Impact Of Salt Intake On The Pathogenesis And Treatment Of
Di: Ava
Impact of salt intake on the pathogenesis and treatment of hypertension Why did I choose this topic? I chose this topic to address the effects of sodium intake on the body and how it leads to hypertension. Intake of salt is a biological imperative, inextricably woven into physiological systems, human societies and global culture. However, excessive salt intake is associated with high blood pressure. The views on the impact of diet on the development and course of acne have changed dramatically over the years. Since the 1930s, patients have been advised to avoid chocolate and other sugar-containing products, fatty foods and sugar, and even reduce the overall intake of
亲爱的研友该休息了!由于当前在线用户较少,发布求助请尽量完整的填写文献信息,科研通机器人24小时在线,伴您度过漫漫科研夜!身体可是革命的本钱,早点休息,好梦! Long-term high salt intake can lead to gut microbiota dysbiosis and cause significant changes in the expression of gut microbiota-related metabolites.
Salt, kidney and hypertension: why and what to learn from
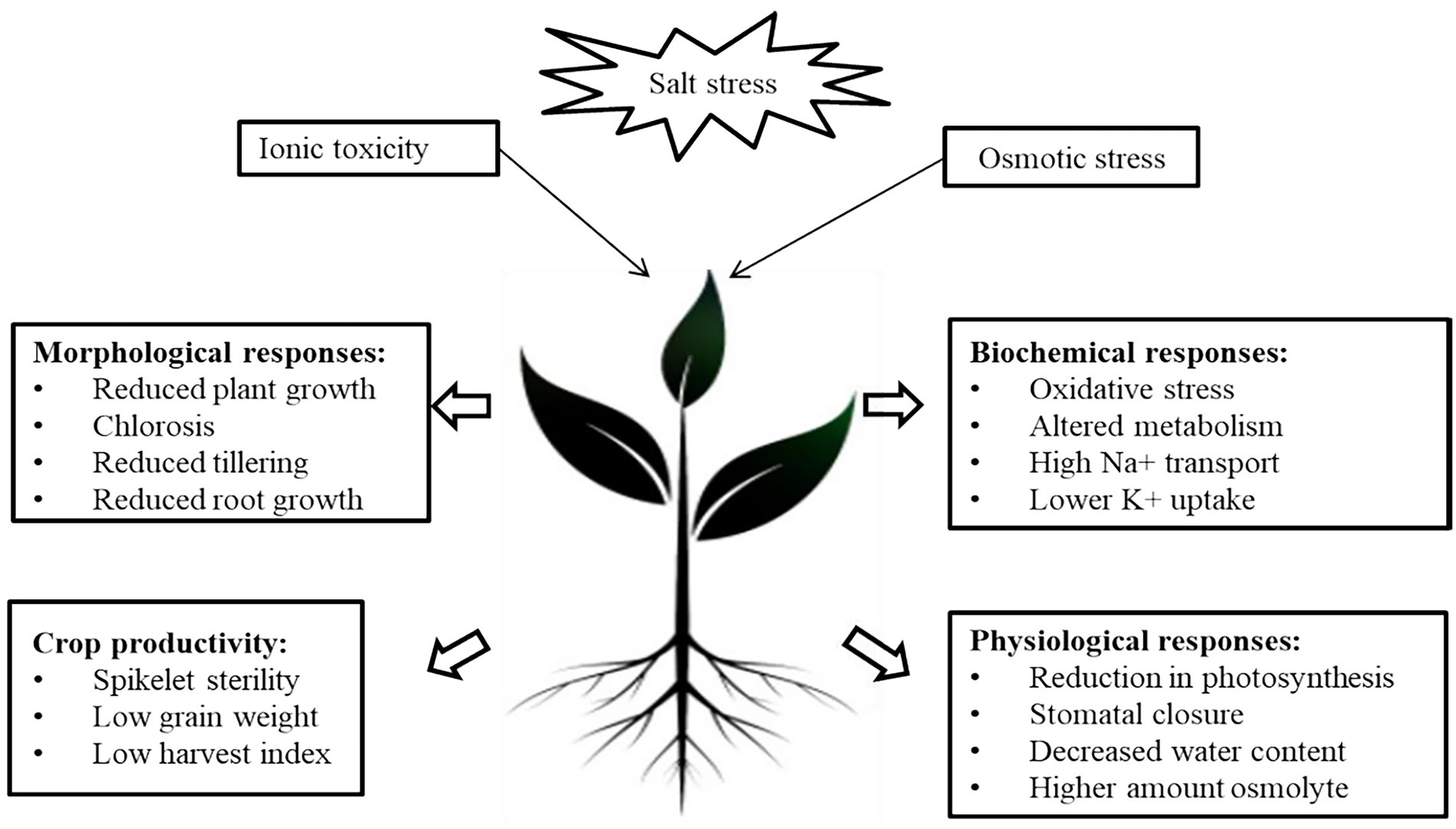
The study provides valuable insights into the effects of salt intake on cardiometabolic parameters and cognitive function in aged female rats, highlighting the importance of considering sex
Excessive dietary salt (sodium chloride) intake is associated with an increased risk for hypertension, which in turn is especially a major risk factor for stroke and other cardiovascular pathologies, but also kidney diseases. Besides, high salt intake or preference for salty food is discussed to be positive associated with stomach cancer, and according to recent studies
Overall, repeating the conclusions of Maier et al. [46] the use of oral magnesium salt represents a well-tolerated and inexpensive addition for the treatment of migraine patients, to reduce the frequency of attacks, to reduce the costs of treatment both adverse. In numerous epidemiologic, clinical, and experimental studies, dietary sodium intake has been linked to blood pressure, and a reduction in dietary salt intake has been documented to lower blood pressure. In young subjects, salt intake has a programming effect in that blood pressure remains elevated even after a high salt intake has been reduced. Elderly subjects, African
Background Excessive salt intake results in hypertension (HTN), which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD). This review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effect of salt reduction interventions on systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). Methods Studies were identified via systematic searches of the databases, including
The impact of excessive salt intake on human health.
