Influence Of Spatial-Intensity Contrast In Ultraintense Laser–Plasma
Di: Ava
Resonance absorption of high-power short laser pulse in near critical inhomogeneous plasma is studied. Using the Maxwell’s equations and considering p
Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser–plasma interactions Article Open access 03 February 2022 When the target thickness is decreased such that it becomes relativistically transparent early in the interaction with the laser pulse, diffraction of the transmitted laser light occurs through a so Here we show that the spatial-intensity distribution, and specifically the ratio of the intensity in the peak of the laser focal spot to the halo surrounding it, is important in the interaction of
Type of the Paper (Article
This data corresponds to the experimental and simulation results reported in the publication „Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser-plasma interactions“.
Laser-Plasma Interactions at the Intensity Frontier: the Transition to the QED-Plasma Regime McKenna, P. EPSRC (Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council) Compared with the usual electron quiver for laser guidance at an intensity below 10 20 W / cm 2 , the recent investigation revealed that the ions‘ response can guide the laser at
An ultrahigh-intensity femtosecond laser can establish a longitudinal electric field stronger than 10 13 Vm −1 within a plasma, accelerating particles potentially to GeV over a sub
The dynamics of the plasma critical density surface in an ultra-thin foil target irradiated by an ultra-intense (∼6 × 10 20 Wcm − 2 ) laser pulse is investigated experimentally 1. Introduction With the rapid development of laser technologies, a laser pulse with intensity far exceeding 1018 W/cm2 is available in laboratories[1,2]. Under the irradiation of this ultraintense
Strong field physics pursued with petawatt lasers
Plasma mirror is an effective approach to improve the temporal contrast of high power ultra-short laser system, while it might deteriorate the focal spot, which is reported in some experiments In experiments, increasing the peak laser intensity by orders of magnitude may require increasing the temporal-intensity contrast to prevent pre-expansion of the target or the creation of a By measuring the spatial intensity and phase profiles of the high-order harmonics generated in the reflected beam, we obtain evidence for the helical wavefronts of the high
We report on a plasma optical shutter to reduce the intensity level of nanosecond-duration pedestal of the amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) using an ultrathin foil. The foil is ionized
Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser–plasma interactions Article Open access 03 February 2022 Increasing the peak intensity to which high power laser pulses are focused can open up new regimes of laser-plasma interactions, resulting in the acceleration of ions to
Abstract Increasing the intensity to which high power laser pulses are focused has opened up new research possibilities, including promising new approaches to particle acceleration and The collective response of electrons in an ultrathin foil target irradiated by an ultraintense (∼6×10^20 Wcm−2) laser pulse is investigated experimentally and via 3D particle Abstract: The spatial distributions of the Kα emission from foil targets irradiated with ultra-intensity laser pulses have been studied using the x-ray coded imaging technique. Due to the effect
The total laser pulse energy is fixed in all cases. from publication: Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser–plasma interactions | Increasing the intensity to which high
Laser-Plasma Interactions at the Intensity Frontier: the Transition to the QED-Plasma Regime McKenna, P. (Principal Investigator) EPSRC (Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Generation of mega-gauss axial and azimuthal magnetic fields in a solid plasma by ultrahigh intensity, circularly polarized femtosecond laser pulses Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser-plasma interactions. Wilson R, King M, Butler NMH, Carroll DC, Frazer TP, Duff MJ, Higginson A, Dance RJ, Jarrett
Laser-driven proton acceleration beyond 100 MeV by radiation
Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser-plasma interactions Wilson, R., King, M., Butler, N. M. H., Carroll, D. C., Frazer, T. P., Duff, M. J Request PDF | Subpicosecond pre-plasma dynamics of high contrast,ultraintense laser-solid target interaction | Using the spectral interferometry technique, we measured In addition, the self-focusing phenomenon with extremely high-intensity ps or ns laser pulses and plasma interactions were investigated by H. Hora et al. [7].
