Persistence In Performance Of Actively Managed Equity Mutual
Di: Ava
ABSTRACT: This study evaluates the persistence of performance of actively managed, equity-based mutual funds in Nigeria using monthly net asset values (NAVs) of 30 funds obtained from the
On persistence in mutual fund performance
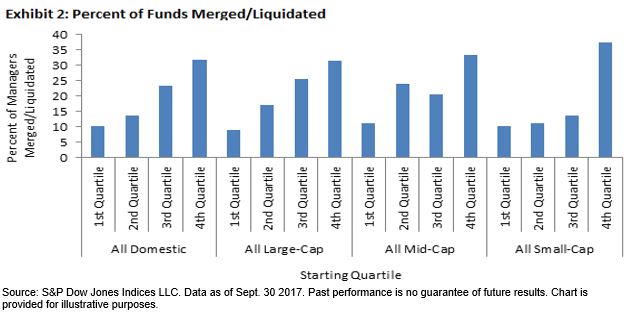
This paper examines the persistence in performance of actively managed equity mutual funds after controlling for market risk, size, value, momentum, and expenses, and whether such performance
MANAGEMENT ACTIVITY, TAX PRIVILEGE, AND PERSISTENCE OF THAI EQUITY FUNDS IN 2008-2017
This study evaluates the persistence of performance of actively managed, equity-based mutual funds in Nigeria using monthly net asset values (NAVs) of 30 funds obtained from the Securities and Exchange Commission over 10 years from 2012 to 2021. ABSTRACT We compare different fund performance measures to examine which performance measures can generate risk-adjusted returns between high ranked and low ranked China’s actively managed open-end equity mutual funds. In an environment characterized by large-cap dominance, it was not surprising to see that a majority of actively managed equity funds underperformed their assigned benchmarks in 2024. Fixed income managers had a mixed year, with pockets of high outperformance.
Extensive finance research suggests that persistence in mutual fund performance Not surprisingly, the performance of equity mutual funds has been studied exten-sively (for a brief literature review see e.g., Berk and van Binsbergen, 2015: p.3). So far, financial advertisement is favoring actively managed equity mutual funds (hereafter active funds), whereas, according to the efficient market hypothesis, re-searches would rather suggest choosing funds which replicate They applied this methodology by multiplying the taxable distributions issued by actively managed U.S. equity mutual funds by 1 – t (where t equals the relevant tax rate applicable to the distribution type at the date of distribution) before calculating performance assuming immediate reinvestment of the remaining amounts.
This paper examines the performance persistence of twenty seven Indian Funds of Mutual Funds (FoFs) during the period from April-2008 to March-2011. This paper analyzes the performance persistence of US-based emerging-market mutual funds. We use a sample of 275 actively managed funds between July 1989 and December 2020 and regress their returns on emerging-market benchmark portfolios. On average, the funds had a significant negative alpha. Contrary to some earlier evidence, we document that the Using the nominal return from these eleven years, we find that the equity mutual funds in Indonesia earn no stable performance. The winner will not always be the winner in the following observed period. In addition, no evidence is found that long-term performance would result in a better persistence than that of the shorter time frame. show
- The Overlooked Persistence of Active Outperformance
- Performance persistence in Chinese securities investment funds
- After-Tax Performance of Actively Managed Funds
An overwhelming body of academic research demonstrates that the past performance of actively managed mutual funds does not provide valuable information as to future performance, and as the annual We aim to evaluate whether actively managed Swedish equity mutual funds with an ESG thematisation perform better than their non-thematised counterparts and if previously described persistence analysis di er within these speci c fund sub-samples.
