How To Calculate Raid Size? , RAID Performance Calculator
Di: Ava
The key to RAID’s effectiveness lies in its diverse configurations, each offering a unique blend of data redundancy and capacity utilization. RAID Levels: The Pillars of Capacity and Overhead RAID configurations, or levels, are the building blocks upon which capacity and overhead calculations rest. Powerful RAID calculator that allows you to quickly and correctly calculate the usable capacity for the RAID of your choice.
Online RAIDz calculator to assist ZFS RAIDz planning. Calculates capacity, speed and fault tolerance characteristics for a RAIDZ0, RAIDZ1, and RAIDZ3 setups.
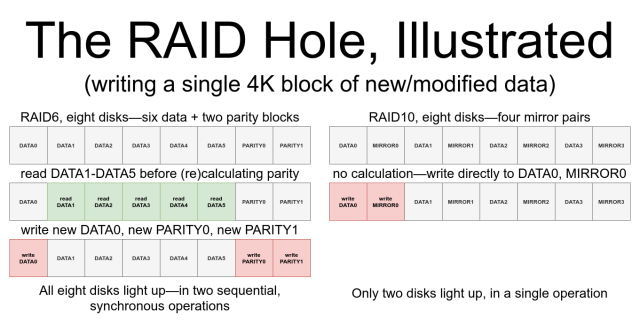
Use our RAID Performance calculator and choose the best RAID level for storage performance, capacity, and fault tolerance. Try it now for free!
RAID Storage Capacity Calculator
This RAID calculator computes array characteristics by calculating the disk capacity, number, and type of the array. For RAID5, add the size of one HDD per RAID Group plus around 10% for Windows overhead. A RAID Group typically consists of all of the data drives plus the parity drive (s) in one RAID chassis but there are occasions where
Raid Points are a mechanic used to determine the size of raids, other major threats, quests, and certain other events. Summary Raid Points are spent by the storyteller to purchase raiders. Each raider has a „cost“, or Combat Power, associated with them. Every 1 raid point roughly equates to 1 combat power. For example, if the storyteller has 180 raid points, See also: RAID Types Overview File / Disk Size Converter RAID Performance Calculator ZFS / RAIDZ Capacity Calculator NetApp Usable Space Calculator DWPD, TBW, PBW, GB/day Calculator Want to create a RAID but not sure on where to start? Learn more and use our Raid Calculator to figure out the size & quantity of hard drives you’ll need.
Disk Raid and IOPS Calculator Expedient’s Disaster Recovery as a Service solutions have been recognized in the Gartner Magic Quadrant for DRaaS and offer fast, total network failover without IP and DNS changes. Inputs: RAID type – Supported RAID levels are: Mirror (two-way mirror – RAID1 / RAID10 equivalent); RAID-Z1 (single parity with variable stripe width); RAID-Z2 (double parity with variable stripe width); RAID-Z3 (triple parity with variable stripe width). Drive capacity – we expect this number to be in gigabytes (powers of 10), in-line with the way disk capacity is marked by the
I’d like to create a parity storage space in Windows 10 with a 5 tb disk and two 3 tb disks. Is there a way to calculate how much usable space this will give me? RAID 5 Usable Capacity Calculator Total Number of Drives: Drive Size (GB): Calculate To calculate the usable capacity of a RAID 5 array, you need to consider the following factors: Number of Drives (N): This is the total number The Failures to tolerate has an important role when you plan and size storage capacity for vSAN . Based on the availability requirements of a virtual machine, the setting might result in doubled consumption or more, compared with the consumption of a virtual machine and its individual devices. For example, if the Failures to tolerate is set to 1 failure – RAID-1 (Mirroring)
- Drive Capacity Calculator
- NetApp Usable Space Calculator
- Raid 5 Capacity Calculator
- "Short" and sweet guide to managing raid sizes
RAID 5 and 6 offer a balance of redundancy and capacity, and RAID 10 combines the benefits of RAID 1 and RAID 0. This calculator helps users to easily determine the usable storage capacity in various RAID configurations, making it This IOPS Calculator is used to calculate the performance and capacity of disk drives, disk arrays and SSD arrays. Based on the parameters of drives, their quantity in the array, RAID level and nature of workload calculates the number of average
RAID Performance Calculator
RAID Calculator is a simple app for determining approximate capacity, speed, and fault tolerance of different RAID configurations. To calculate the storage capacity of a RAID 5 array, we need to consider several factors, such as the number of drives and their sizes. Press enter or click to view image in full size
RAID Calculator The RAID calculator is a straightforward tool designed to help you understand and calculate various RAID configurations. Whether you’re planning a new storage setup or optimizing an existing one, the RAID storage calculator provides the information needed to make informed decisions about your storage solution. This tool is particularly useful for evaluating Breaking Down the Storage Calculation Now that we’ve covered the key variables, here’s the core formula for estimating usable storage capacity: Let’s walk through an example cluster to determine its usable capacity. Example 1: 8-Node AV36P Cluster Each AV36P node has 19.2TB of raw capacity (you can find raw capacities for all node types here). To make
But not everyone has drives of the same size so it helps understanding how to calculate it, particularly since the RAID calculator is limited to 16TB for now (I’m sure it will be updated soon). Our RAID calculator helps you calculate the usable space on your storage drives based on different RAID configurations, such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, etc.