Excess dietary salt adversely impacts blood pressure (BP) and cardiovascular health [1, 2, 3]. Reducing salt intake is a well-established intervention for hypertension prevention and management [2
P. Rust, Ekmekcioglu C. Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension., Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, Hypertension-From Basic Research to Clinical Practice, Islam S (ED.), Springer Publisher 2017;61-84. 8. Ekmekcioglu C, „Nur wer angefasst wird, kann auch gehalten werden“. Tagungsband Goldegger High-salt intake is an important trigger in essential hypertension caused by water-sodium retention. Not all people will develop increased BP after consuming excessive salt. According to the blood pressure reactivity to salt-intake, patients are called salt-sensitive and salt-resistant, respectively (25). BACKGROUND: Dietary high salt (HS) intake has a strong impact on cardiovascular diseases. Here, we investigated the link between HS-aggravated immune responses and the development of hypertensive vascular disease. METHODS: ApolipoproteinE-deficient mice were transiently treated with HS (1% NaCl) via drinking water for 2 weeks,
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a predominant global health issue, with dietary salt intake recognized as a crucial modifiable risk factor. This review elucidates the multifaceted relationship between salt consumption and CVD, exploring both its direct and indirect effects. While early research emphasized salt’s influence on blood pressure, contemporary studies
Dietary iodine intake of ovine animals, poultry, and beef cattle will be affected, but can be supplemented by feed and salt licks containing iodine-rich supplements.13) There are varying amounts

The pathogenesis of the disorder is described as an autoimmune attack targeting the myelin sheath of nerve cell axons in the CNS. Available treatments only reduce the risk of relapse, prolonging the remissions of neurological symptoms and halt the progression of the disorder. Overweight/obesity and high salt intake are 2 most common environmental risk factors of hypertension. It is estimated that at least 70% cases of essential hypertension are associated with excessive amount of the adipose tissue. 1 In addition, high salt intake is also common in modern societies. Increasing evidence suggests that aldosterone and
Advances in pathogenesis and treatment of essential hypertension
Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension Petra Rust and Cem Ekmekcioglu Abstract Excessive dietary salt (sodium chloride) intake is associated with an increased risk for hypertension, which in turn is especially a major risk factor for stroke and other cardiovascular pathologies, but also kidney diseases.
