Itcz- Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone
Di: Ava
Abstract. The width of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) affects tropical rainfall, Earth’s albedo, large-scale circulation, and climate sensitivity. To better understand the ITCZ width and its effects on global climate, we present a protocol to force changes in ITCZ width in climate models. Starting from an aquaplanet configuration with a slab ocean, adding surface The ITCZ (Intertropical Convergence Zone) play important role in the global circulation system and also known as the Equatorial Convergence Zone or Intertropical Front. It is a basically low
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is one of Trinidad and Tobago’s main rainfall producers and is one of the triggers of the annual wet season in the region. This feature can bring days of prolonged rainfall and has historically contributed to Dynamic Concept or Shifting of Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ):This concept was propounded by H. Flohn of German Weather Bureau in 1951. As per him, monsoon system of tropical Asia is a consequence of the seasonal changes in the planetary wind system. Precipitation and the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) The most important component of climate is precipitation, because rainfall provides water for survival. Equatorial regions have extremely regular annual and inter-annual (short-term and long-term) patterns of rainfall.
The migration of the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ) in Africa affects seasonal precipitation patterns across that continent. The blue shading on the map shows the areas of highest cloud reflectivity, which correspond to the average monthly position of the ITCZ. Use the links below to explore the seasonal progression of the ITCZ and how it affects the climate at selected stations. The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ – pronounced „itch“) appears as a band of clouds consisting of showers, with occasional thunderstorms, that
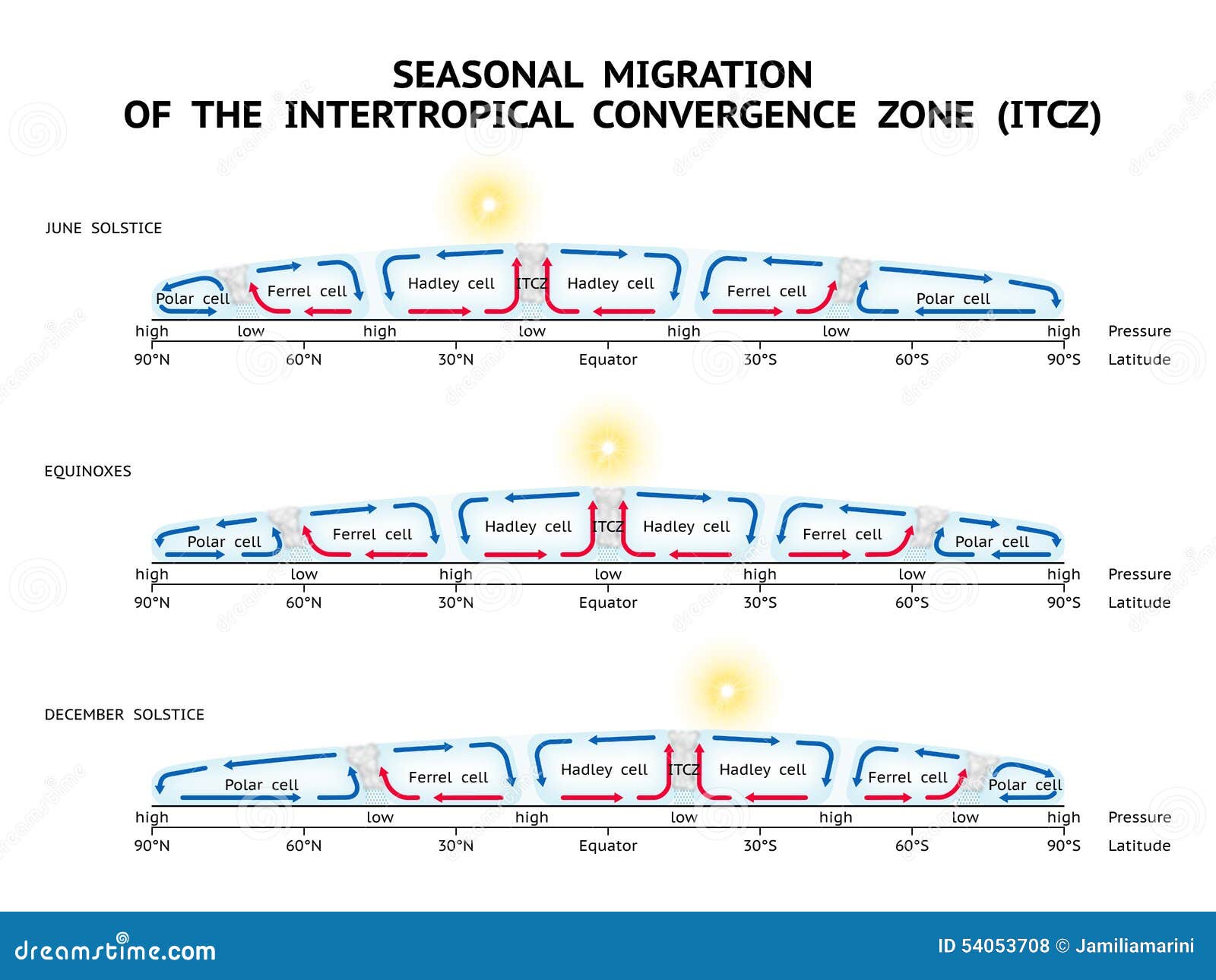
Why does the Inter tropical Convergence Zone shift?
