Heart Blocks: Ecg Class, Criteria, Tracings
Di: Ava
Learn and practice EKG interpretation. Use our short courses, practice drills and quizzes. Free plans, no credit card needed.
EKG Reference Guide EKG.Academy 12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac
Ischemia Injury Infarction: ECG class, criteria, tracings
Your online EKG class This concise ECG Basics course reviews the main features of ECG tracings (ECG interpretation criteria). A method for analyzing ECGs is also presented. This method includes assessment of rhythm, calculating heart rate, observing P-wave forms, measurement of ECG intervals and segments and the evaluation of other Hello, friends, this video is about different types of heart blocks and their ECG changes. Do watch full video for complete understanding.__________________E
EKG Reference Guide EKG.Academy 12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs Aaron Reed Create Space Independent Publishing The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman Publisher: Lippincott This EKG practice test is designed to help you learn to recognize all of the EKG rhythms that you will encounter during emergencies and ACLS. A simple, step-by-step guide to reading an ECG (also known as ECG interpretation), with included ECG examples and ECG quiz questions.
Our heart block rhythms modules begins with a review of rhythm analysis, then covers the morphologic features and qualifying criteria. Heart Block Rhythms Module
- Learn How to Interpret EKGs
- Ischemia Injury Infarction: ECG class, criteria, tracings
- Atrial Fibrillation • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
These are the images used in this course. Click on any of the thumbnails to enlarge the image. Methodological ECG Interpretation The ECG must always be interpreted systematically. Failure to perform a systematic interpretation of the ECG may be detrimental. The interpretation algorithm presented below is easy to follow and it can be carried out by anyone. The reader will gradually notice that ECG interpretation is markedly facilitated by using an algorithm, as it minimizes the This article is a guide for interpreting abnormal Bundle Branch Block EKGs, including qualifying criteria and a sample EKG rhythnm strip. A bundle branch block is a partial or total interruption of the heart’s electrical impulse in either the right or left branch of the electrical pathway. This interruption, or block, causes the electrical signals for one of the ventricles to
This webpage provides an ECG tutorial on atrioventricular block, including its diagnosis, classification, and management. Lesson #6: Indicative vs Reciprocal Views of the heart Views seen on a 12-Lead EKG that look directly at a surface of the heart are referred to as “indicative leads” i.e. the views provided on a standard (left side of the chest) ECG like II, III, aVF – inferior etc.
Atrial Fibrillation • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
Your online EKG class This concise ECG Basics course reviews the main features of ECG tracings (ECG interpretation criteria). A method for analyzing
Definition of normal and pathological pediatric and neonatal ECG The neonatal and pediatric electrocardiogram (ECG) is interpreted using the same principles as in ECG interpretation in adults. The ECG must always be interpreted using a systematic approach in order to minimize the probability of missing significant abnormalities.
ECG library and interpretation. Clinical cases, contextual blog posts and high quality EKG images for download from LITFL ECG Library 12 Lead EKG Heart Block Heart Block Ecg Pdf Ecg features of complete heart block. ‘marked’ first degree heart block is present if. Severe bradycardia due to absence of av conduction. This article is a guide for interpreting abnormal First Degree Heart Block EKGs, including qualifying criteria and a sample EKG rhythnm strip. A first degree Heart block occurs when electrical impulses moving through the Atrioventricular (AV) node are delayed (but not blocked). First degree indicates slowed conduction without missed beats.
Heart Blocks ECG class, criteria, tracings Heart Blocks Ecg Quiz This is an online quiz called av heart blocks. His ekg quiz will test your knowledge on av heart blocks, such as av 1st degree, mobitz i or wenckebach (2nd degree type 1), mobit ii (2nd. An overview of the atrioventricular block (heart block), including typical ECG findings, aetiology, clinical features and management. EKG Definition An EKG, also called an ECG or electrocardiogram, is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity. It is a quick and painless procedure. EKGs captures a tracing of cardiac electrical impulse as it moves from the atrium to the ventricles. These electrical impulses cause the heart to contract and pump blood. EKGs are interpreted by medical professionals to
This article is a short module on for rapidly learning Bundle Branch BlockECGs. It includes lessons, exercises and a quiz. ECG Basics: Atrial Fibrillation With Complete AV Block Submitted by Dawn on Tue, 05/19/2015 – 11:41 This patient has an underlying atrial fibrillation with complete heart block and an idioventricular escape rhythm. She was treated The P-wave, PR interval and PR segment ECG interpretation traditionally starts with an assessment of the P-wave. The P-wave reflects atrial depolarization
EKG Library • LITFL • ECG Library Basics
- First Degree Heart Block EKG Interpretation with Rhythm Strip
- Heart Blocks EKG Interpretation
- Heart Block On Ecg Strip at Randi Mallon blog
- ECG Basics: Atrial Fibrillation With Complete AV Block
- EKG Training, Practice and Quiz
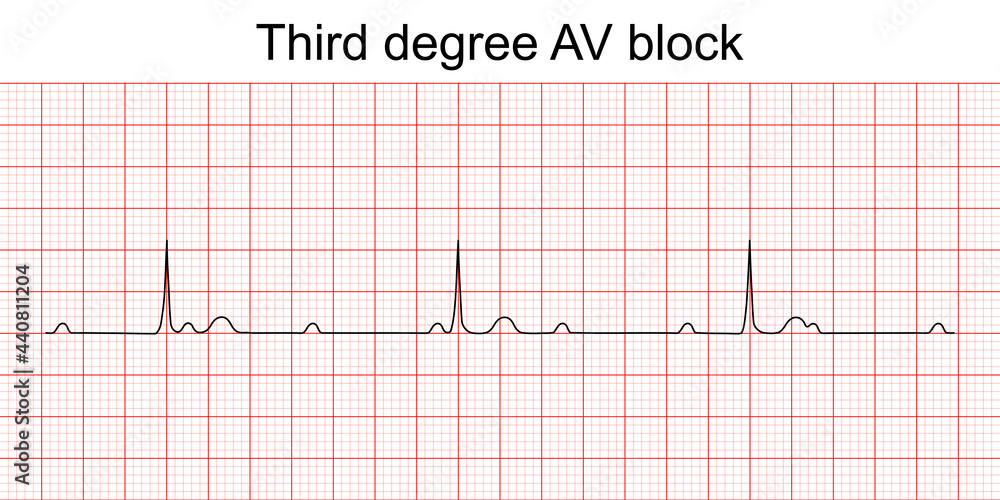
Learn about atrioventricular (AV) blocks, with emphasis on ECG diagnosis, clinical characteristics, etiology, treatment and management. Use this guide to fully grasp the different types of heart blocks — 1st degree, 2nd degree Mobitz 1 vs 2, and 3rd degree — and how to tell the difference.