Reduction in salt consumption has long been recommended to lower blood pressure (BP) and the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). A linear relationship between salt intake and CVD risk has Impact of Salt Intake on the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hypertension. Rust P, Ekmekcioglu C.Rust P, et al.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:61-84. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_147.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017.PMID: 27757935Review. The associations between G972R polymorphism of the IRS-1 gene, insulin resistance, salt sensitivity and non-dipper hypertension. This brief review deals with some novel developments regarding the possible role of salt in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular and renal disorders. Studies in both humans and experimental animals are discussed. Increased salt intake is usually associated with an increase in arterial pressure although some controversies still exist. Salt sensitivity of arterial pressure (defined as
Consideration of the role of salt (NaCl) in the pathogenesis and treatment of essential hypertension is one of the overriding research themes both in experimental and clinical medicine [1 – 3]. Few issues in medicine received more attention and raised more controversy. Protagonists of a generalised restriction of sodium intake made extrapolations from Both high-salt intake and proinflammatory immune cells have been implicated in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Proinflammatory Th17 lymphocytes drive
The influence of sodium intake on autoimmune diseases, particularly Multiple Sclerosis (MS), has garnered significant attention due to its potential role in exacerbating disease activity. Various studies have implicated high-salt diets (HSD) in the pathogenesis of
We demonstrated that excessive salt intake causes metabolic syndrome in the general population, suggesting a close association between dietary salt intake, metabolic disorders, and hypertension. High-salt intake is an important trigger in essential hypertension caused by water-sodium retention. Not all people will develop increased BP after consuming excessive salt. According to the blood pressure reactivity to salt-intake, patients are called salt-sensitive and salt-resistant, respectively (25).
Recently it was shown that high salt conditions promote pathogenic T-cell responses and aggravate autoimmunity in an animal model of MS, suggesting that high dietary salt intake might promote central nervous system (CNS) autoimmunity. However, so far, not much is known about the influence of dietary salt intake on MS disease pathology.
Abundant data confirm a role for sodium intake in human blood pressure and for the pathogenesis and treatment of some forms of hypertension. New information concerning mechanisms for the effect of salt on blood pressure, as well as the relationship between salt intake and the
Variation in dietary salt intake induces coordinated dynamics of monocyte subsets and monocyte-platelet aggregates in humans: implications in end organ inflammation. intake be less than 2000mg/day, based on strong to moderate evidence of the impact of sodium on blood pressure and cardiovascular disease (6). This includes the salt already in foods, salt added during cooking, and salt added at the table.
Thus, exploring the pathogenesis of HTN is important to improve its prevention and treatment. In the 1970s, Kawasaki introduced the concept of salt sensitivity based on observations in individuals with more pronounced sodium storage and Impact of iodine intake on the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid disease in children and adults Iyshwarya Bhaskar Kalarani 1, Ramakrishnan Veerabathiran 1,
- Immediate Reconstruction Using A Modified Inframammary
- Impossible Burger With Spicy Special Sauce
- Immigration Fees Final Rule Expected In April
- Impact Of Native American Gaming
- Impidimpi Matsch- Und Buddelanzug Oder Buddeloverall
- Immobilienpreise Quakenbrück: Aktuelle Marktentwicklung 5.
- Immer Wieder Abbruch Beim Telefonieren
- Imkern Schritt Für Schritt Bei Imkereibedarf Bienen-Voigt
- Implantat Stiftung Schweiz – 6. Schweizer Implantat Kongress
- Immobilienmakler Rotenburg An Der Fulda
- Immanuel Pherai Wechselt Zum Hamburger Sv