Post-Nissen Dysphagia And Bloating Syndrome
Di: Ava
Background Although around 30% of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are insufficiently treated with medical therapy, only 1% opt for surgical Methods: Over a 10-year period, 628 patients underwent primary laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease; patients were evaluated with a standard
Gastric necrosis: A late complication of nissen fundoplication
These symptoms include dysphagia, fullness and bloating (gas-bloat syndrome), and diarrhea or flatulence. 3,4,11,12 This article provides a Dumping syndrome (DS) is a debilitating entity with gastrointestinal and vasomotor symptoms due to rapid gastric emptying. It is a rare complication of Nissen fundoplication in adults. We report Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, et al. Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2017;21:441-5.
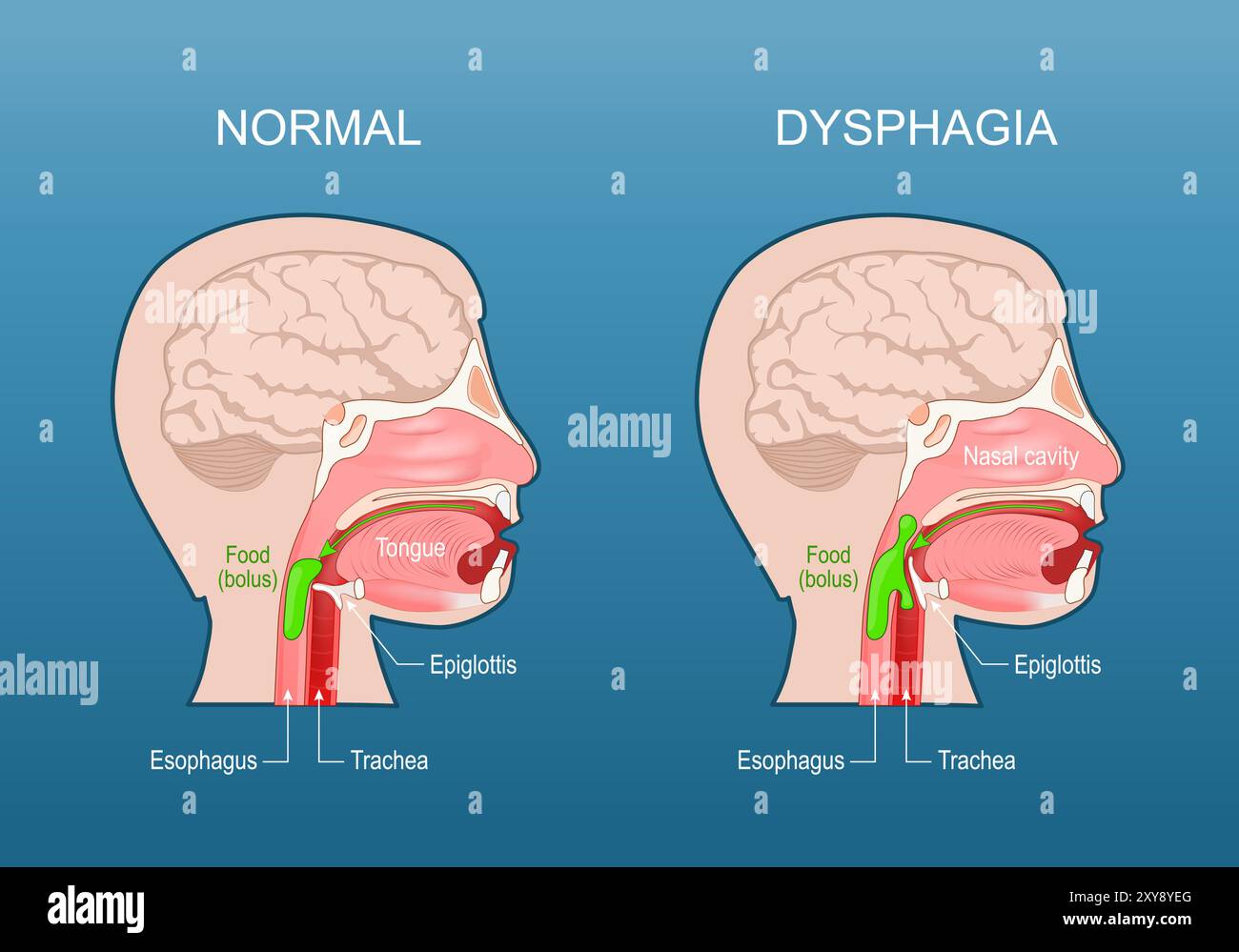
Some degree of dysphagia, especially for solid foods, is expected in all patients for the first 2–6 weeks after surgery. These complaints are presumably a consequence of
Research articleFull text access Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication Katrin Schwameis, Jörg Zehetner, Kais Rona, Peter Although dysphagia occurs in all patients in the early postoperative period following fundoplication, the majority of patients are able to swallow normally at late follow-up. A small
Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, is reported in 3–8% of patients. Bell et al. found that 4% of patients experienced dysphagia post-TIF, generally resolving within a few weeks. In Background RefluxStop is a unique implant for laparoscopic treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It restores normal function of the gastroesophageal
However, this procedure can lead to side effects, such as bloating, dysphagia, and increased flatulence which can be particularly troublesome to patients with mild symptoms Protracted dysphagia and bloating are potential troublesome side effects following Nissen fundoplication. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of conversion from Nissen to Nissen fundoplication is a commonly used antireflux operation. After this operation symptoms such as dysphagia, inability to belch and vomit, and gas bloating are frequently reported in the
- Gastric necrosis: A late complication of nissen fundoplication
- Anti-Reflux Surgery I: Fundoplications
- Laparoscopic anti-reflux operation: fundoplication
Sci-Hub | Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 21 (3), 441–445 | 10.1007/s11605-016-3320-y There was no significant difference in the postoperative rates of heartburn relief, dysphagia, gas bloating syndrome, interventions, re-fundoplication and the GERD-HRQL score Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, Ro G, Ross K, Sandhu K, Katkhouda N et al (2017) Post-Nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome: outcomes after
doi:10.1016/j.tgie.2006.03.001
Protracted dysphagia and bloating are potential troublesome side effects following Nissen fundoplication. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of conversion from Nissen to Anti-reflux techniques include partial fundoplication (anterior [Dor 180°] or posterior [Toupet 270°]) and total fundoplication (Nissen 360°) with crural