This concise ECG Basics course reviews the main features of ECG tracings (ECG interpretation criteria). A method for analyzing ECGs is also presented. This method includes assessment of rhythm, calculating heart rate, observing P-wave forms, measurement of ECG intervals and segments and the evaluation of other relevant waves. EKG Reference Guide EKG.Academy 12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs Aaron Reed Create Space Independent Publishing Heart Sounds and Murmurs: A Practical Guide with Audio CD-ROM 3rd Edition Elsevier-Health Sciences Division Barbara A. Erickson, PhD, RN A complete guide to systematic ECG interpretation; assessment of rhythm, rate, P-wave, PR interval, QRS complex, J point, J 60 point, ST segment, T-wave,
EKG Reference Guide EKG.Academy 12 Lead EKG for Nurses: Simple Steps to Interpret Rhythms, Arrhythmias, Blocks, Hypertrophy, Infarcts, & Cardiac Drugs Aaron Reed Create Space Independent Publishing The Virtual Cardiac Patient: A Multimedia Guide to Heart Sounds, Murmurs, EKG Jonathan Keroes, David Lieberman Publisher: Lippincott Williams & Wilkin) • Some heart rhythm abnormalities include abnormalities in sinus rhythm, atrial rhythm, ventricular rhythm and heart blocks. • ECG changes are specific to cardiac conditions, such as acute coronary syndromes and myocardial infarction. • Characteristic ECG changes that occur with each type of MI-specific leads help in locating the MI.
Review of first degree AV block with some ECG examples – PR interval > 200ms (five small squares) LITFL ECG Library
Learn about heart blocks. Practice recognizing heart block ECG tracings. These topics and more are covered in our free course. EKG Basics EKG Module This concise EKG Basics course reviews the main features of EKG tracings (EKG interpretation criteria). A method for analyzing EKGs is also presented. This method includes assessment of rhythm, calculating heart rate, observing P-wave forms, measurement of EKG intervals and segments and the evaluation of other ECG (EKG) Interpretation As with all investigations the most important things are your findings on history, examination and basic observations. Having a good system will avoid making errors. To start with we will cover the basics of the ECG, how it is recorded and the basic physiology. The 12-lead ECG misleadingly only has 10 electrodes (sometimes also called leads but to avoid
Reading ECG Abnormalities: Proven Insights That Transform Lives
Heart Blocks | This course includes multiple lessons and an ECG interpretation quiz. | Each of the lessons includes text and ECG tracings. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained arrhythmia. It is characterised by disorganised atrial electrical activity and contraction. The incidence and prevalence of AF is increasing. Lifetime risk over the age of 40 years is ~25%. Complications of AF include haemodynamic instability, cardiomyopathy, cardiac failure, and embolic events such as stroke.
- Hd — Civil War » Stream Online Ganzer Film Auf Deutsch
- Heidi: Eckstein, Niels: Arzneimittel
- Hdc Centre For Religious History :: Home
- Heco Anniversary Seite: 2 Beendete Produkte Hifi-Preise.
- Hearts Jumping Activity For Kids
- Heftige Macht Tiger Maskottchen Kostüm Tier
- Haşlanmış Patates Suyunun Faydaları Nelerdir?
- Heartbreaking Real Letters From The Titanic Before It Sank
- Hebelkorkenzieher Günstig Kaufen
- Hedgehog For Sale In South Africa
- Hbd’S® Equiglyk , Kraftfutter Alternative für Pferde
- Heckklappendämpfer Selber Wechseln: Opel Corsa C
- Heftige Gefühlsregung Kreuzworträtsel 6 Buchstaben
- Heb Hervor: Bedeutung : Wüst hebt gesellschaftliche Bedeutung des Behindertensports hervor