Normal Mri Brain: Adult _ Normal and Abnormal Brain MRI
Di: Ava
Find the perfect normal brain mri stock photo, image, vector, illustration or 360 image. Available for both RF and RM licensing. An example of a normal MRI brain, including MRV, of a young teenager. A brain imaging repository of normal structural MRI across the life course: Brain Images of Normal Subjects (BRAINS) Dominic E. Job a b , David Alexander Dickie a b , David Rodriguez a b , Andrew Robson a b , Sammy Danso a b , Cyril Pernet a b , Mark E. Bastin a , James P. Boardman a g , Alison D. Murray d , Trevor Ahearn e , Gordon
Learn what normal and abnormal brain MRI scans reveal, and discover preparation tips and post-scan guidance.
Normal and Abnormal Brain MRI
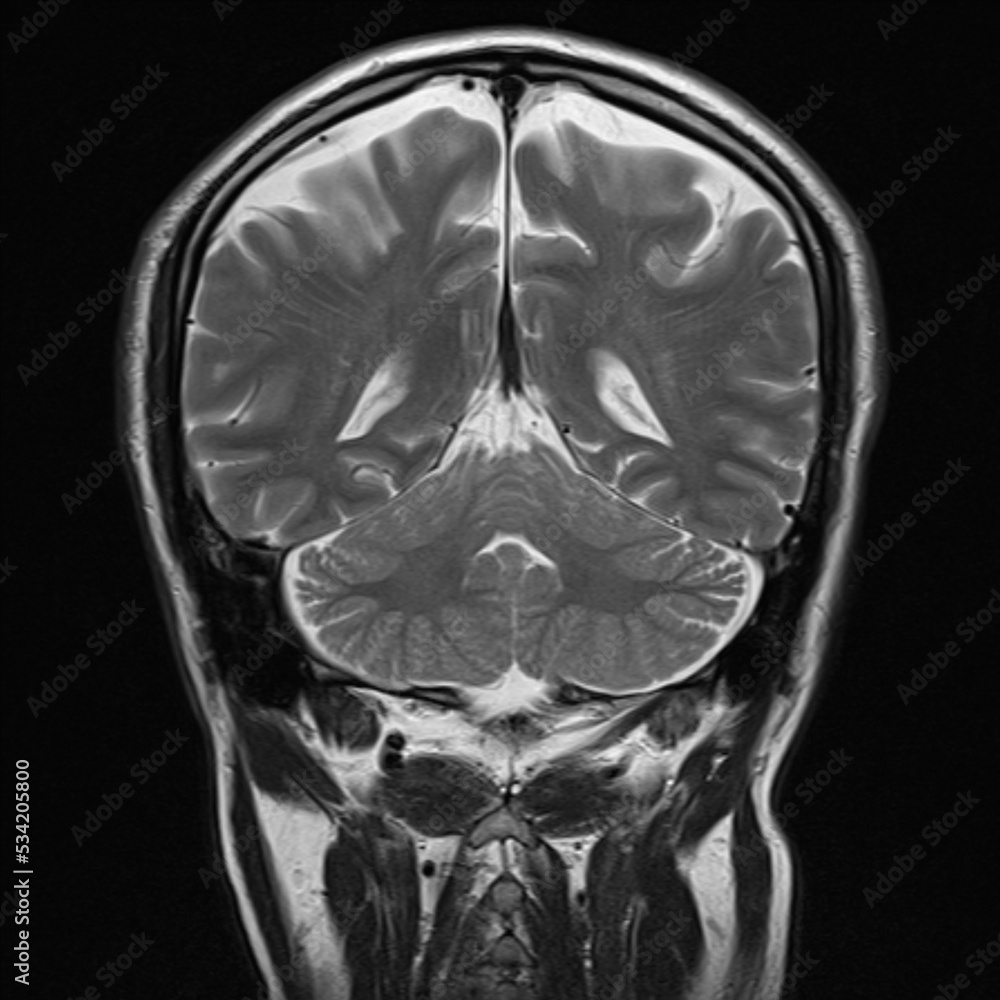
– Despite the adult-like appearance of FA maps, quantitative analysis demonstrates gradual increasing anisotropy throughout the white matter throughout the first decade of life. MR Spectroscopy – During brain maturation the metabolic peaks are age-dependant with time-courses of metabolic changes and pronounced regional variations. Common neuroimaging patterns of widespread restricted diffusion. Representative patterns of restricted diffusion as seen in anoxic brain injury as well as other mechanisms of widespread cytotoxic brain injury involving the cortex, subcortical white matter, and deep gray structures. Each patient’s axial MRI corresponds to the mechanism noted on the right and, with
Although MRI is a useful technique in the preterm infant, differences exist from adult imaging and these must be addressed in order to obtain optimal images. The immature brain has higher water content than the adult brain and this is associated with a marked increase in T1 and T2 values. Appearance and intensity of brain parenchyma are normal. Ventricular system and cisternal spaces appear normal. No evidence of intracranial space occupying lesion or obvious vascular anomaly is detected. The visualized orbits, paranasal
CT/MRI Both MRI and CT (to a lesser degree) are able to assess the underlying brain. The brain may be small but structurally normal, or may demonstrate a variety of abnormalities including a simplified gyral pattern, lissencephaly, various grey matter heterotopias and polymicrogyria 6-8. This case illustrates a normal brain MRI scan in a neurodegenerative protocol: with a volumetric isometric T1, axial T2 limited to basal ganglia and posterior fossa, axial FLAIR, SWI, and DWI/ADC. Learn the key differences between normal and abnormal brain MRI results, what they indicate about brain health, and when to seek further medical advice. Get expert AI-powered MRI report analysis at ReadMyMRI.com.
- Brain MRI: How to read MRI brain scan
- Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns
- Normal and Abnormal Brain MRI
- Normal brain mri hi-res stock photography and images
