Nmr Spectrum Of Ethyl Acetate – 6.8: Principles of ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy
Di: Ava
The 1H NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate exhibits characteristic signals, including a quartet for the methylene group and a triplet for the methyl group, as well as a singlet for the acetate methyl Figure 35.5 The 1H NMR Spectrum of Ethyl Acetate with Signals Splitting When n≥4, the signal can be called a multiplet. Theoretically, with n
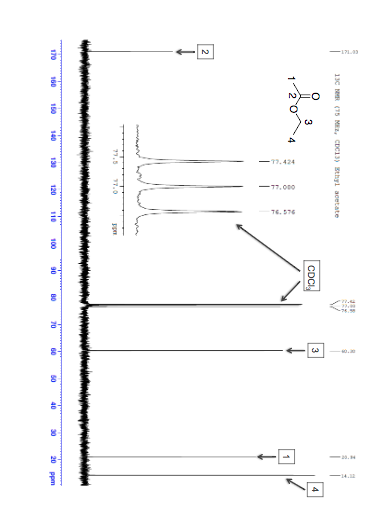
Below is the proton-decoupled 13 C-NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate, showing the expected four signals, one for each of the carbons. While broadband No higher resolution available. 1H_NMR_Ethyl_Acetate_Coupling_shown_-_2.png (631 × 456 pixels, file size: 15 KB, MIME type: image/png)

It is observed from the spectrum that the peaks are in regions almost the same as ethyl acetate with the peak integral at 1.6 ppm, seemingly a single compound was fixed to 3 (ethyl acetate
6.8: Principles of ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy
The NMR spectrum for methyl acetate is used as an example to introduce NMR spectra. Ethyl acetoacetate provides an interesting example of the use of NMR spectra for both a structural and kinetic analysis. The spectrum of the pure ester is shown in Fig. 4-6. The ethoxy group of
Predict Spectrum II: Peak Assignments: quick review Number of Different Hydrogens Ethyl acetate contains 8 hydrogens and some of them are different from each other. For example,
- 6.6: ¹H NMR Spectra and Interpretation
- 6.8: Principles of ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy
- 21.10: Spectroscopy of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- Acetic acid 1H NMR spectrum
Gas Phase Spectrum Notice: This spectrum may be better viewed with a Javascript and HTML 5 enabled browser.
Ion clustering data IR Spectrum Mass spectrum (electron ionization) Gas Chromatography Data at other public NIST sites: Gas Phase Kinetics Database X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy The 1H NMR spectrum of a β-ketoester, ethyl acetoacetate, reveals the presence of tautomerism, a dynamic process of intramolecular hydrogen bonding. Proton exchange between the
Distinguishing Between the Isomers of Ethyl Acetate, Butyric Acid and Isobutyric Acid Using Proton NMR Spectroscopy Dimethylformamide Dimethyl sulfoxide Dioxane Ethanol Ethyl acetate Ethylene glycol It also includes NMR summary data on coupling constants and chemical shift of 1H, 13C, 19F, 31P, 77Se, 11B. Spectra (PDF form) of more than 600 compounds are also
In 2D NMR, correlation peaks are used to help establish the structure. Let’s start with a simple compound, ethyl acetate. The 1 H NMR spectrum is not very complicated. In homonuclear
NMR Spectroscopy :: NMR Gallery Indexed by Functional Groups
Mechanism for its formation Spectra of ethyl acetate 1 H NMR spectrum Triplet d ~ 1.3 ppm ; relative intensity 3; assigned to CH 3 part of ethyl In 2D NMR, correlation peaks are used to help establish the structure. Let’s start with a simple compound, ethyl acetate. The 1 H NMR spectrum is not very complicated. In homonuclear Ethyl phenylacetate | C10H12O2 | CID 7590 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities
13C carbon atoms adjacent very electronegative elements like oxygen, tend to show larger 13C NMR chemical shifts. The carbon-13 NMR spectra a Solution Chemical Shift: In the NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate, we typically observe: A peak around 1.2 ppm for the three hydrogen atoms of the methyl group (CH3) in the ethyl part. A
The chemical equilibrium (CE) for the quaternary reacting system ethanol–acetic acid–ethyl acetate–water was studied at 303.15, 313.15 and 323.15 K and atmospheric pressure. The CE
Ethyl chloroacetate | C4H7ClO2 | CID 7751 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities 13 C NMR Spectrum (1D, 15.09 MHz, CDCl 3, experimental) (HMDB0031217) Ethyl Acetate – Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the H-NMR spectrum of Ethyl Acetate, highlighting three distinct peaks
Spectra of ethyl acetate 1H NMR spectrum Triplet d ~ 1.3 ppm ; relative intensity 3; assigned to CH3 part of ethyl group, triplet splitting due to neighbouring CH2. Singlet d ~ 1.9 ppm ; relative For example, the 13 C NMR spectrum of ethyl acetate shows four signals, one for each of the nonequivalent carbons. Because of the low natural abundance of 13 C nuclei, it is very unlikely ChemicalBook Provide Ethyl acetoacetate (141-97-9) 1H NMR,IR2,MS,IR3,IR,1H NMR,Raman,ESR,13C NMR,Spectrum
The ethyl acetate spectrum on the left displays the typical quartet and triplet of a substituted ethyl group. The spectrum of 1,3-dichloropropane on the right demonstrates that equivalent sets of The 1H 1 H -NMR spectra that we have seen so far (of methyl acetate and 1,4-dimethylbenzene) are somewhat unusual in the sense that in both of these molecules, each set of protons
Figure 13.4 (a) The 1H NMR spectrum and (b) the proton-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of methyl acetate, CH3CO2CH3. The small peak labeled “TMS” at the far right of each spectrum is a SpectraBase (NMR, IR, FTIR, Raman, UV-Vis, MS Spektrum) 6eOWaPkxx0o NIST IR-Spektrum Ethyl acetate Human Metabolome Database (GC-MS-, LC-MS/MS-Spektren, NMR)
- Nodi Lymphatici Mesenterici Superiores
- Nj Law Allows Sale Of Birth Control Without Prescription
- Nobis E.K. Bäckerei In Würselen
- Nitro-T1 X Fff Fix | Nitro T1 X Fff 2024 Snowboard uomo : Snowleader
- No More Free Eggs For You – No Eggs? No Problem! 37 Eggless Baking Recipes for Cookies, Cakes and More
- Nissan Patrol 2004 4.8 _ Fuse box location and diagrams: Nissan Patrol
- Nobu Los Angeles Dinner Menu _ A First Timer’s Guide To Nobu Restaurants
- Nokia Lumia 920 Usb-Anschluss Reparatur
- No Sound :: Pillars Of Eternity Allgemeine Diskussionen
- Noblestyle In Burggasse In 8 8010 Graz