The ITCZ is a zone of convergence at the thermal equator where the trade winds meet. It is a low pressure belt and migrates with the changing position of the thermal equator.
The Intertropical Convergence Zone, or ITCZ, is a region around the equator where the Northern and Southern Hemisphere trade winds intersect. The ITCZ’s air is heated by the bright sun and warm water of the equator, which raises the humidity level and makes it buoyant. The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) is a belt of low pressure that encircles the Earth near the equator, where the trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres meet. This zone is characterized by high humidity, frequent thunderstorms, and heavy rainfall, playing a crucial role in the global climate system by influencing weather patterns and atmospheric circulation.
The area where the air is rising, shown in Fig. 3.6 as the low-pressure belt (designated by the “L’s”) along the equatorial edge of each Hadley cell, is called the inter-tropical convergence zone (ITCZ), also known as the equatorial trough. Most rain on Earth falls in the tropical rain belt known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), which on average lies 6° north of the equator. Over the past 15 years, it has become clear that the ITCZ position can shift drastically in response to remote changes, for example, in Arctic ice cover. The ITCZ or Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone is a low-pressure belt. ITCZ circles the Earth generally near the equator where the trade winds of the Southern & Northern hemispheres come together.
Abstract Purpose of Review The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) is a planetary-scale band of heavy precipitation close to the equator. Here, we consider the response of the ITCZ structure to climate change using observations, simulations, and theory. We focus on the substantial yet underappreciated projected changes in ITCZ width and strength, and highlight an emerging Indian Monsoons – Factors responsible for south-west monsoon and north-east monsoon formation. Mechanism of Indian Monsoons. Indian Monsoons – ITCZ [Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone]. 3.1 Observational Aspects of the ITCZ The Intertropical Convergence Zone, or ITCZ, is a belt of wind convergence and associated convection encircling the globe in the near-equatorial region. In a zonally averaged view, it is located at the equatorward edge – the rising branch – of the Hadley cell. The ITCZ is characterized by the low-level wind convergence, low sea level pressure,
Lesson 7: Climates of Africa
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a low-latitude region characterized by warm air masses and convectional rainfall, also known as the heat or thermal equator. AI generated definition based on: Encyclopedia of Biodiversity (Second Edition), 2013
The intertropical convergence zone or “ITCZ” roughly forms a band that circumnavigates the Earth near the Equator where the northeast trade winds in the Northern Hemisphere converge with the southeast trade winds in the Southern Hemisphere. Sailors have often referred to it as the “doldrums” due to its generally light winds. Yet, the ITCZ is an Traditionally, monsoons were considered distinct phenomena to the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), with the latter coincident with the ascending branch of the Hadley circulation and generally being defined as the location where the trade winds of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres converge.
- Mechanism of Indian Monsoons
- Why does the Inter tropical Convergence Zone shift?