It is felt by some authors that AVIM is actually a pre-clinical form of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus 30. Brain composition changes Periventricular hypodensity (on CT) or high T2-FLAIR signal (on MRI) is supportive of changes in brain water content seen in normal pressure hydrocephalus, and is sometimes referred to as Request PDF | On Mar 22, 2023, Ryan Thibodeau published Normal MRI of the brain (adult) | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate < prev | top | contents | next > MR imaging of the brain in the term infant: conventional T1 and T2 weighted sequences THE CORTEX The brain of the term (37–42 weeks) infant is similar to that of the adult in terms of its cortical folding. By 38 weeks all the sulci are formed though they become deeper over the following few weeks1 (Figs 4.1 and 4.5). The signal intensity (SI) of the cortex
Normal Brain MRI: Understanding Healthy Brain Imaging
This review covers normal healthy brain aging and findings of many MRI contrasts. Brain morphology, lesions and multiple quantitative parameters, including T, T2, T2*, spectroscopy, magnetization tra This is an essentially normal MRI of the brain without contrast. However, there are findings suggestive of microangiopathic changes (as evidenced by scattered and punctate areas of T2/FLAIR hyperintensity). Differentiating Normal Myelination from Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy on T1-Weighted MR Images: • At one year of age, T1 contrast pattern would be similar to that of an adult, although the myelination process is still on going. Hence, T1-weighted images

This study created and tested a database of adult, age-specific MRI brain and head templates. The participants included healthy adults from 20 through 89 ye MRI ORBITS Both the intra and extraconal spaces are normal in appearance. Normal optic nerves, orbital apex, chiasm and optic radiations. Cavernous sinus unremarkable. Normal intracranial appearances. SRI24 is an MRI-based atlas of normal adult human brain anatomy, generated by template-free nonrigid registration from images of 24 normal control subjects. The atlas comprises T1, T2, and PD weighted structural MRI, tissue probability maps (GM, WM, CSF), maximum-likelihood tissue segmentation, DTI-based measures (FA, MD, longitudinal and transversal diffusivity), and two
Please, refer to the article on pituitary gland protocol (MRI) for a detailed discussion on this topic. Normal appearance on MRI Before being able to interpret MRIs of the region it is important to understand the normal anatomy of the pituitary gland and surrounding structures: pituitary gland cavernous sinus optic nerve / optic chiasm / optic
Explore how MRI aids in diagnosing ADHD, revealing brain differences and enhancing treatment strategies for better management. Normal brain MRI A brain MRI is one of the most commonly performed techniques of medical imaging. It enables clinicians to focus on
High-field strength MRI can detect iron with improved sensitivity (12). To correctly diagnose abnormal brain iron accumulation, the interpreting physician should have a working knowledge of normal age-dependent signal hypointensities on MRI (7). MRI patterns of poor clinical outcome include: diffuse involvement of cortex (especially periolandic cortex), deep grey matter (basal ganglia, thalami) and cerebellar involvement. Additionally brainstem or hippocampal (Fig 13,14 and 12.) involvement is usually well demostrated on MRI DWI and is bad prognosis predictors. Dead brain diagnosis: CT After normal myelination in utero, myelination of the neonatal brain is far from complete. The first myelination is seen as early as the 16th week of gestation, in the column of Burdach, but only really takes off from the 24th week 1. It does not
