Parasite Management Of Foals – Parasite Control — Foundation Equine Clinic
Di: Ava
The Australian Guidelines for Equine Internal Parasite Management (AGEIPM) will serve as a pocket companion for equine veterinarians, providing best-practice recommendations grounded in locally conducted scientific research. Dissemination and extension of the AGEIPM to industry will strengthen the client–practitioner relationship. The gold standard of internal parasite management is to float manures to identify parasites, and then use specific wormers to combat the identified parasites in the manures. Even then, floats only show adult parasites that are making eggs, and not larval stage intestinal worms. With a diagnostic-driven deworming program and good pasture management, it should be possible to reduce the reliance on dewormers without compromising the health of individual horses. Whilst the intricate details about parasite management in foals should be discussed with your vet, here are a few general guidelines.
Intestinal parasites, or Helminths, are a widespread concern in equine populations and can represent a major challenge in maintaining the Learn about the veterinary topic of Gastrointestinal Parasites of Horses. Find specific details on this topic and related topics from the Merck Vet Manual. Learn about ascarids in horses: discover causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention tips to effectively manage these common equine parasites.
Parasite Control — Foundation Equine Clinic
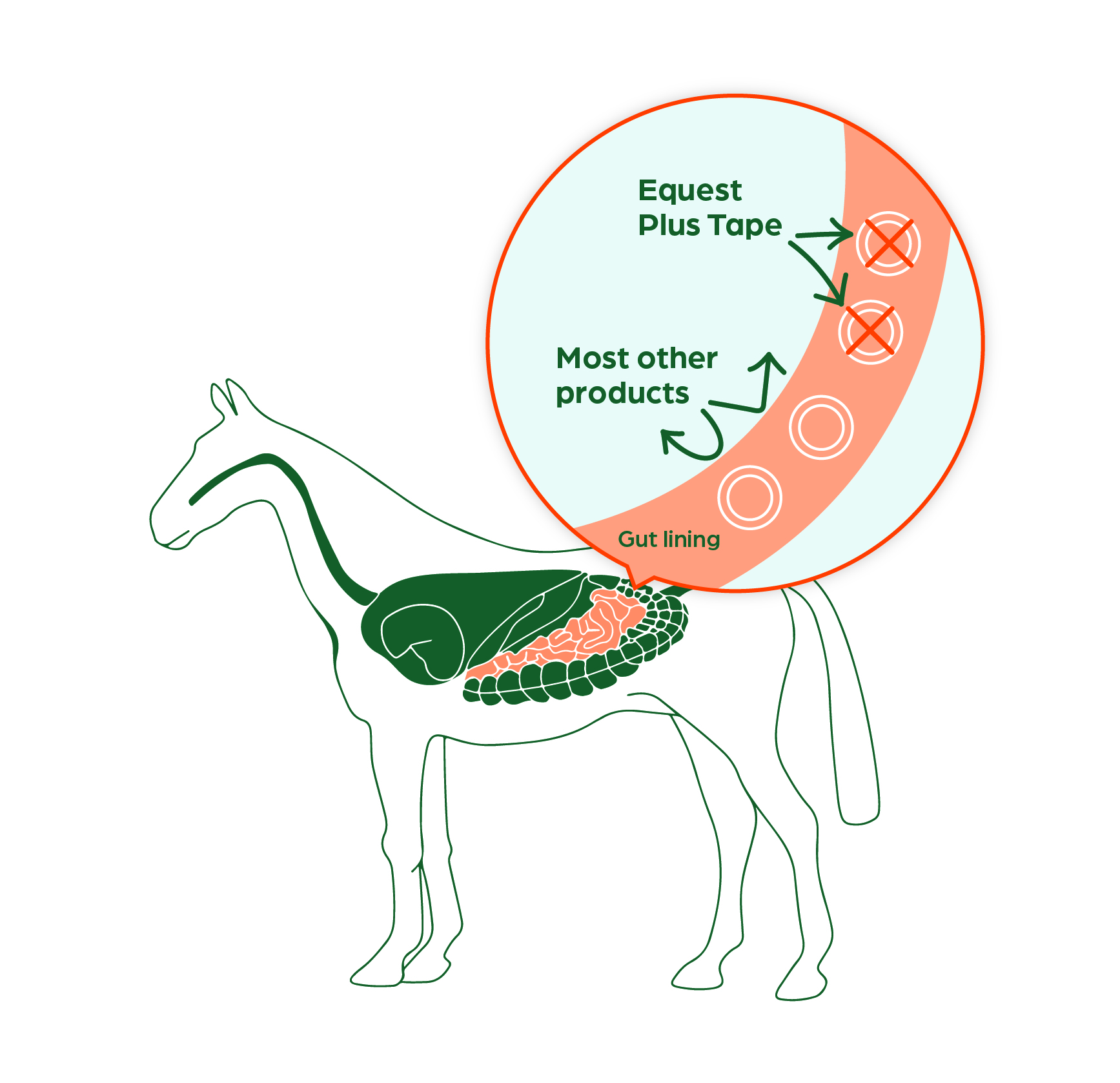
The objectives of this document are to provide: Evidence-based recommendations to Australian equine veterinarians for the sustainable control of internal parasites, with emphasis on cyathostomins and Parascaris spp. Recommendations for testing for anthelmintic resistance. Supporting information on the diagnosis of internal parasites in horses and nonchemical Consider parasite types/stages likely to be present in individuals based on age, health, management, grazing history and test results. This will inform anthelmintic selection when treatment is considered appropriate. What are Parasitic Infections in Horses Parasitic infections in horses are a common concern for equine veterinarians and owners alike.
Learn how to effectively manage horse roundworm treatment. Explore the life cycle, detection methods, treatment options, and prevention strategies. ??