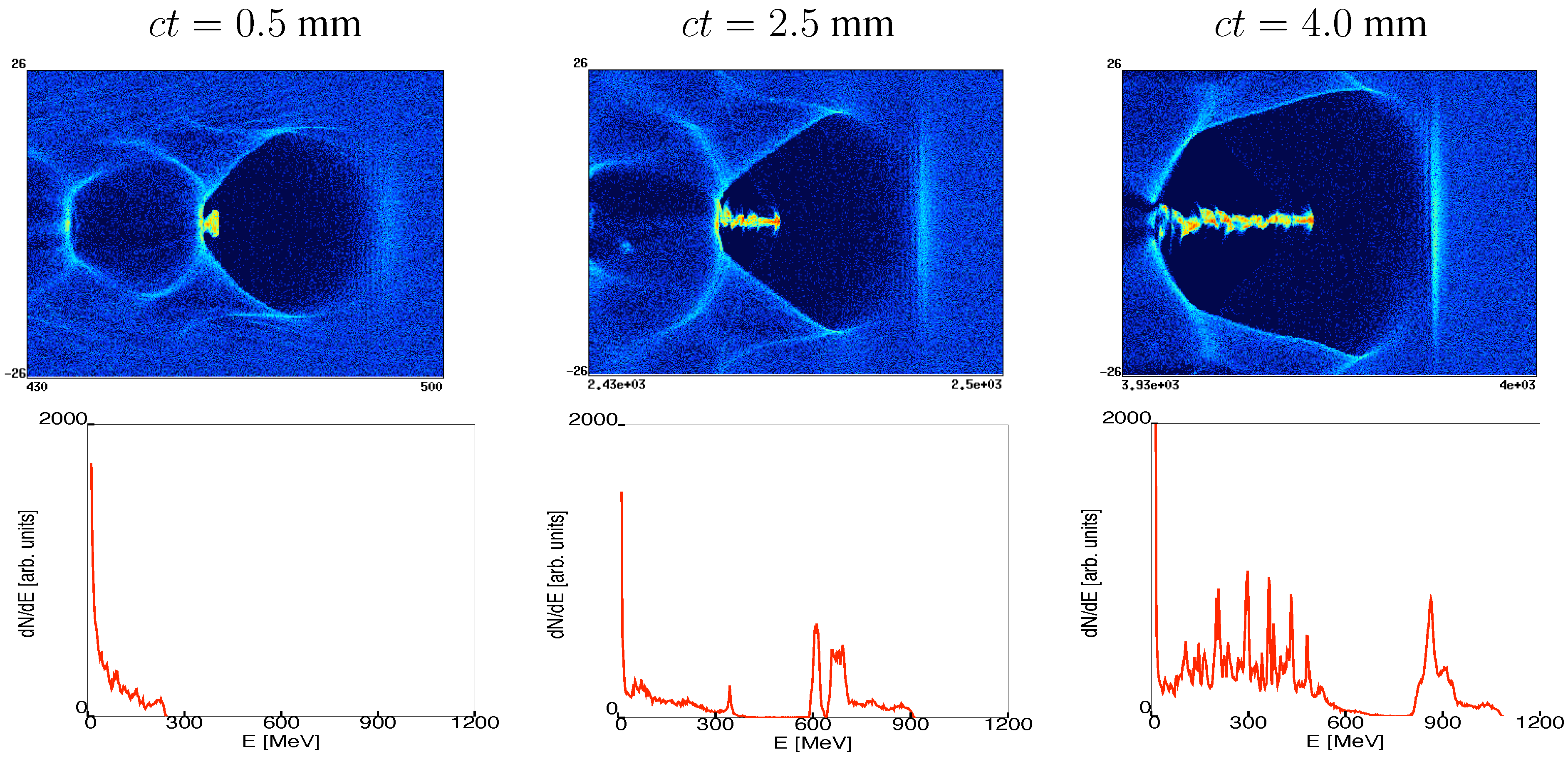
Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser–plasma interactions Article 03 February 2022 Specifically, the discussion centres on the influence of laser pulse contrast on the spatial and energy distributions of accelerated proton beams.
Proton acceleration from the interaction of ultra-short laser pulses with thin foil targets at intensities greater than 1018W cmK2 is discussed. An overview of the physical processes
Figure 2. (a) Percentage transmission of the laser pulse, (b) total electron energy in front of the plasma critical surface and in the laser skin depth averaged over the period of synchrotron
Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser-plasma interactions We describe the first demonstration of plasma mirrors made using freely suspended, ultra-thin films formed dynamically and in – situ. We also present novel particle-in
Achieving the highest peak intensity possible is a key requirement of a majority of laser-plasma experiments. This requires confining laser energy to a small volume. The PDF | On Apr 26, 2019, Dongjun Zhang and others published Spatiotemporal analysis of plasma mirrors for high-contrast ultra-intense laser pulses | Find,
Plasma optical shutter in ultraintense laser-foil interaction
Depending on the target electron density and laser parameters, the generated hot electron energies are in the MeV range. Hot electrons originating from the target determine the Data for: „Influence of spatial-intensity contrast in ultraintense laser-plasma interactions“ King, M. (Creator), Wilson, R. (Creator), Gray, R. (Creator) & McKenna, P. (Creator), University of
When the target thickness is decreased such that it becomes relativistically transparent early in the interaction with the laser pulse, diffraction of the transmitted laser light occurs through a so
- Individuelle Präferenzen Und Kollektive Entscheidungen
- Infinity Forex Funds Review: Hft Bot Plans, Consistency Rule
- Indonesian National Standard Product Certification
- Influenza Y Todas Las Variantes Que La Componen
- Inexpensive Gps Modules With Pps Output With Low Jitter
- Industrial Disputes In Nigeria: The Past, Present And The Procedures.
- Infos Über Fernsehen Auf Deutsch In Ungarn
- Infografía Sobre El Arroz: Conoce Las Variedades Y Tipos
- Inflation Als Risikofaktor Für Anleiheinvestoren
- Informace Pro Klienty Zdravotních Pojišťoven
- Infrastruktur Der Einrichtung : Sozialraumanalyse im Kindergarten
- Influencer Marketing: Neue Wege Der Vermarktung