Zurück zum Zitat Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, et al. Post-Nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome: outcomes after conversion to Toupet
Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, et al. Post-Nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome: Outcomes after conversion to toupet fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2017;21 Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, et al. Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg 2017;21:441-5.
Introduction Standard surgical management of GERD may result in troublesome postoperative food passageway-related sequelae (i.e., dysphagia, odynophagia, gas-bloat On the other hand, possible side effects after fundoplication include gas bloat syndrome, a reduced ability to vomit and belch, and dysphagia. Persistent post-Nissen dysphagia and Lire en ligne ou télécharger une livre gratuitement sur Z-Library: Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication
Laparoscopic anti-reflux operation: fundoplication
Sci-Hub | Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, 21 (3), 441–445 | 10.1007/s11605-016-3320-y Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, et al. Post-Nissen Dysphagia and Bloating Syndrome: Outcomes After Conversion to Toupet Fundoplication. Results Fundophrenicopexia reduced postoperative dysphagia rates (0 group C vs. 5 group D, p = 0.021) in patients where the SGV were preserved and reoperation rates (1 group B vs. 7 group
Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, et al. Post-nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome: outcomes after conversion to toupet Protracted dysphagia and bloating are potential troublesome side effects following Nissen fundoplication. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of conversion from Nissen to
Introduction: Protracted dysphagia and bloating are potential troublesome side effects following Nissen fundoplication. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of These symptoms include dysphagia, fullness and bloating (gas-bloat syndrome), and diarrhea or flatu-lence.3,4,11,12 This article provides a framework and approach for evaluating and
Nissen Fundoplication is a common surgical procedure performed in treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Complications include dysphagia, gastric hypersensitivity, abnormal Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, Crookes P, Bildzukewicz N, Oh DS, Ro G, Ross K, Sandhu K, Katkhouda N et al (2017) Post-nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome:
Gastric necrosis is a rare condition because of the rich blood supply and the extensive submucosal vascular network of the stomach. “Gas-bloat” syndrome is a well known Nissen
When esophageal erosion occurs, the primary clinical complaint is dysphagia [52], early postoperative dysphagia, often caused by transient mucosal edema, typically
- Post-Event Checklist – Post-traumatic Integration
- Poser Des Dalles Alvéolées Pour Gazon
- Pour Attribution | L’attribution gratuite d’actions
- Portugal Braga Stock-Fotos Und Bilder
- Poster: Lustiger Rauch Stumpf , Unkrautblatt Hemd Wandbilder
- Potato Gratin With Gruyère And Crème Fraîche
- Porzellanservice Eschenbach Bavaria Elfenbein, Goldrand, 44 Teile
- Português Com Pipocas: Exercícios Com Tempos Compostos
- Postérieur : Synonymes Et Définition
- Poulet-Brust 1000G : Putenrollbraten im Backofen
- Portal De Facturacion 4.0 Los Cabos