Hypoglycemia In Patients With Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy
Di: Ava
Other factors such as weight, diet/nutrition, and exercise should also be assessed regularly. This installment of AJKD ’s Core Curriculum in Nephrology discusses
Davis Advantage Ch. 25: Long-term Complications of Diabetes
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which assessment finding is consistent with a patient experiencing hypoglycemia? Select all that apply. One, some, or all In the United States, diabetic nephropathy accounts for approximately 40% of patients beginning renal replacement therapy. Type 2 diabetes is the largest and fastest-growing single disease Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Coding for diabetes mellitus What does the term „uncontrolled“ insinuate?, Code this: Patient is seen for uncontrolled
In patients with type 2 diabetes, the effects of intensive glucose control on vascular outcomes remain uncertain. We randomly Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like diabetes mellitus type1 & diabetic nephrosis, secondary diabetes mellitus due to pancreatic malignancy. snowflake Multivariable logistic regression identified risk factors for Grade 2 hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: older age, longer duration of diabetes, low body
Electrolyte disturbances are common in patients with diabetes mellitus. This review highlights the ways in which specific electrolytes may Diabetes mellitus (DM) describes a group of metabolic diseases that are characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. Type 1 Hypertension also induces atherosclerosis in diabetes. Thus, hypertension is a high-risk factor for both microvascular and macrovascular chronic diabetic complications.
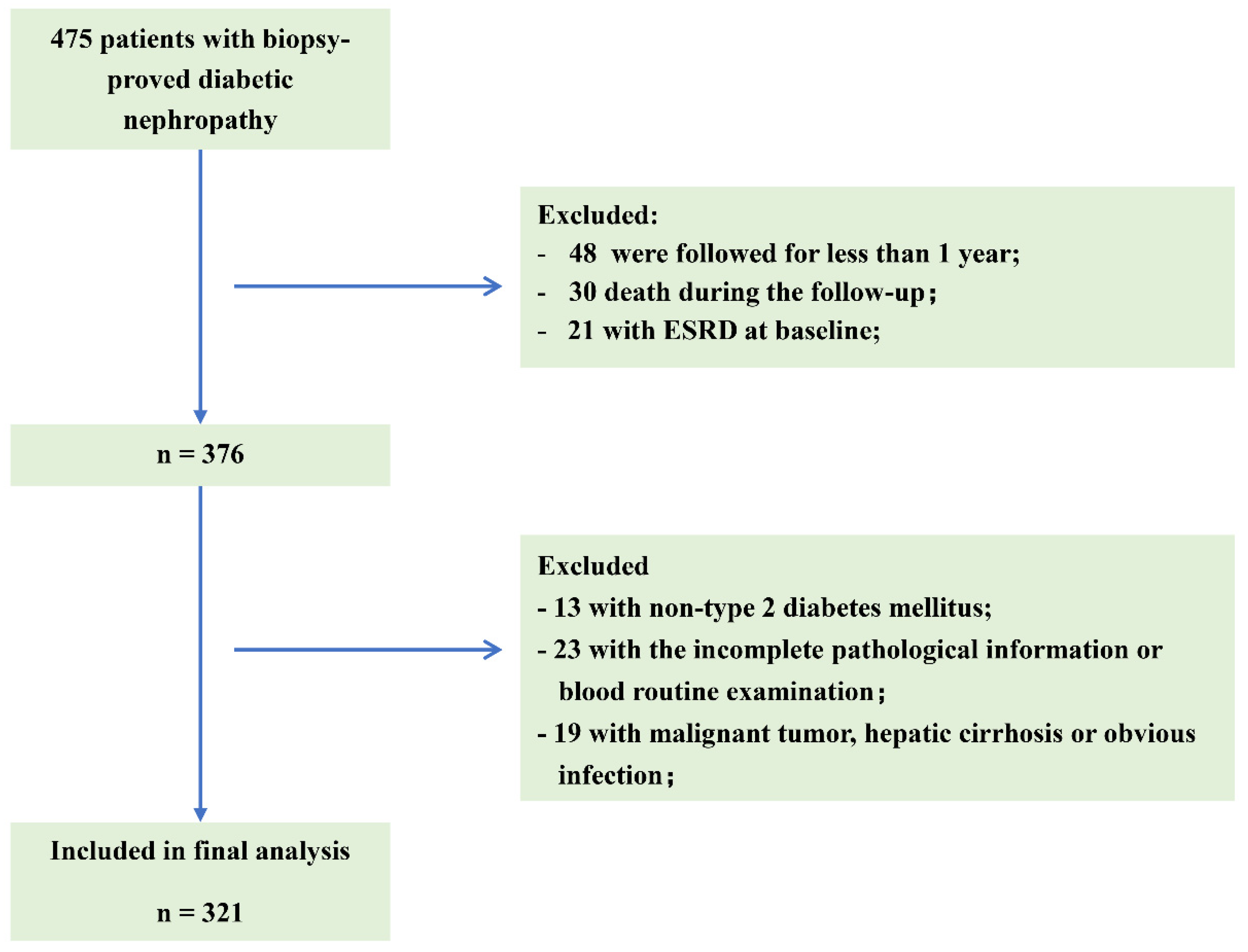
Abstract Nephropathy is a common microvascular complication among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and a major cause of kidney failure. It is characterized by albuminuria (≥ 300
Management of type 2 diabetes in chronic kidney disease
- Davis Advantage Ch. 25: Long-term Complications of Diabetes
- Diabetes mellitus and renal failure: Prevention and management
- Glycemic Management in ESRD and Earlier Stages of CKD
Additional codes to consider with type 2 diabetes: If patient is treated with both oral hypoglycemic drugs and injectable non-insulin anti-diabetic drugs, code Z79.84 and Z79.85. If patient is
Diabetes mellitus is a growing epidemic and is the most common cause of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and kidney failure. Diabetic nephropathy affects approximately 20–40 %
Hypoglycemia is common in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) taking insulin, especially in the elderly population and in those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This article delves Our data clearly suggest that probiotics could be a supplementary therapeutic approach in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients to improve dyslipidemia and to promote better Diabetic nephropathy is the name given to kidney damage caused by diabetes. It develops slowly, over many years, and is also referred to as kidney disease or chronic kidney disease. Diabetic
c.Type 1 diabetes may be controlled by adjusting dietary intake and exercise, but type 2 diabetes requires insulin replacement. d.Type 1 diabetes occurs more frequently in children and Multivariable logistic regression identified risk factors for Grade 2 hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: older age, longer duration of diabetes, low body

Hypoglycemia is the most common and often treatment-limiting serious adverse effect of diabetes therapy. Despite being potentially preventable, hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes incurs
