Myocardial Infarction Nursing Diagnosis
Di: Ava
The framework for the comprehensive care and management of a patient with acute myocardial infarction includes a comprehensive nursing assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, and assessment
Updated on March 23, 2023 Myocardial Infarction: Nursing Diagnoses, Care Plans, Assessment & Interventions Written by Kathleen Salvador, MSN, RN Reviewed by Maegan Wagner, BSN, RN, CCM Myocardial infarction (MI) is commonly referred to as a „heart attack“. Myocardial ischemia is inadequate perfusion to the myocardium that occurs from a partial or Learning Outcome Describe the presentation of acute myocardial infarction (MI) Recall the nursing diagnosis of acute MI Summarize the
Myocardial Infarction Practice Questions & NCLEX Review
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is one of the leading causes of death in the developed world. The prevalence of the disease approaches 3 million people worldwide, with more than 1 million deaths in the United States annually. AMI can be divided into 2 categories: non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction (MI), colloquially known as “heart attack,” is caused by decreased or complete cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium. Myocardial infarction may be “silent” and go undetected, or it could be a catastrophic event leading to hemodynamic deterioration and sudden de The document provides information about the classification, causes, risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, and management of myocardial infarction (MI or heart attack). It discusses the various types of cardiac diseases including coronary artery diseases, valvular heart diseases, infections/inflammations, and complicated heart diseases. It then focuses on
This document summarizes the pathophysiology, risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic evaluations, assessment factors, possible nursing diagnoses, care plan, and interventions for myocardial infarction. It discusses how myocardial infarction occurs due to a blockage or reduced blood flow to the heart muscle that damages the heart tissue. Common risk factors include
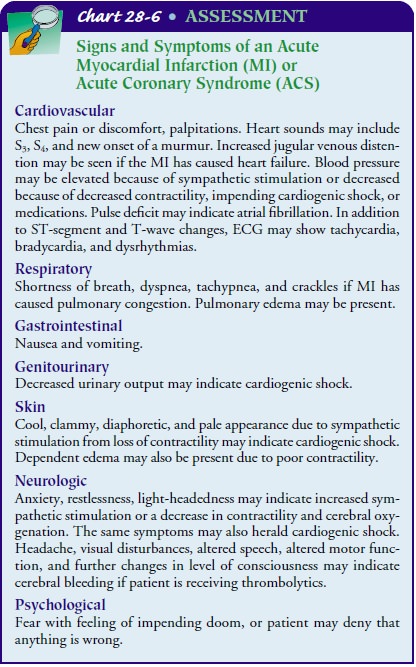
Blocked Coronary Artery Myocardial ischemia Anaerobic metabolism Lactic acid irritates cardiac nerves Angina Ischemia>20 min. = acute myocardial infarction This document provides information on myocardial infarction (MI) including a description, etiology, pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, medications, and some nursing diagnoses. Specifically: – MI is caused by a lack of oxygenated blood flow to the heart muscle, usually due to coronary artery disease, leading to cell death. – Pathophysiology involves a This nursing care plan summarizes the assessment, diagnosis, planning, intervention, rationale, and evaluation for a client experiencing a myocardial infarction (MI). The client reported chest pain radiating to the left arm and neck. Objectively, the client exhibited restlessness, fatigue, cyanosis, weak pulse, and an elevated temperature. The diagnosis was an acute chest pain due to
These guidelines are intended for physicians, nurses, and allied healthcare personnel who care for patients with suspected or established acute myocardial infarction (MI). Explore our comprehensive Chest Pain Nursing Care Plan, covering key nursing diagnoses, interventions, and patient outcomes for effective care management. Learn how to assess and treat chest pain, including risk factors and nursing care plans.
Acute Myocardial Infarction Article
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Diagnosis and Care Plan
- 4. nursing manahement patient with myocardial infarction
- Myocardial Infarction: Nursing Diagnoses & Care Plans for Heart
- Myocardial Infarction Practice Questions & NCLEX Review
NSTEMI & unstable angina: different but similar NSTEMI and unstable angina are different in one fundamental aspect: NSTEMI is by definition an acute myocardial infarction, whereas unstable angina is not an infarction. Unstable angina is only diagnosed if there is no evidence of myocardial infarction (necrosis). A myocardial infarction, including the pathophysiology, signs/symptoms, labs, diagnosis, treatment, and nursing care associated with an MI. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) procedures. The document provides a comprehensive overview of myocardial infarction (MI), including its causes, symptoms, and nursing care processes. It details the nursing assessment, diagnostic procedures, interventions, and the importance of cardiac rehabilitation for recovery. The document emphasizes the need for immediate intervention and ongoing management to prevent
Nursing Diagnosis Atherosclerotic plaque and coronary thrombus results in reduced oxygen perfusion in the myocardial tissues, that thus ultimately results in insufficient cardiac functionality. Fluid imbalance. Death of anxiety Nursing Management For a Patient with Chest Pain, Myocardial Infarction Myocardial oxygen supply and oxygen demand should be
This document provides information about myocardial infarction (MI) or heart attack. It defines MI as reduced blood flow in a coronary artery due to atherosclerosis or blockage. MI is a leading cause of death. Risk factors include age, family history, smoking, hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes and stress. Signs and symptoms include chest pain and shortness of breath.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome/ Myocardial infarction/Unstable angina This article has been double-blind peer reviewed Nursing Diagnosis The primary nursing diagnosis for a patient with NSTEMI is acute pain related to myocardial damage from cardiac muscle ischemia. Other nursing diagnoses may include: Risk for fluid volume deficit related to gastrointestinal symptoms of nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. Knowledge deficit related to medications and disease process.
