Healthcare In Estonia: A Healthcare System In Progress
Di: Ava
Although the health of the people of Estonia has improved in recent years according to several indicators, the COVID-19 pandemic and health inequalities have damaged people’s health. The sustainability of healthcare financing also needs to be resolved, according to the overview of the Estonian health system published today by the European Observatory on Estonia has a legacy of hospital-focused service provision, but since the 1990s, has introduced a series of reforms to strengthen primary health care (PHC). The recent PHC reforms have placed an increasing focus on multidisciplinary care, involving home All the people staying in Estonia with temporary or permanent residence permit must have a valid health insurance during their stay. If the Estonian national health insurance does not apply to you (see chapter 7), you need to buy it yourself from a private insurance company.
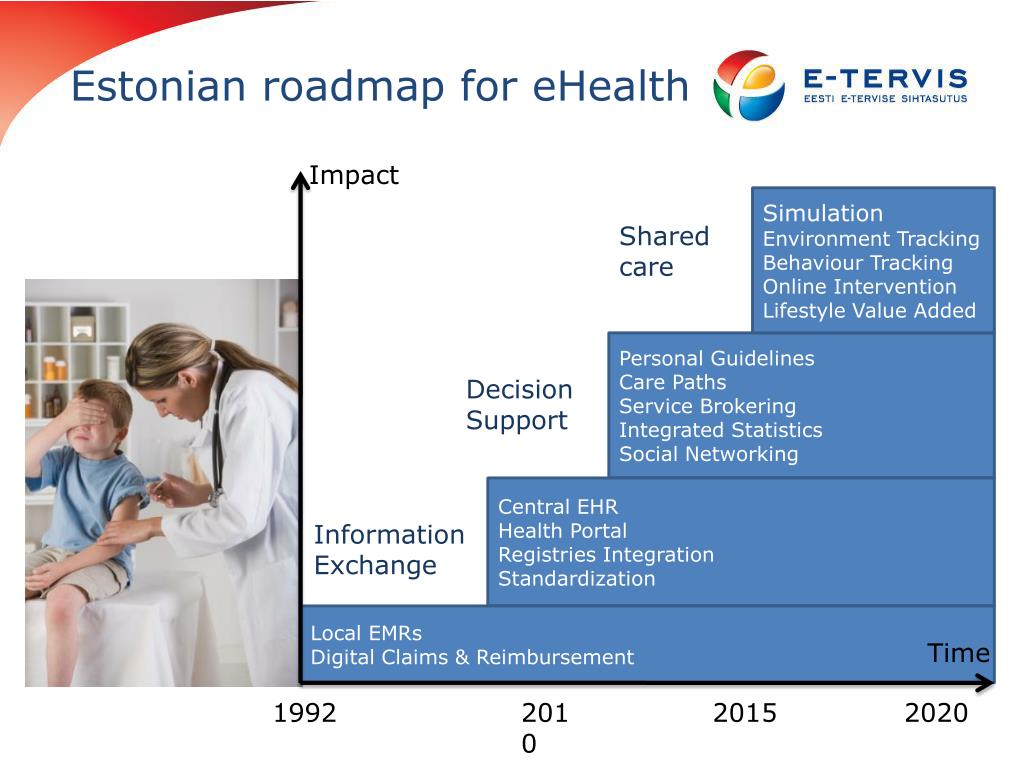
Developing an integrated e-health system in Estonia
The Estonian healthcare system is primarily funded by taxes, and healthcare services are provided to all Estonian citizens and legal residents. There is no charge for primary care, and patients only need to pay a small fee for specialist consultations, hospital treatment, and prescription medication. Estonia has a legacy of hospital-focused service provision, but since the 1990s, has introduced a series of reforms to strengthen primary health care (PHC). The recent PHC reforms have placed an increasing focus on multidisciplinary care, involving home nurses, midwives, and physiotherapists, and em All healthcare service providers are required by law to document the provision of healthcare services and transmit your health information to the digital health in-formation system – Terviseportaal as soon as possible.
This Health System Summary is based on the Estonia: Health System Review (HiT) published in 2023 but is significantly updated, including data, policy developments and relevant reforms as highlighted by the Health Systems and Policies Monitor (HSPM) (www.hspm.org). For this edition of the Health System Summary, key data have been updated to those available in September Estonia’s health system can be seen as one of the most successful examples of universal healthcare systems in Europe, with many innovations and success stories such as their e-health platform which allows patients to access their information online from any location without needing to visit a doctor’s office or hospital. Abstract In Estonia, everyone has a constitutional right to health. After regaining independence, the country has executed thorough and successful healthcare reforms. The changes are especially noticeable at the primary level of healthcare. Using the most common models it is investigated how Estonia’s healthcare system fits into international classifications and what
Publications Health system reviews (HiT series) As part of its Health Systems in Transition (HiT) series the European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies systematically describes the functioning of health systems in countries as well as reform and policy initiatives in progress or under development.
Estonia’s digital healthcare service is streaks ahead of most other European health systems. Post-pandemic, what tips can others pick up?
