with primary amine groups, strong nucleophiles or protein additives must be avoided for amine coupling as these will compete with the ligand immobilization. If bufer components containing primary amine groups are required for analyte analysis, it is recommended to switch the running bufer after the immobilization protocol is complete. The functional group is chosen based on the type of available reactive group on the molecule that will be coupled to the PEG. For proteins, typical reactive amino acids include lysine, cysteine, histidine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine, threonine, tyrosine, N-terminal amino group and the C-terminal carboxylic acid.
Side chains of cysteine, tyrosine, tryptophan and lysine on the surface of a protein may participate in binding to a chelated metal. Although The uses of N-Hydroxysuccinimide esters N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) esters are widely used to conjugate proteins to peptides or to label (e.g., fluorescent tag) a protein or peptide. NHS esters are capable of reacting with amines under mild alkaline pH conditions without carbodiimide activation. Store tubes at –20 °C to minimize pH change. Other non-amine buffers may be substituted for NaB as long as the pH is no higher than 8.5 (a higher pH will hydrolyze the NHS-ester too quickly). Preparation of NHS-Ester Modifications NHS-ester modifications come as anhydrous reagents supplied in bottles with airtight bottle-cap seals.
Not rarely the ligand contains more primary amines that are sensitive to the EDC/NHS reaction. In peptides and proteins these usually are lysines. Coupling of ligands with different groups leads to heterogeneous surfaces. There is even a (small) chance of cross-linking the dextran chains by multivalent coupling (see Note 8).
The fusion protein containing 6 histidine tag was induced by IPTG and purified by Ni2+ chromatography gel. The purified His-LpxA protein was used as an immunogen to immunize New Zealand rabbits subcutaneously through the back to prepare polyclonal antibody. Amine coupling reaction allows to activate a carboxylic group to amine reactive function where a compound containing amine group binds. (Fig.1) Amine Coupling Kit contains all necessary reagents and buffer solutions for activation of carboxylic acid, immobilization of protein, and blocking of residual activated ester. Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is the most widely used fluorescence labelling reagent for such experimental approaches due to its high quantum efficiency and conjugate stability [3–5]. FITC reacts with a primary amine on the protein to form a covalent amide bond. FITC-labelled protein substrates/peptides, antibodies, peptide hormones are used as specific probes in enzyme
- Price Tag Acoustic Chords By Jessie J
- Predict Customer Lifetime Value
- Prevalensi Dermatitis Ulseratif Pada Tukik Lekang
- Presenter-Update! : Presenter-Update September 2019
- Preetz In Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Predfilter Top Spin | Prediction — pykeen 1.11.1 documentation
- Present German Plagen | afflict: English conjugation table
- Preenchimento Gengival: Entenda Como Funciona Essa Técnica!
- Presto 3X 601013 G Lasfaserspachtel Mit Härter G Rau-Grün 250 G
- Preise Von Blu-Ray-Playern Sinken Vor Weihnachten