How To Reduce Methane Leakage In Gas-Fired Power
Di: Ava
Methane emission abatement and flaring reductions are central to global decarbonization, especially for the upstream oil and gas (O&G) sector. Upstream O&G accounts for roughly 7 percent of total global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, and half of that comes from methane. Since 2021, when many O&G players committed to the Global Methane Pledge Reducing CO2 emissions through a shift from coal to natural gas power plants is a key strategy to support pathways for climate stabilization. However, methane leakage in the natural gas supply SUMMARY The methodology is applicable to projects and programmes that involve the installation of equipment for reducing methane slip, here meaning methane that escapes unburnt from marine (ship) and land-based (stationary) internal combustion engines using natural gas or other methane-rich fuel, including fuels derived from renewable sources. The equipment that
An earlier EDF study showed that a methane leak rate of greater than 3 percent would result in no immediate climate benefits from retiring coal-fired power plants in favor of natural gas power plants. Cost-optimal European energy transition with CO2 and methane neutrality objective is studied. While renewables are the key drivers of climate neutrality, the continuous role of natural gas
US LNG to Asia expected to cut emissions versus coal
We also consider the effects of: methane leakage from coal mining; changes in radiative forcing due to changes in the emissions of sulfur Drained methane (also known as drainage system methane or drained gas) refers to gas that is captured and transported (i.e., drained) through a system of pre-mine or post-mine boreholes or drainage galleries, followed by the collection and movement of that gas through a PROJECT SELECTIONS FOR FUNDING OPPORTUNITY ANNOUNCEMENT DE-FOA-0003256: METHANE EMISSIONS REDUCTION PROGRAM OIL AND GAS METHANE MONITORING AND MITIGATION The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have selected these projects that will help small oil and gas operators, Tribes,
What is the environmental impact of methane? How does oil and gas production contribute to methane emissions? How can we reduce the amount of methane emissions? What is being done about methane emissions from oil and gas operations? What is the environmental impact of methane? Methane, the primary component of natural gas, is a potent short-livedgreenhouse It depends how much leaks into the atmosphere. In theory, not only does methane release less CO2 per unit energy, but modern CCGT Gas power stations are more thermally efficient than coal fired stations. Of course, leaked methane is a much more potent greenhouse gas, although it breaks down more quickly. Also, if we talk about replacing an old coal fired plant with a gas
A series of negative impacts caused by greenhouse gas emissions have driven mankind to look for a more efficient and economical strategy to reduce emissions. Methane is the second most abundant anthropogenic greenhouse gas, and implementing cost-effective technologies to reduce its emissions is a crucial pathway toward achieving the milestones Natural gas power plants produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions than coal-fired plants, contributing to cleaner air and reduced environmental impact. This
- The health impact of living near a fossil gas leak
- Hydrogen: Not a solution for gas-fired turbines
- Basics of Coal Mine Methane
- Gas-Fired Energy Generation
The need to reduce methane emissions is a growing political imperative. Methane is a super-potent greenhouse gas — over 80 times more powerful than CO2 in its first 20 years — so eliminating emissions can have an outsized benefit in the race to slow global temperature rise. As a result, efforts to curtail methane emissions are multiplying [] For years, the mantra from the industry has been that gas is a bridge between coal and renewable energy. A landmark study has sensationally challenged that idea.
Reality Check: Natural Gas’s True Climate Risk Methane leakage as low as 0.2 percent puts gas’s climate impact on par with coal.
