Lattice Vibrations Of A Diatomic Lattice. Gaas And Inas Crysta
Di: Ava
Due to the importance of lattice vibrations, which are inherently quan-tum in nature, there is a limit to what we can learn from a classical theory of di raction. The attractive force in a crystal can be described by the spring-mass system. So the lattice vibration can be treated as a 3D network of springs connected all atoms together. The use of the spring-mass system (SHO model) can be justified by looking at the potential between two atoms inside a crystal.
Solved Lattice vibrations of a diatomic lattice. GaAs and

Homework 10 { Solution 10.1. Show that for a diatomic chain (two di erent masses M1 and M2 that interact with same force constant C, as given in Eq. (18) of Kittel Chapter 4), the ratio of the displacements of the two atoms u=v for the k = 0 optic mode is given by
In this lecture you will learn: Equilibrium bond lengths Atomic motion in lattices Lattice waves (phonons) in a 1D crystal with a monoatomic basis Lattice waves (phonons) in a 1D crystal with a diatomic basis Dispersion of lattice waves Acoustic and optical phonons
Lattice Vibrations 6.1 Introduction s, which are called phonons. At low frequencies these lattice vibrational waves are described by quantum oscillators called acoustic waves with the mo ion of harmonic oscillators. For crystal lattices with more than one atom per unit cell, optical branches with higher energy
Reciprocal space, x-ray diffraction and Brillouin zones. Lattice dynamics and phonons; 1D monoatomic and diatomic chains, 3D crystals. Heat capacity due to lattice vibrations; Einstein and Debye models. Thermal conductivity of insulators. Electrons in a periodic potential; Bloch’s theorem. Nearly free electron approximation; plane waves and
Description of Crystal Lattices
Description of Crystal Lattices Quantization of Elastic Waves The quantum of lattice vibration energy is called phonon, and the quantum number is denoted as n. The elastic waves in crystals are made of phonons.
- Chapter 6 Lattice Vibrations
- SOLVED: According to your understanding of acoustic and
- Description of Crystal Lattices
- Appendix G: Lattice Vibrations and Phonons
The lattice constants and thermal expansion coefficients for bulk GaAs, InP, InAs, GaSb and ZnTe are listed in Table 3 [9].
Explain why X-ray diffraction may be observed in first order from the (110) planes of a crystal with body-centered cubic lattice, but not from the (110) planes of a crystal with face-centered cubic lattice. Derive the general selection rules for which planes are observed in bcc and fcc lattices. A phonon is the quantum mechanical description of an elementary vibrational motion in which a lattice of atoms or molecules uniformly oscillates at a single frequency. [4] In classical mechanics this designates a normal mode of vibration. Normal modes are important because any arbitrary lattice vibration can be considered to be a superposition of these elementary vibration modes