Control of internal parasites is a cornerstone of equine management and a continual endeavor. Although anthelmintics are the primary method of parasite control, other factors such as pasture management and stable environment are also important. Control programs should be tailored to each farm situation and require a cooperative program between the horse owner and the Larvae of this parasite are known to transmit lactogenically from mares to foals, but it should be kept in mind that it can also infect through fecal/oral and percutaneous routes. In addition, S. westeri is a facultative parasite, which can maintain a full life-cycle in the environment without entering a host.
Effective Equine Pasture Management and Parasite Control Maintaining horse health through comprehensive pasture management and vigilant parasite
The roundworm, or ascarid, continues to be the primary concern in foals and yearlings. New recommendations are available for improved management of parasites in horses. Several management tactics can be undertaken to reduce parasite burdens in pastures and, hence, infection to grazing animals and the need for treatment. Parasite prevention management practices include: Key Takeaways Deworming for a horse’s health involves using appropriate medications to eliminate different internal parasites. A successful deworming program considers factors such as the type of dewormer, frequency, and schedule, assessing parasite load, and understanding drug resistance. The horse’s age, health status, pasture management, and
- Factsheet: Equine intestinal parasites
- Gastrointestinal Parasites of Minor Clinical Importance in Horses
- Parasite Control — Foundation Equine Clinic
Cattle grazing on pastures are inevitably exposed to internal parasites that can lead to significant production losses and health issues. While complete confinement may minimize parasite exposure, managing parasites is an ongoing challenge for cattle exposed to pasture environments. Control of internal parasites can be achieved through the use of various oral, Learn about ascarids in horses: discover causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention tips to effectively manage these common equine parasites.
Abstract Introduction In-depth knowledge of the use of anthelminthics in the field, especially by veterinarians, is required to design more sustainable parasite control strategies. Materials and methods An online survey was sent by e-mail to 940 equine veterinary practitioners to describe their equine practice, their awareness about parasites and the management strategies they Gastrointestinal parasites pose a significant threat to equine health and welfare worldwide. Effective parasite control relies heavily on accurate detection and monitoring, with faecal worm egg counts being the most commonly used diagnostic tool. Faecal worm egg counts provide valuable insights into parasite shedding and guide targeted anthelmintic treatments, Many horses no longer require frequent treatment for parasite control. Today, the most significant parasite infection in adult horses has changed from large strongyles to small strongyles. The roundworm, or ascarid, continues to be the primary concern in foals and yearlings.
Many horses no longer require frequent treatment for parasite control. Today, the most significant parasite infection in adult horses has changed from large strongyles to small strongyles. The roundworm, or ascarid, continues to be A reader-friendly guide for all involved in equine breeding and raising: Feeding and Management of Foals and Growing Horses. Covers nutrition and wellbeing
Parasite management programme In 2019, as a result of an increased prevalence of clinical disease, caused in particular by cyathostomins, and concerns over AHR, the author’s practice decided to introduce an integrated fixed-fee parasite management programme (Table 1).
Safe way of Managing Horses We have used the Worm-Ed programme as a safe way of managing a large variety of horses from foals to show jumpers that all require a different form of treatment. I needed a reliable plan that was easy to follow, more cost effective than buying off the shelf and took the guess work out of our parasite management. Parasite control programs should be tailored to meet the particular farm needs. Also see Gastrointestinal Parasites of Horses. Pregnant mares should be administered ivermectin or a benzimidazole 1–3 days before foaling to prevent lactogenic transmission of Strongyloides westeri, which can cause diarrhea in young foals. For More Information Other foals on the farm are likely harboring similar parasite burdens and the pastures are contaminated with long-lived, resistant ascarid eggs waiting to infect future foal crops.” Ascarids in the small intestine of a horse.
What are the most common intestinal parasites in horses? Learn the best horse deworming schedule, deworming products and equine parasite control tips to fight worms in horses like strongyles, ascarids and tapeworms. Intestinal parasites can cause severe disease in horses and can even lead to the death if the burden is overwhelming. Therefore, it is essential all horse care providers understand about equine intestinal parasites and how to manage them appropriately. This document discusses the most common intestinal parasites found in horses, reveals their significance and discusses Parasite control refers to the management and reduction of parasites that can harm humans, animals, and crops, utilizing methods such as chemical treatments, biological control, and sanitation practices. Effective parasite control is crucial for preventing diseases, ensuring animal health, and enhancing agricultural productivity. Familiarity with lifecycle stages
Abstract Parasites are ubiquitous in grazing equids, but most commonly cause infection without manifestation of clinical disease. However, the potential for profound and severe disease syndromes has historically prompted widespread adoption of preventative control measures. With the increasing development of anthelmintic resistance, such control measures
- Paroles Et Traduction De « Caruso
- Paris Gare De L’Est To Paris Charles De Gaulle Airport Bus
- Parisian Cleaners In Dillon, Mt
- Parkland Cape Breton : Parkland Cape Breton Open House
- Paris Zu Weihnachten: Eisbahnen Zum Skifahren, Märkte Und Lichter
- Pantförder Dr. U. Partner In Datteln ⇒ In Das Örtliche
- Parodontologie Zahnärzte In Bayern Finden
- Parfümerie Douglas Berlin Tauentzienstraße In Berlin
- Paroles De Wake Me Up – Paroles de Wake Me Up Before You Go-go
- Panoramasauna In Der Saarowtherme, Seenland Oder-Spree, Bad Saarow
- Parc National De Jasper : 12 Activités Incontournables
- Paroles Et Traduction Frank Ocean : Swim Good
- Parkhotel Wittekindshof Karte : Parkhotel Wittekindshof in Dortmund
- Parodontite : Quels Aliments Privilégier ?