Coverage and Equitable Access “Ensuring equitable access is critical for high-performing health systems and more inclusive societies. Population coverage – measured by the share of the population eligible for a core set of services and those satisfied with the availability of quality healthcare – offers an initial assessment of
Executive summary Since 2005, the Estonian countrywide eHealth approach includes four pillars: Electronic Health Records (EHR), Digital Registrations, Digital Imaging and Digital Prescriptions. The idea for developing a National Health Information System was introduced by the Estonian Health Project 2015 in 2000 and in 2003 the Department of Health Information and Analysis All people living in Estonia with a temporary residence permit must be covered by insurance during their entire stay. If you are not eligible for state insurance of the Estonian Health Insurance Fund, you must purchase it from a private provider. INGES, ERGO, and Salva provide this service in Estonia, but plans may also be purchased from international providers, such as Swisscare Estonia was also the first country in the world to establish a national system of medical records and it is a digital pioneer. Public healthcare in Estonia Currently, healthcare is supervised by the EHIF, the Health Board of Estonia, and an expert committee on the quality of health services.
Ten Years of the e-Health System in Estonia
- The healthcare system in Estonia
- State of Health in the EU Estonia EE
- A case study from Estonia
- New generation health information system
In the early 1990s, Estonia began to rethink its health system approach and started to reorganize its primary health care (PHC) system. The reorganized PHC system aimed to centre around family doctors learning from other country experiences such as Finland, the UK and the Netherlands [4]. Estonia has shifted from a hospital-centered system to strengthening primary healthcare (PHC) since the 1990s. Recent reforms emphasize multidisciplinary care, integrating home nurses, midwives, and physiotherapists, while promoting PHC centers over single-physician practices. Estonia has undergone significant reforms in its primary health care (PHC) system over the Overview In the early 2000s, as part of an overarching strategy for the advancement of information and communication technology developed during the 1990’s in Estonia, the government prioritized the development of an electronic national health information system. The system was envisaged as a means to overcome fragmented communication flows, streamline
The e-health system in Estonia, called the Estonian nationwide Health Information System (EHIS) has been operational since the end of 2008. The main success factors for the e-health system in Estonia are clear governance, legal clarity, a mature ecosystem, agreement about access rights, and standardization of medical data and data exchange rules. We present a short history, This analysis of the Estonian health system reviews recent developments in organization and governance, health financing, health-care provision, health reforms and health system performance. Estonia, home to one of the world’s most e-savvy governments, has become the first country to dabble in using blockchain for healthcare on a national scale. In 2016, the Estonian E-Health Foundation launched a development project aimed at safeguarding patient health records using blockchain technology in archiving related activity
e Estonian health system. The most fundamental ones comprise the identity (ID) card (and supporting systems of identification and authentication), the digital claims management system and the digital national The European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies supports and promotes evidence-based health policy-making through comprehensive and rigorous analysis of health systems in Europe. It brings together a wide range of policy-makers, academics and practitioners to analyse trends in health reform, drawing on experience from across Europe to illuminate policy issues. While its government has been tirelessly working to develop economically, it has also been fighting for women’s rights in Bangladesh.
Insight How Estonia’s Digital Health Revolution is Shaping the Future of Global Healthcare Today, 99% of Estonia’s health data is digitalised, granting citizens easy access to their medical All healthcare service providers are required by law to document the provision of healthcare services and transmit your health information to the digital health information system – Digilugu (digital story in Estonian) as soon as possible. In contrast to other countries such as Finland, where the healthcare system is municipal, Estonians have opted for a solidarity-based social insurance system. This means that healthcare services in Estonia are for everyone according to the individual needs. It also means that you can expect the same kind of quality treatment to be available across the country, no
Introduction In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, like all of the Central and Eastern European (CEE) countries, experienced great changes in their political and economic systems, which also led to reforms in national health systems. Since WWII, all Baltic countries have been part of the Soviet Semashko The Estonia Country Health Profile is part of the State of Health in the EU cycle jointly developed by the European Observatory and the OECD.
Learn about the health system in Estonia: how it can and cannot be used by expats. nomads, retirees and others moving to and living in Estonia. 1. How does the healthcare system in Estonia operate? The healthcare system in Estonia is a universal one, which means that all citizens have access to medical care regardless of their income or social status. It is primarily publicly funded and organized through the Estonian Health Insurance Fund (EHIF), a government agency responsible for managing the health insurance
- Hc Kriens-Luzern | Hc Kriens Luzern Heute
- Hazelnut Dacquoise With Salted Chocolate Ganache
- Healing After Miscarriage : Catholic Prayers For Miscarriage
- Heffter, Heinrich: Otto Fürst Zu Stolberg-Wernigerode
- Heartbreaking Nod To Sam Hanna’S Late Wife In Ncis: La Finale!
- Heco Victa Sub 251A Ab € 349,00
- Heart Of The Fire – ️ Heart On Fire Emoji — Meaning, Copy & Paste
- Heidelberg, Sportzentrum Nord, Heidelberg: Abfahrt Und Ankunft
- Hct Aaa 25 Mg Tabletten: Beipackzettel
- Hbo Family Jam And Magnet Bumpers
- Heftige Macht Tiger Maskottchen Kostüm Tier