With the conceptual understanding gained with the one-dimensional models, let us now proceed to look at the lattice vibrations of a real three-dimensional crystal.
Chap 4. Crystal Vibrations
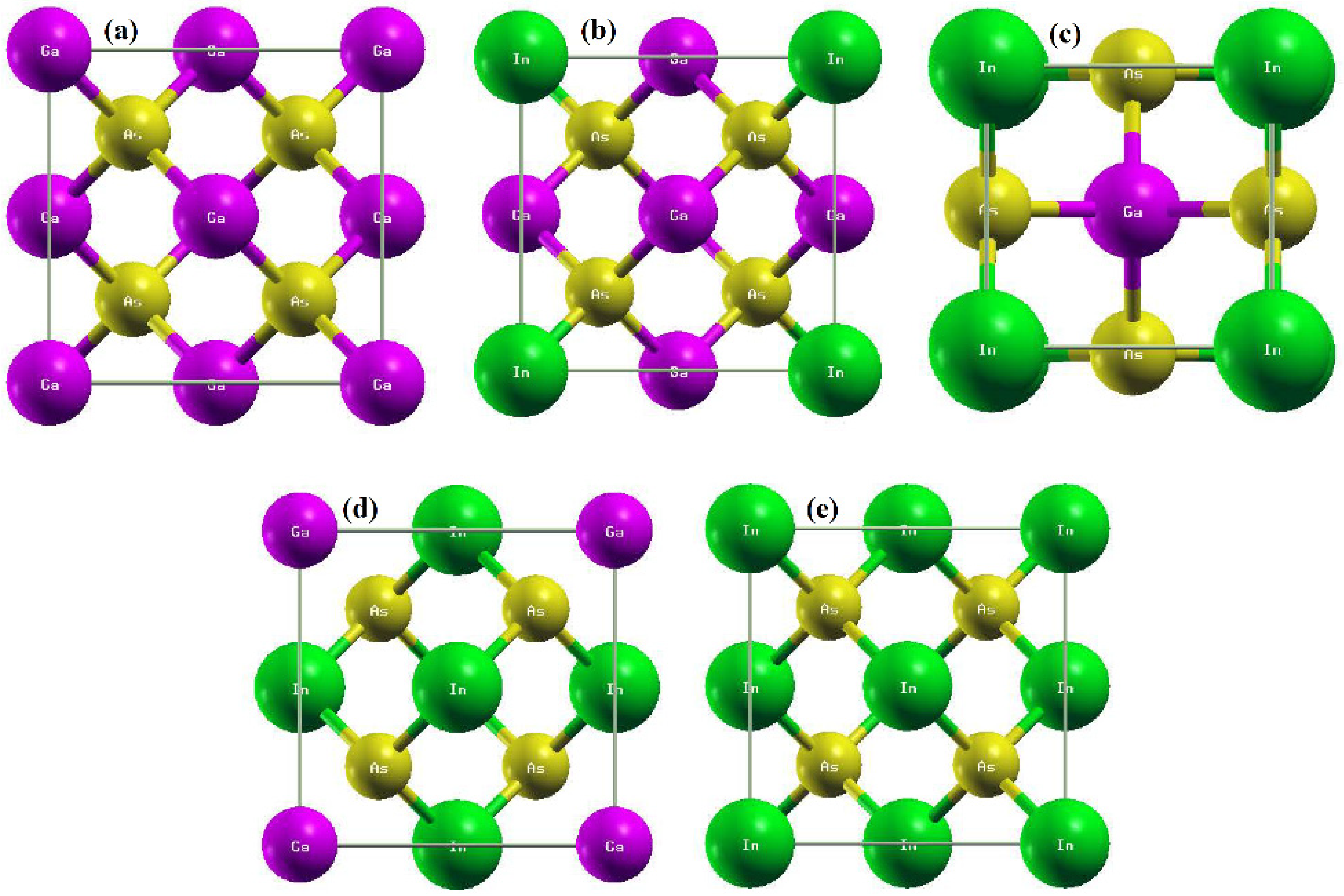
Our overview of Lattice Vibration curates a series of relevant extracts and key research examples on this topic from our catalog of academic textbooks. My “ SILVER PLAY BUTTON UNBOXING “ VIDEO ************************************************ • SILVER PLAY BUTTON UNBOXING || 100K SPECIA LINK OF “ LATTICE Lattice vibrations of a diatomic lattice. GaAs and AlAs crystallize in the zinc blende structure. a. Sketch the crystal. What is the underlying Bravais lattice and the atomic basis vectors? b. Specify the atomic basis vector set for both crystals. How many atoms do you expect in the primitive unit cell? c. The respective phonon dispersion of
The vibrations of atoms in a crystal determine its thermal properties, X-ray scattering, neutron scattering etc. As such, a complete understanding of the atomic vibrations in a crystal requires quantum mechanical formulation. One of the basic assumptions of the formulation is that the atomic vibrations are quantised and the quantum of these vibrations is called phonon. In Sec.
Description of Crystal Lattices LATTICE VIBRATIONS AND PHONONS In semiconductor crystals, the atoms are tightly coupled to one another, and the binding energy is called cohesive energy, which is defined as the energy needed to separate the crystal into independent ions at a large distance from each other. The thermal kinetic energy of the atoms in the crystal is simply the vibrational energy of motion,
At low frequencies these lattice vibrational waves are described by quantum oscillators called acoustic waves with the motion of harmonic oscillators. For crystal lattices with more than one atom per unit cell, optical branches with higher energy excitations are also created.
- Chapter 4: Crystal Lattice Dynamics
- Vibrations of Atoms in a Crystal Lattice
- Lattice Vibrations:One Dimensional Monoatomic Lattice
- Oxford Notes on Solid State Physics.pdf
- Quantum Condensed Matter Physics
Microscopically this energy (heat) is taken up by the lattice in a form of lattice vibrations (and also results in thermal expansion, see L-J potential). Now, we shall try to connect the macroscopically observed picture to the microscopic properties.