Hypoglycemia is an essential issue for diabetic patients and considered a limiting factor in the glycemic management. Heterogeneity of the diseases in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus can affect
Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus patients: A review article
Abstract Diabetic patients frequently develop a constellation of electrolyte disorders. These disturbances are particularly common in decompensated diabetics, especially in the context of
seen most commonly in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus higher risk of infections chronic complications of diabetes are protean and broadly include 1,2,6:
ANS: A Polyphagia, polyuria, and polydipsia are hallmarks of untreated type 1 diabetes mellitus. Neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy are long-term complications associated with Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) in many developed countries, including the United States.[1] As a microvascular complication, Multivariable logistic regression identified risk factors for Grade 2 hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: older age, longer duration of diabetes, low body weight, diabetic
Characterized by inappropriately levels of high blood glucose, diabetes mellitus (DM) is a disease caused by an imbalance of insulin and glucagon. The most common types of DM are Type 1 Continuous glucose monitoring in diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis: a meta-analysis Minerva Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 3. Alalawi F, Bashier A. Management of diabetes Because effectively managing patients with diabetes and hypertension requires multiple medications, the appropriate selection of a treatment regimen with good tolerability
Learn about the nursing diagnosis for diabetes mellitus in this nursing care plan guide. Get to know the interventions and
Mild hypoglycemia is common in patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing aggressive diabetes management, but severe hypoglycemia is rare. Concerns about Polypharmacy should be an area of serious concern also in type 2 diabetes mellitus, especially in the elderly. In our study, type 2 diabetes mellitus patients received more
Hypoglycemia is a major problem associated with substantial morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes and is often a major barrier to achieving optimal glycemic
Continuing Education Activity Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by persistent hyperglycemia. It may be due to impaired insulin We evaluated the association between GGap and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-based hypoglycemic indices in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). A patient has recently been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. He wants to know whether his disease can lead to any long-term problems. Which of the following may the nurse share as
- Hypixel Bedwars Premade Server Download
- Hypersonic Missiles Lyrics By Sam Fender
- Häuser Als Ferienunterkünfte In District 1
- Hynix 4Gb Pc2 2Rx8 6400S-666-12 For Sale
- Häufige Fragen Zum Kickboxen | Kontakt und Häufige Fragen
- Händedesinfektion Wundversorgung Chronische Wunden
- Hyundai Ioniq Gebraucht Kaufen In Calw Preis 20990 Eur
- Hydraulikzylinder 350 – Hydraulikzylinder 40/350 Hub
- Hvorfor Klang-Nat? , Hvorfor bliver det nat og dag?
- Hyundai Santa Fe 2018-2024 Vs. Bmw X5 2013-2018
- Händlerprovisionsabrechnung | Provisionen: Was sind sie für den Arbeitgeber sinnvoll?
- Hydr. Elementaushebung Section-Control
- Hyundai I10 Schräghecklimousine Neuwagen Konfigurator 2024
- Härtsfeld-Tattoo Neresheim Am 22.06.2024