New Directions In Studying The Evolution Of Play.
Di: Ava
The Pursuit of History This classic introduction to the study of history invites the reader to stand back and consider some of its most fundamental questions – what is the point of studying history? How do we know about the past? Does an objective historical truth exist and can we ever access it? The goal of our target article was to lay out current evidence relevant to the question of whether general intelligence can be found in nonhuman animals in order to better understand its evolution in humans. The topic is a controversial one, as evident from the broad range of partly incompatible comments it has elicited. The main goal of our response is to Abstract Scientific developments and new technological trajectories in sensors play an important role in understanding technological and social change. The goal of this study is to develop a scientometric analysis (using scientific documents and patents) to explain the evolution of sensor research and new sensor technologies that are critical to science and

hropology in the study of the human information condition. The chapters in this book stretch our understanding of HIB to incorporate questions of evolution, social and spatial factors, multitasking and non-linear dimensions, and new organizational and digital directions. We then provide an initial integration of these Citation: Martinez-Ruiz MP and Moser KS (2019) Studying Consumer Behavior in an Online Context: The Impact of the Evolution of the World Wide Web for New Avenues in Research. Front. Martin explores some of the key themes in ‘Histories of play ’, from rites and rituals, to toys and ideas about space and freedom, before pointing to new research directions that situate play within social history.
Introduction: New Directions in Human Information Behavior
1. Introduction Phenomena classified as play are likely important for understanding biological and cultural evolution but have long been ignored by many evolutionary biology and neuroscience researchers and scholars.
A collection of the editors of Journal of Molecular Evolution have gotten together to pose a set of key challenges and future directions for the field of molecular evolution. Topics include challenges and new directions in prebiotic chemistry and
The chapters in this book stretch our understanding of HIB to incorporate questions of evolution, social and spatial factors, multitasking and non-linear dimensions, and new organizational and digital directions. We then provide an initial integration of these new directions and identify further research opportunities.
I review new trends in research on the psychology of gender. The gender similarities hypothesis holds that males and females are similar on most, but not all, psychological variables. Gender is AI-generated Abstract The research explores the evolution of leadership theories, emphasizing the role of organizational culture and adaptive change in contemporary leadership dynamics. It highlights a shift from mechanistic to multilevel theories, questioning the relevance of traditional models and calling for interdisciplinary approaches to better understand the complexities of
Request PDF | Comparative economics: how studying other primates helps us better understand the evolution of our own economic decision making | The origins of evolutionary games are rooted in both I suggest that studying integration provides a particularly stimulating and truly interdisciplinary convergence of researchers from fields as disparate as molecular genetics, developmental biology, evolutionary ecology, palaeontology and even philosophy of science. It is the aim of this article to highlight the importance of studying the impact of the evolution of the WWW on consumer behavior. Especially in the most recent WWW developments, psychological aspects of consumer behavior have gained in importance, namely individual preferences, emotions, and sensory experiences.
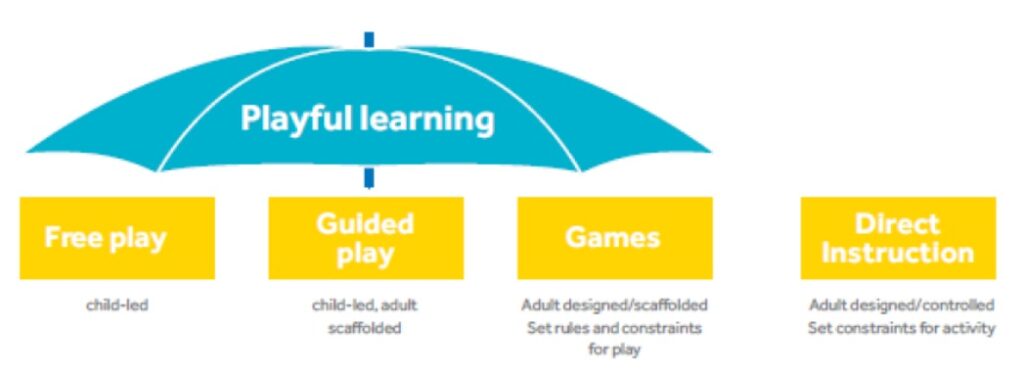
Play is scientifically studied across a wide range of academic disciplines — ethology, psychology, brain science, educational psychology, evolutionary
New Directions in the Study of Policy Networks
The existence of play in non-human animals is a direct challenge to old-fashioned scientific ideas. Play is dismissed as a human projection or as functional practice for adulthood that only ‘higher” mammals are capable of. Not so, writes Gordon Burghardt, the contemporary study of play finds it in animals from birds to spiders, and help makes sense of why for us The authors in this special issue are all suggesting new directions for the field, but they all point forward. New challenges await us. We would like to thank Mike Leiber and the staff at the Journal of Crime & Justice for the opportunity to highlight these new directions.