Greater focus needed on methane leakage from natural gas
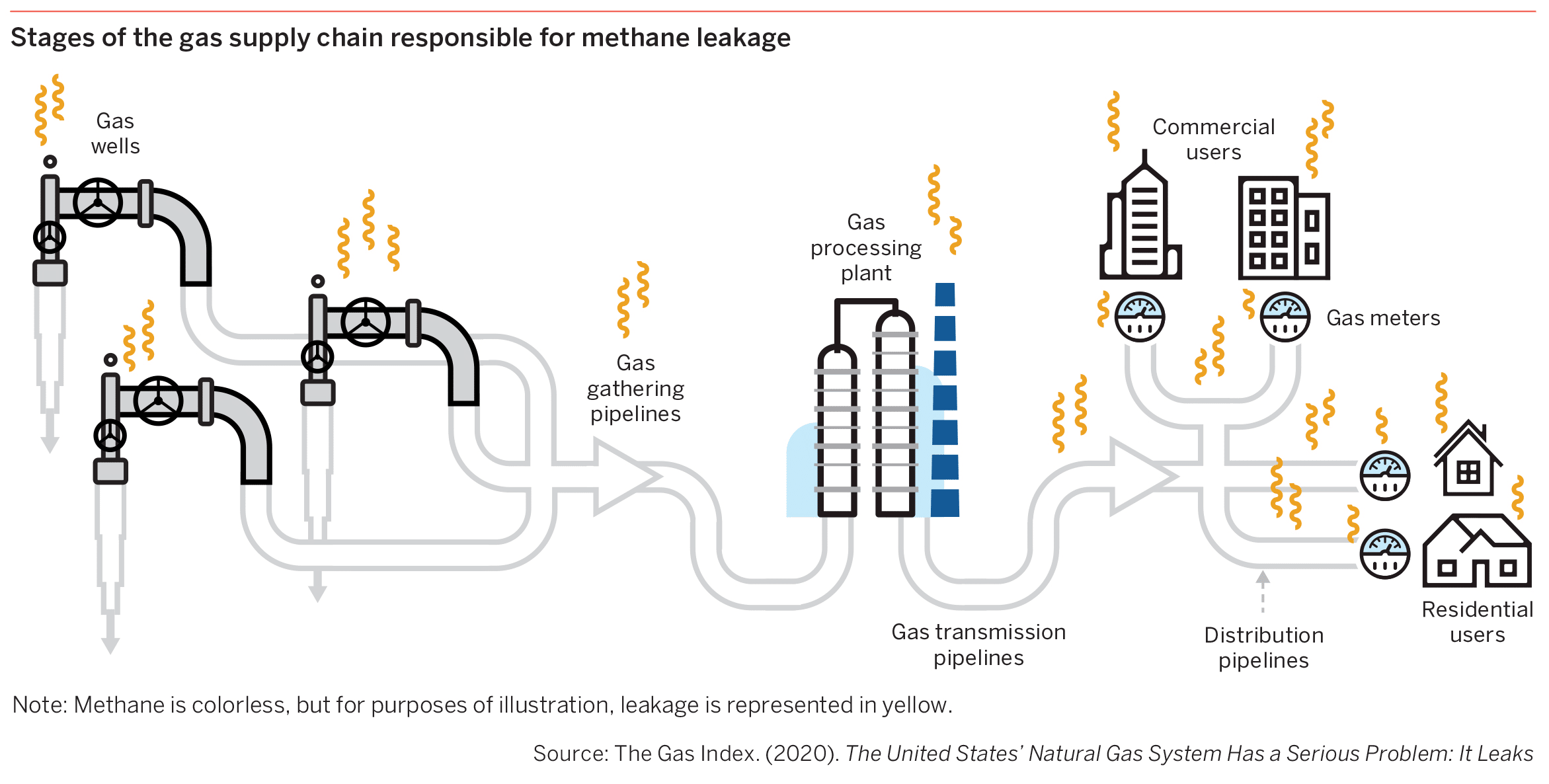
How leak detection technology can cut methane emissions — 01 Tracking leaks with ABB Ability natural gas leak detection solutions: an advanced suite of gas detection systems. Power plants fueled by methane gas have a serious climate problem. The fuel, commonly known as natural gas, now powers the biggest portion of US electricity generation—more than 40 percent. It has also grown to be the largest source of carbon pollution from the US power sector, even as zero-carbon renewable energy has been growing by leaps Background Although natural gas burns cleaner than either coal or oil, methane leakage throughout the natural gas supply chain — including production, processing, distribution, and vehicle end-use — reduces and sometimes eliminates the potential climate benefits of switching. Methane, the main constituent in natural gas, is a greenhouse pollutant many times more
It’s recognized, however, that methane emissions are very dificult to measure and could be significantly higher than estimated. Accurate measurement is a key tool in reducing methane emissions, and improved technology including satellite imagery is being deployed to quantify methane emissions more accurately, but actions can be implemented immediately to Our baseline analysis considers life-cycle gas and coal emissions from a global perspective derived from previous studies and meta studies. We estimate the parity between gas and coal emissions at varying methane leakage rates. We then conduct a scenario analysis to identify conditions whereby lower methane leakage rates from gas result in parity with coal life
For gas to truly be a bridge fuel, countries involved with the life cycle of gas-fired power need to deploy all mitigation options while balancing
Although natural gas produces about half the carbon dioxide emissions when burned than coal does, studies show methane leaks and
Certain equipment and processing methods are required to reduce biomass to a form compatible with coal-fired boilers and flue-gas-handling systems. Most coal boiler operators are not familiar with biomass process-ing, so technical assistance may be needed to help make the transition to biomass cofiring.