RAID 5 (Redundant Array of Independent Disks, Level 5) is one of the most popular solutions for achieving this balance. To help users plan and configure RAID 5 arrays effectively, the RAID 5 Capacity Calculator provides a quick way to determine usable storage based on the number of drives and their individual sizes.
Please note The QNAP RAID Capacity Calculator estimates the storage utilization of various drive configurations and RAID levels on QNAP NAS. Actual drive storage space will vary based on the system space capacity and drive manufacturer. The estimated result may differ from the actual storage space. Refer to the QTS Storage & Snapshots Manager for the actual space allocation Calculation Formula The usable storage capacity of a RAID array depends on the RAID level chosen and the number of disks in the array: RAID 0: Total capacity is the sum of all disk capacities. No redundancy. \ [ \text {Usable Storage} = N \times \text {Disk Size} \] RAID 1: Total capacity is half of the sum of all disk capacities.
The RAID 6 Calculator on our site helps you plan your storage with confidence by giving you fast, accurate results based on the number and size of your disks. This article will walk you through how to use the tool, offer real-world examples, and answer the most common questions users have about RAID 6 storage planning. What is the RAID Drive Calculator? The RAID Drive Calculator is a user-friendly online tool designed to calculate the total usable storage available in a RAID array. It takes into account: The number of drives in the array The size of each individual drive (in terabytes) The RAID level selected By entering these parameters, the calculator outputs the effective storage capacity
By providing realistic estimates, the calculator helps manage expectations and prevent potential shortfalls in storage capacity planning. Formula of Drive Capacity Calculator Calculating usable drive capacity involves considering formatting overhead and, for RAID arrays, the specific configuration’s redundancy scheme. 1. Single Drive This calculator computes usable space for NetApp FAS storage system based on the disk size and aggregate configuration parameters. Supported RAID levels are RAID 4, RAID-DP and RAID-TEC.
Please note The QNAP RAID Capacity Calculator estimates the storage utilization of various drive configurations and RAID levels on QNAP NAS. Actual drive storage space will vary based on the system space capacity and drive manufacturer. The estimated result may differ from the actual storage space. Refer to the QTS Storage & Snapshots Manager for the actual space allocation The RAID calculator enables you to input individual drive sizes and the number of drives, calculating the usable storage after accounting for redundancy. This estimation helps you understand if you have enough disk space for your needs or if
- How To Calculate The Time 16 Hours From Now
- How To Build A Bashed Patch? _ Maximize Skyrim’s Potential With Wrye Bash
- How To Check If A String Contains A Substring In Bash Script
- How To Clean Out Candle Jars: 3 Ways
- How To Aim A Bell Expressvu Dish
- How To Change Key Functions On Your Keyboard
- How To Change New Mail Desktop Alert Settings?
- How To Clear Cookies On Samsung Galaxy A52S 5G
- How To Apply Ai Effectively For Sales Enablement
- How To Auto Generate Regex From Given List Of Strings?
- How To Color Cell Based On Text Criteria In Excel
- How To Be Antisocial | How to Stop Being Antisocial and Build Social Skills
- How To Assemble And Decorate A 3 Tier Cake
- How To Change The Language In Ps5
- How To Cancel Segpay Subscription: A Step-By-Step Guide