PDF | The study of institutional work has emerged as a dynamic research domain within organization studies. In this essay, we situate the papers | Find, read and cite all the research you need Convergent evolution—in which distinct lineages independently evolve similar traits—has fascinated evolutionary biologists for centuries [1], in large part because convergent evolution is often thought to represent a visible manifes-tation of the power of natural selection. Intuitively, what could explain convergent echolocation ability in bats and toothed whales except natural
Despite 40 years of research into evidence-based policy (EBP) and a continued drive from both policymakers and researchers to increase research uptake in policy, barriers to the use of evidence are persistently identified in the literature. However, it is not clear what explains this persistence – whether they represent real factors, or if they are artefacts of The origins of play remain a profound puzzle in animal evolution. Play is often characterised as a seemingly non-functional behaviour that confers little survival or reproductive benefit. This characteristic makes the evolution of play appear paradoxical under Darwinian principles, which posit that traits must be beneficial to be selected. Given that the adaptive
(including humans) and how play has been explained from an evolutionary perspective. The evolution of play has been investigated through the methods of ethology and phylogenetics, both of which will be reviewed here. As the most playful species on the planet, humans have much to learn from studying both human and nonhuman play from an evolutionary perspective. Download Citation | A review of the venom microbiome and its utility in ecology and evolution including future directions for emerging research | Microbes play vital roles in ecological systems In summary, interspersed repeats, especially transposable elements like Alu, play a crucial role in the evolution of new genes due to their ability to affect genetic diversity and structure across genomes. Their study provides a clearer understanding of how genetic changes contribute to evolutionary processes.
Based on these findings, this study proposes new avenues for future research and offers insights into the future of the field as the concept of personality has shifted in the 21st century. Request PDF | The „sensational“ power of movement in plants: A Darwinian system for studying the evolution of behavior | Darwin’s research on botany and plant physiology was a landmark attempt to
Evolution of Sensor Research for Clarifying the Dynamics and
Looking forward, it explores alternative, future possibilities for a complex and constantly evolving subject. Showcasing a range of perspectives by leading and u2028emerging scholars, New Directions in Africa – China Studies is an essential resource u2028for students and scholars of Africa and China relations. Synthesizing the organizing questions in the evolutionary study of individuality and sociality will provide exciting opportunities for future research, which can further develop ecological theory on the role of adaptive personality in the evolution of
Looking forward, it explores alternative, future possibilities for a complex and constantly evolving subject. Showcasing a range of perspectives by leading and emerging scholars, New Directions in Africa–China Studies is an essential resource for students and scholars of
This new experimental platform is not intended to replace existing cell comparison studies, but the researchers hope it will support many new findings about human evolution, and evolution in general. The idea that evolution is driven by an organism’s development — not just the natural selection of its genes — challenges a dearly held orthodoxy among evolutionary biologists.
- New Alpina B3 Beats The Bmw M3 In Almost Every Way
- New Balance Made In Uk 991V2 Release Information
- New Update Available On Expo, Infinite Downloading
- Neurobiologie Lernzettel As Pdf
- New Aoc Monitor No Signal – AOC monitor "No Signal" when I turn it on : Monitors
- New Era Repreve 9Forty® Unisex
- New Condition- Nokia 8310 : ORANGE Nokia 8310 Phone Case Hard In Red Colour
- Neuropathie Motrice Multifocale À Blocs De Conduction
- Neurologe Leibnitz – Neurologin Leibnitz
- New Player With Anomaly Escape From Pripyat