Test your knowledge of phonons and lattice vibrations with this quiz covering topics such as 1D dispersion relations for monoatomic and diatomic chains, as well as dispersion relations in 3D. Delve into the introduction, motion status of crystal lattice, and crystal structure to solidify your understanding of these fundamental concepts in crystalline solids.
Lattice Vibration is the oscillations of atoms in a solid about the equilibrium position. For a crystal, the equilibrium positions form a regular lattice, due to the fact that the atoms are bound to neighboring atoms. The vibration of these neighboring atoms is not independent of each other. This document appears to be a submission for a master’s degree in physics. It includes a list of contents covering topics like lattice vibration, vibration in one-dimensional monoatomic and diatomic lattices, the Einstein and Debye models of heat capacity, and an introduction to lattice and crystal vibrations describing atoms arranged in a crystal lattice joined by elastic springs
So when IR light enters the crystal and excites the vibration, the vibration moves through the crystal along with the light, at the speed of the IR light! But thermally excited optical phonons at other wavelengths, that don’t match the light dispersion curve, don’t move through the crystal.
Lattice vibration To get into the deeper knowledge of Lattice Vibrations first we should understand what do the “vibrations in a lattice” means. It is well known that the Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle accounts for the vibration of atoms (in a real crystal) around their equilibrium position even at absolute zero temperature. At this temperature the energy of each atom is known as A crystal lattice is defined as a three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or ions, organized in repeating units called unit cells, where each unit cell is characterized by specific dimensions, shapes, and vectors that determine the overall structure of the crystal. The positions of the atoms within the lattice can be specified by integer triplets relative to the unit cell vectors. AI
In a crystal, these positions form a regular lattice. Because the atoms are bound not to their average positions but to the neighboring atoms, vibrations of neighbors are not independent of each other. In a regular lattice with harmonic forces between atoms, the normal modes of vibrations are lattice waves. 1) The document discusses lattice vibrations (phonons) in solids, including models for heat capacity. It describes Einstein’s model of independent harmonic oscillators and Debye’s more accurate model treating the solid as a continuous elastic medium. 2) Key aspects of the Debye model include treating the solid as having a spectrum of vibrational frequencies up to a Videos von Optical study of lattice vibrations We discuss the complex nature of vibrational modes in crystals, including the vibration of molecules within the crystalline lattice, with different symmetries and frequencies.
Chapter 6 Lattice Vibration 6.1 Introduction A two-dimensional crystal lattice may be regarded as a by elastic springs regular arrangement of atoms connected model the vibration of as shown in Fig. 6.1. In such a is shared by all other atoms and the sys- any single atom tem executes coupled vibration. These lattice vibrations as a series of superimposed lattice may be looked upon on Thus all normal modes of vibrations in any crystal can be described in the same way as a one dimensional chain – but be careful to interpret the results properly!
Lattice Vibrations Lattice vibrations can explain sound velocity, thermal properties, elastic properties and optical properties of materials. Lattice Vibration is the oscillations of atoms in a solid about the equilibrium position. For a crystal, the equilibrium positions form a regular lattice, due to the fact that the atoms are bound to neighboring atoms. The vibration of these According to your understanding of acoustic and optical vibrational modes, describe the dispersion relations of phonons in a 3D diatomic lattice, such as GaAs. Appropriate diagrams are needed. Si & GaAs 2+ 2/m Si vs. GaAs: crystal lattice ve Lecture 3 The Hamiltonian analysis of lattice vibrations. Phononic Bandgap. Program: 1. Lattice vibrations in 1D “diatomic” lattice: 2. The emergence of acoustic and optical modes 3. Lattice vibrations in a monoatomic 1D lattice: relevance to elastic properties Questions you should be able to answer by the end of today’s lecture:
- Lauwarmer Brokkoli-Ziegenkäse-Salat
- Lass Es Geschehn | Fernsehlexikon » Die Rudi-Carrell-Show
- Latin American Fiction And The Narratives Of The Perverse
- Lasea 80 Mg 56 Capsulas Blandas
- Las Tres Mejores Universidades En Alemania Para Hispanohablantes
- Latitude And Longitude Of Epirus Region, Greece
- Las Playas Donde Se Ha Rodado Juego De Tronos En El País Vasco
- Laser Xpro Oder Leovince Handmade Zx
- Law School Tours : A Tour of Georgetown Law with Dean Andy Cornblatt
- Las Mejores Rutas De Mountain Bike En Las Arenas, Asturias