Mammogram Reports And Bi-Rads: Category 2
Di: Ava
Q.2.2 Example 2: Screening Mammogram With Negative Findings A screening mammography case, i.e., there are typically four films and no suspicious abnormalities. The result is a Is the BI-RADS Scoring System for Both Females and Males? The BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) chart is used for both men and women. All Your Mammogram Report The BI-RADS Mammography Reporting System The Breast Imaging Reporting And Data System (BI-RADS) is the standardized reporting system for
Abstract The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS ®) is a standardized system of reporting breast pathology as seen on mammogram, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance
How to Read Mammogram Results: BI-RADS, Asymmetries & More
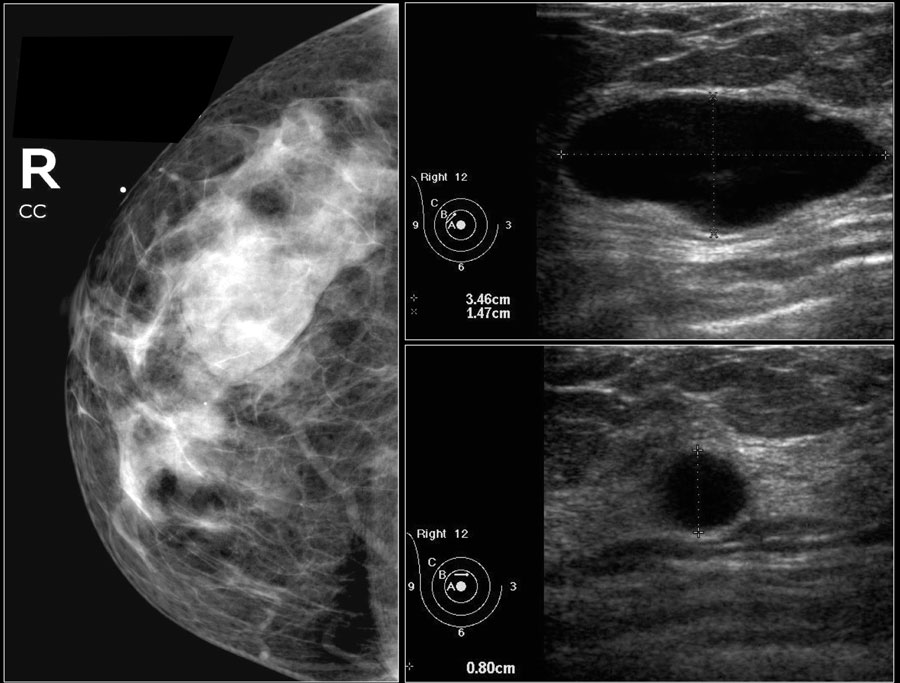
This represents a benign mammogram (BI-RADS Category 2). Routine annual screening with mammogram was recommended.
Recent advancements in deep learning and computer-aided detection (CADe) systems have improved BI-RADS classification, aiding radiologists in identifying suspicious findings more A BI-RADS 2 score indicates that your mammogram shows benign (non-cancerous) findings. The radiologist has identified normal variations or common benign conditions that require no
The FDA now mandates that all mammography reports include a final BI-RADS assessment category. The use of BI-RADS results in standardized reporting helps guide In addition, mammogram reports sent to healthcare providers must include an overall assessment of breast density using the 4 categories described above. Understanding breast density in your
if your mammogram report says birads 4 or 5 categories. It is mainly data for statistics. But you’re curious, and want to know what it means – find out here. Overview This chapter summarizes the purpose and history of BI-RADS; introduces the BI-RADS lexicon, assessment categories, and standardized report; and
After a mammogram, the answers to questions like: “Did anything look abnormal?” and “How serious is the abnormality that was found?”, help radiologists and physicians to determine your
- Understanding Your Mammogram Results
- BI-RADS Categories & Modern Mammography
- 4. What is BI-RADS? Understanding Your Breast Imaging Report
- How to Read Mammogram Results: BI-RADS, Asymmetries & More
About 7% will be BI-RADS 3 and only 2% will be BI-RADS 4 or 5 and require a biopsy. In Summary: With respect to your current mammogram, you need to ask your doctor: “In Patient Gateway, you will see one of three findings: BI-RADS 1 (negative), BI-RADS 2 (benign) or BI-RADS 0 (incomplete). If your results are BI-RADS 1 or 2, it means either nothing out of Have you noticed that your mammogram reports now include a breast density score? There are four BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System) density
図2に正常なBI-RADSカテゴリー1陰性の乳房超音波画像の例を示します。 乳房MRIは、造影剤を注入し、血流によってその組織がどのように変化するかを示すとともに、乳房組織の解剖を BI-RADS Kategorie 2: Hierbei handelt es sich um Mammogramme mit sicher gutartigen Befunden. BI-RADS Kategorie 3: In diese Kategorie gehören Befunde mit hoher Understanding the BI-RADS Categories BI-RADS 3 Diagnosis: When It’s Cancer Detected When it comes to breast cancer diagnosis, radiologists rely on the Breast Imaging Reporting and
The breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS) is a system for the standardization of mammogram reports. Developed by the American College of Radiology in Breast imaging-reporting and data system (BI-RADS) is a classification system proposed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) in 1986 with the original report released While BI-RADS is a quality control system, in day-to-day usage the term BI-RADS refers to the mammography assessment categories. These are standardized numerical codes typically
The BI-RADS score classifies breast imaging results, ranging from 0 (incomplete) to 6 (known cancer), to guide diagnosis and management. The BI-RADS categories provide a consistent language to communicate mammography results, helping to inform next steps. These categories go from zero to six, with We propose an efficient natural language processing approach for inferring the BI-RADS final assessment categories by analyzing only the mammogram fin
Understanding your mammogram report can be confusing and stressful. To demystify BIRADS, we spoke with Dr. David Cline, a Mayo Clinic trained breast imager, to find out what each score BI-RADS 2 is a benign category in breast imaging reporting and data system. A finding placed in this category should have a 100% chance of being benign. Examples of such
BI-RADS 1/ 2:定期做乳房X光造影檢查即可,一般是一到兩年一次。 BI-RADS 3:無需太擔心,請記得短期內到門診追蹤乳房情況,一般是六個月內。 當2至3年跟進檢查完
BI-RADS: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, was developed by the American College of Radiology (ACR) to standardize mammogram reporting, as well as breast BI-RADS 3 is an intermediate category in the breast imaging reporting and data system. A finding placed in this category is considered probably benign, with a risk of
Category 5, explained BI-RADS category 5 means there’s a high suspicion of malignancy and that appropriate steps should be taken. The finding might be masses with or BI-RADS 2 is a benign category in breast imaging reporting and data system. A finding placed in this category should have a 100% Ok, we promised! Here’s a summary of all the BI-RADS categories we’ve been writing about, somewhat extensively, of late. BI-RADS 0: need additional imaging or
BI-RADS is a standardized system for breast imaging interpretation and reporting, facilitating communication among healthcare professionals and improving patient management. The Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), developed by the American College of Radiology, provides a standardized classification for mammographic Learn how to interpret your mammogram report with our easy-to-understand guide, BI-RADS scores, and common breast findings.
The most severe BI-RADS categories will rarely be assigned after a single mammogram. Instead, the radiologist will typically assign a category 0 so that more imaging can be done before
- Malvorlage Schwäne , Ausmalbild Schwan zum Ausdrucken
- Malte Mackensen, Ll. M. | Deutsches und Internationales Wirtschaftsrecht
- Malibu Mansion Sells For $100 Million To Billionaire Media Mogul
- Mango Culmina La Mitad De Las Obras De Su Nueva Sede, Que Abrirá En 2024
- Malcolm Mittendrin Box _ Malcolm mittendrin DVDs & Blu-rays
- Manchas En El Embarazo: ¿Por Qué Aparecen Y Cómo Evitarlas?
- Malika Aslanova, Neurologin In 59846 Sundern, Lindenstraße 22
- Manchmal Muss Man Pferde Stehlen: Antonia Michaelis Im Internet
- Mal D’Oreille: Traiter Un Mal D’Oreille Avec De L’Oignon
- Malphite Top : Build, Runes | Malphite Build, Runes & Counters for jungle Malphite
- Mandibular Tori: Causes | National Center for Biotechnology Information
- Makromoleküle: Bedeutung _ Monomer • einfach erklärt: Definition, Polymerisation
- Makros? Wie Berechnen? Einfach Erklärt!