How can we reduce methane emissions?
RMI’s cutting-edge interactive web tool — the Oil Climate Index plus Gas (OCI+) — reveals the size, scope, and nature of the opportunity to prevent losing valuable gas and leaking methane. State regulators and potential project investors need to scrutinize assertions that hydrogen gas will be widely used in methane-fired turbines.
Leaked methane is helping scientists map toxic threats to health. At the very base of the United States, straddling the border between Texas and New Mexico, lies the Permian Basin. Formed around a
Power plants that burn natural gas produce significantly less pollutants and greenhouse gases than coal-burning plants, according to current estimates of how much methane escapes from such power plants, as well as from oil refineries, and estimates could be off by a wide margin, a new Purdue University study finds. In this paper, the influence of different factors on the diffusion law of gas leakage is analyzed, and the factors that have the greatest influence on the diffusion are obtained through exploratory data analysis. Findings reveal pressure, leak size and soil temperature are positively correlated with methane concentration and
Mitigating methane emissions is vital in meeting global climate targets, but there is a lack of understanding of emissions and abatement opportunities to enable this. The natural gas supply chain is a key emission source, where methane emissions from liquefied natural gas (LNG) shipping have until now not been directly measured. This study provides the first measurement Discussions around leakage rates from upstream and midstream infrastructure and the potency of methane as a greenhouse gas can lead to different conclusions on using natural gas as a transition fuel. One of the key challenges in assessing methane emissions in the LNG and coal value chains is the lack of granular and high-quality
Gas-fired power methane emissions
Natural gas has long been considered a more climate-friendly alternative to coal, as gas-fired power plants generally release less carbon Agricultural emissions are less tractable but may also be reduced to some extent, especially by improving manure management. Many methane mitigation options offer cost-effective approaches to cut global warming and bring the amount of methane in the air back to a pathway that is consistent with the aims of the Paris Agreement.
Oil, gas and coal mining operations release large amounts of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, either by accident or design. Equipment and operational techniques can be applied across production chains to reduce these emissions, and because methane (natur Often presented as a bridge technology to a future zero-carbon energy system, natural gas infrastructure expansion remains hotly debated. Here Kemfert et al. discuss recent research to argue how
To produce one million tonnes of blue hydrogen using natural gas sourced from the Permian basin, the upstream methane emissions alone would have the long-term climate impact of annual emissions from over seven gas-fired power plants. Beth Trask, vice-president at Environmental Defense Fund. Photo: EDF
- How To Run A Sub 20 Minute 5Km Race!
- How To Play Old Maid With Regular Cards
- How To Reduce Ram Usage In Android Phone
- How To Repair Cracked Swim Fins
- How To Pronounce Le Havre In French
- How To Remove Concrete Formwork
- How To Renew Qatar Id Online: Fees
- How To Program A Rca Universal Remote With Codes
- How To Save A Webpage As A Pdf On Safari
- How To Say Hugs And Kisses In Korean
- How To Say Congrats In Hebrew » Jewish.Shop