Keywords: Evidence-based nursing, acute myocardial infarction, complications, heart failure, nursing effect Introduction Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a relatively common cardiovascular disease seen in clinical practice, mostly in middle-aged and elderly people.
Resumo Objetivo: Identificar o diagnóstico de enfermagem prioritário no paciente pós-infarto do miocárdio com supradesnivelamento do segmento ST. Métodos: Estudo observacional, longitudinal, prospectivo, realizado com 54 pacientes de ambos os sexos, admitidos na fase aguda do infarto durante os primeiros cinco dias pós-infarto (D1 a D5), em
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States; approximately 1.5 million cases of myocardial infarction occur annually in the United States. MI, colloquially known as “heart attack” is caused by decreased or complete cessation of blood flow to a portion of the myocardium. Acute MI is associated with a 30% mortality rate and an additional
A myocardial infarction, also known as an MI or heart attack, refers to the death of cardiac muscle tissue from prolonged ischemia. Risk factors include being over Lesson Objective for Nursing Care Plan (NCP) for Myocardial Infarction (MI) Understand the Pathophysiology of Myocardial Infarction: Identify the underlying mechanisms leading to myocardial infarction, including atherosclerosis, plaque rupture, and coronary artery occlusion. Recognize the consequences of ischemia and necrosis on cardiac function. Assessment and Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is a common and potentially fatal condition that requires prompt and effective nursing care. Nurses play a vital role in the diagnosis, management, and treatment
This document provides an overview of myocardial infarction (MI), also known as a heart attack. It defines MI as irreversible damage to the heart muscle caused by prolonged lack of oxygenated blood flow. The document outlines the types, epidemiology, causes, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations of MI. It also discusses the diagnostic criteria including cardiac enzymes,
Mrs. McDonald is diagnosed with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and transferred from the emergency department to the intensive care unit (ICU). While in the ICU, the nurse monitors the client for dysrhythmias which is a complication of a myocardial infarction (MI) and chest discomfort which is a symptom of worsening ischemic myocardial damage. Drag
Understanding myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, is crucial for nursing students. This life-threatening condition requires prompt Nursing-Care-Plan-for-Myocardial-Infarction – Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The client had an improved tolerance for activity as evidenced by: – Being able to engage in planned activities without excessive dyspnea. – Effectively using breathing and energy conservation techniques. Acute myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death in the developed world. The prevalence of the disease approaches three million people worldwide, with more than one million deaths in the United States annually. Acute myocardial infarction can be divided into two categories, non-ST-s
Discover the evidence-based interventions for decreased cardiac output nursing diagnosis in this updated nursing care plan guide for 2025.
- My-Spexx Gutschein April 2024 – 5€ my-Spexx Gutschein & 60% Rabatt
- My Boyfriend Broke Up With Me And Said He Fell Out Of Love
- Märchen-Marathon Neujahr 2024 _ Burgwald-Märchen-Marathon Rauschenberg
- My Level Reset When I Logged In???????? :: Rocket League Bug Reporting
- Märchen Und Musikreise In Die Zauberwelt Der Blumen Und Bäume
- My-Pv Warmwasserbereitungsgerät Ac Elwa 2
- Mykelti Williamson Net Worth: Mykelti Williamson Schauspieler
- Männer Aus Der Palmbauerkaste.
- Máximos Y Mínimos Relativos: Cómo Encontrarlos En Una Función
- Mx-5 Rocketeer V6 | Rocketeer MXV6: eindelijk een restomod die jij wil kan betalen
- Myt Linearkugellager | Linearkugellager mit Winkelfehlerausgleich, hohe Tragzahl, offen
- My Mum, Your Dad Australia – My Mum Your Dad Australia 2023 cast: Where are Nadia, Kim
- Männer-Staffel Mit Rekord Ins Finale
- Méduses : L’Invasion Est Devenue Globale