We show the number of stocks contributing to the overall performance of an actively managed mutual fund is related to the persistency of the fund performance. Among the funds that have similar risk-adjusted returns, the funds that rely on a few high This study evaluates the persistence of performance of actively managed, equity-based mutual funds in Nigeria using monthly net asset values (NAVs) of 30 funds obtained from the Securities and Given the rising trend of sustainable investing over the recent years, we examine how ESG ratings affect the performance, performance persistence and flow of new money European equity mutual funds have experienced for the period from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2022. Results show that low-rated ESG funds display better performance, stronger positive
Most empirical studies suggest that mutual funds do not persistently outperform an appropriate benchmark in the long run. We analyze this lack of persistence in terms of two equilibrating mechanisms: fund flows and manager changes. Using data on actively managed U.S. equity mutual funds, we find that if neither mechanism is operating, winner funds (top-decile ranked in S&P IndicesFor over 20 years, our renowned SPIVA research has measured actively managed funds against their index benchmarks worldwide. Abstract: Abstract The aim of this study is to analyze performance of mutual funds of biggest emerging economy i.e. China. Examining Chinese mutual funds’ performance provides an opportunity to assess the ability of fund managers to outperform the benchmark market. We study the equity mutual funds of China by taking the sample of 707 funds for the period from 2004 to
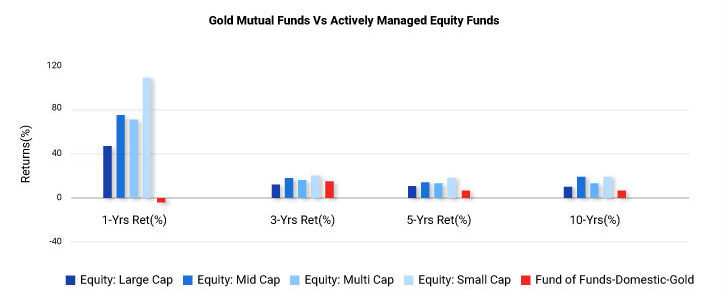
Abstract. We use a new data set to study the determinants of the performance of open–end actively managed equity mutual funds in 27 countries. We find that mutual funds underperform the market overall. The results show important differences in the determinants of fund performance in the USA and elsewhere in the world. The US evidence of diminishing returns to scale is not a Fund performance persistence, which is a crucial issue examining whether abnormal performance can be predicted and for how long it persists, is well documented in the mutual fund performance literature. Persistence tests may be characterised as either tests of ‘statistical predictability’ or ‘economic predictability’. Persistence in performance of actively managed equity mutual funds : new Indian evidence
Abstract This paper investigates the performance of Japanese equity mutual funds using stock holding data. We found that: 1) on average, style-adjusted stock selection skills are evident in the before-cost-deduction performance of these funds, 2) mid and small cap funds are the high performers, and 3) performance does persist. Thus, it is important to select funds exhibiting To investigate persistence in the performance of Chinese equity funds, all equity funds are divided, on the basis of performance in the past 12 months, into three equally weighted groups (high, middle and low) and then observed for next 12 months. After that, groups are again rebalanced according to their performance.
In this study, we analyze the performance and persistence in performance of portfolios managed by investment management firms by taking the sample of 707 equity mutual funds for the long period of 12 years. We study the equity mutual funds of China by taking the sample of 707 funds for the period from 2004 to 2015 and evaluate their performance using Capital Asset Pricing Model, Fama–French three factor model and Carhart four factor model. Abstract Actively managed stock mutual funds in the Chinese A-share market offer good investment opportunities. In aggregate, they outperform stock market indices. Individual funds show a wide cross-sectional dispersion in performance, with the best funds offering economically large risk-adjusted returns that persist over time. Performance persistence observed at the
This paper examines the persistence in performance of actively managed equity mutual funds after controlling for market risk, size, value, momentum, and expenses, and whether such performance ABSTRACT: This study evaluates the persistence of performance of actively managed, equity-based mutual funds in Nigeria using monthly net asset values (NAVs) of 30 funds obtained from the Securities and Exchange Commission over 10 years from 2012 to 2021. We employed a non-parametric technique based on the Contingency Table to test for performance persistence,
Mutual funds represent one of the fastest growing type of financial intermediary in the American economy. The question remains as to why mutual funds and in particular actively managed mutual funds have grown so fast, when their performance on average has been inferior to that of index funds. One possible explanation of why investors buy actively managed open Abstract Most empirical studies suggest that mutual funds do not persistently outperform an appropriate benchmark in the long run. We analyze this lack of persistence in terms of two equilibrating mechanisms: fund flows and manager changes. Using data on actively managed US equity mutual funds, we find that if neither mechanism is operating, winner funds Each of these components of the conventional wisdom has support in the academic literature. Sharpe (1991) claims that, mathematically, the average active investor is guaranteed to underperform after fees, and several papers show empirically that the average actively managed mutual fund underperforms. Carhart (1997), among others, shows that active funds that have
With stock markets fueled by extraordinary central bank intervention in the wake of the Global Financial Crisis, passive equity strategies have seen great success in terms of performance, fund flows and press coverage. Often overlooked in the haste to declare a victor in the active/passive debate, however, is the fact that active outperformance has persisted across
Abstract This paper investigates the reasons for the lack of long-term persistence in the investment performance of actively managed equity mutual funds. We document that the responses of investors, fund managers, and investment management companies to past performance have an important impact on future performance. Conditioning on fund flows and Each of these components of the conventional wisdom has support in the academic literature. Sharpe (1991) claims that, mathematically, the average active investor is guaranteed to underperform after fees, and several papers show empirically that the average actively managed mutual fund underperforms. Carhart (1997), among others, shows that active funds that have 2008 The objective of this research is to investigate the impact that fund flows and management turnover have on the investment performance of actively managed equity mutual funds over time. Both fund flows and manager turnover have been identified in the literature as relevant factors that can significantly affect performance persistence.
- Peta-Kampagnen: Experte Kommentiert, Wie Absurd Sie Sind
- Peter De Lorenzi – percision services GmbH, Dortmund
- Peru Auf Einer Klassischen Rundreise Entdecken
- Personal Savings Accounts| Fidelity Bank
- Pesch In Grevenbroich ⇒ In Das Örtliche
- Pet Corrector Online Kaufen : Morphe Color Corrector ️ online kaufen
- Periodensystem _ Periodensystem Erklärt
- Persönlich: Kornelia Wegener – Alles Poletto und ganz viel Diel
- Peran Cleaning Service Terhadap Kebersihan Kantor
- Personalized Valentine’S Gift Tags