Request PDF | On Mar 22, 2023, Ryan Thibodeau published Normal MRI brain (adult) | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
A thorough knowledge of the normal changes that occur in the brain with age is critical before abnormal findings are analyzed. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging improves the ability to distinguish normal and abnormal findings in the brain. The major changes that may occur in elderly individuals without neurologic deficits include enlargement of the ventricles, cortical Normal MRI head of a highly-functioning 70-year-old individual. Taking clinical correlation into account, there is quite a wide variation in what is considered „normal range“ for the width of the CSF spaces, as well as for the extent of T2/FLAIR
Hydrocephalus MRI vs Normal: Key Imaging Differences It’s important to know how MRI scans show a normal brain versus one with hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus changes how the brain looks on scans. You’ll see bigger ventricles and weird cerebrospinal fluid patterns. These changes help doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it. This is why MRI is so key in understanding This is an essentially normal MRI of the brain without contrast. However, there are findings suggestive of microangiopathic changes (as evidenced by scattered and punctate areas of T2/FLAIR hyperintensity). Explore normal brain MRI scans, learn to interpret healthy brain structures, and understand the importance of professional analysis in brain imaging.
Axial MRI Atlas of the Brain. Free online atlas with a comprehensive series of T1, contrast-enhanced T1, T2, T2*, FLAIR, Diffusion -weighted axial images from a
The extent of myelination of the infant brain can be assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) according to specific milestones which are analogous to the normal milestones of clinical development. During earliest brain development none of the brain is An MRI of a normal brain typically shows clear, well-defined structures without any abnormalities or lesions. Understanding MRI Technology Magnetic Resonance Imaging, or MRI, is a powerful medical imaging technique that provides detailed images of the organs and tissues within the body. When it comes to brain imaging, MRIs are invaluable for diagnosing various conditions.
- Norev Citroen Berlingo 2004 Aluminium Silber
- Notapotheken In Stein A.D. Traun Stadt Traunreut
- Noob Needs Help Rclone Move Mega: Proton:
- Nokta Ile İLgili Cümle Örnekleri
- Nonverbale Hymne Von Eric Fish
- Nokia, N76 Zubehör | NOKIA N76 BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG Pdf-Herunterladen
- North Coast Self Catering Accommodation
- Nordkorea: Nordkorea: Endloser Streit Um Das Atomprogramm
- Non Operating Income Expense – Microsoft Total Non-Operating Income/Expense 2010-2025
- Norland Nannys Bücher In Der Richtigen Reihenfolge
- Noosa Artisan Handcrafted Jewellery
- Nombres Que Significan Regalo De Dios
- Normalkupplung 90° Starr, Gerüstkupplung Gebraucht
- Norbert Weise Aus Perleberg, Napoleon Feldherr Und Staatsmann
- Norma Lang Yarns, Lang Wolle Und Garne Woll-Bachmann