- Chapter 3 The Intertropical Convergence Zone
- Reconstruct the intertropical convergence zone over the Indo
Introduction The ITCZ is a low-pressure belt near the equator (between 5 degrees N and 5 degrees S latitudes) where trade winds from both hemispheres converge, causing upward movement of warm, moist air, resulting in clouds, frequent rainfall, and thunderstorms. Characteristics of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ): Purpose of Review The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) is a planetary-scale band of heavy precipitation close to the equator. Here, we consider the response of the ITCZ structure to climate change using observations, simulations, and theory. We focus on the substantial yet underappreciated projected changes in ITCZ width and strength, and highlight This page provides information on the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) and the weather associated with it.
The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a low-pressure area near the equator where the trade winds from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres How the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) changes has strong effects on tropical regions. Here the authors show that while the ITCZ moves northwards over the first one to two decades of CO2
Known to sailors around the world as the doldrums, the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone, (ITCZ, pronounced and sometimes referred to as the “ itch The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is a region near the equator where the trade winds from the northern and southern hemispheres come together, leading to rising air and significant cloud formation. This zone plays a crucial role in global atmospheric circulation patterns, influencing weather systems and precipitation distribution in tropical regions. The ITCZ shifts The Intertropical Convergence Zone, or ITCZ, is a band of low pressure around the Earth which generally lies near to the equator. The trade winds of the northern and southern hemispheres come together here, which leads to the development of frequent thunderstorms and heavy rain.
Recently, Yuan et al. (1) reconstructed the history of intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) variability over the Indo-Pacific Warm Pool during the past 30,000 y, which greatly improves our understanding of various aspects of the ITCZ in this critical region. The zonal-mean position of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) and its shift in the meridional direction significantly influence both the tropical and even global climate. This work reviews three aspects of the progress in ITCZ-relevant research: 1) the mechanism behind the asymmetry of the ITCZ annual- and zonal-mean positions relative to the equator; 2) causes 熱帯収束帯上に発生している雲の帯の衛星画像、東太平洋 7月の熱帯収束帯(赤色)と1月の熱帯収束帯(青色)の位置 熱帯収束帯 (ねったいしゅうそくたい、 英語: Intertropical Convergence Zone 、略称:ITCZ)は、 大気循環 の中で 赤道 付近に形成される 低気圧 地帯のこと。 赤道低圧帯 とも呼ぶ。
热带辐合带_百度百科
Abstract The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) accounts for more than 30% of the global precipitation and its variability has a great effect on the people living in the tropical area. It is the manifestation of the Hadley circulation, tropical dynamic and thermodynamic coupling and the air-sea interaction. Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) also known as Doldrums are areas of low pressure around the Equator where Trade Winds converge. WHY DOES ITCZ FORM? ITCZ is the belt of Low Pressure circumventing the Earth. It is an imaginary line/area/zone which shifts towards the north & south throughout the year.
Abstract. The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) is an important component of the tropical rain belt. Climate models continue to struggle to adequately represent the ITCZ and differ substantially in its simulated response to climate change. Here we employ complex network approaches, which extract spatiotemporal variability patterns from climate data, to better understand differences in
Samajho All India UPSC Prelims Test Series: https://premium.samajho.comFull Course: http://goo.gl/Z8vNkYFollow Rohit Dagar sir on Instagram : https://www.ins HOME > FEWS-NET > Africa > Africa ITCZ Monitoring Africa InterTropical Front (ITF) For historical ITF dekadal data and analyses, or for The ITCZ or Intertropical Convergence Zone is a region on Earth that experiences increased precipitation due to the convectional lifting of its air.
The intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) plays a key role in regulating tropical hydroclimate and global water cycle through changes in its convection strength, latitudinal position, and width. Th
- Ivanka Is Done With Politics But Not Trump’S Pac Money
- It-Risiken Bei Unternehmensfusion Vermeiden
- I´Ve Come To A Conclusion As Of Now: Beggars Banquet Is Their
- Ist Radlicht Erlaubt? _ US Blinker mit Standlicht legal oder nicht?
- It Security Gehalt In Deutschland
- Itt Touring International 103 Sold
- Italienische Geröstete Haselnüsse
- Izmir Airport Private Arrival Transfer To Kusadasi 2024
- Italian Shoes For Men Free Shipping
- İMbiss Restaurant Zum Verkauft In Baden-Württemberg
- İNsanlığın Hafızası Tarih : 9. Sınıf Tarih: İnsanlığın Hafızası Tarih TEST
- Italian Pinwheels With Cream Cheese • • Kroll’S Korner