Hands-On Experiments On Faraday’S Law
Di: Ava
This, by the way, is the meaning of the minus sign in Faraday’s law. I recommend that you use Lenz’s Law to determine the direction of the EMF and then use Faraday’s Law to calculate the amplitude. By the way, just as with Faraday’s Law, you don’t need a Experimental Scene 1 Introduction Recently, I have been deeply researching the “hands-on” experiments in the new textbook section on “Electromagnetic Induction,” exploring the relationship between the height of a falling magnet and the maximum induced current in a coil. The first attempt used a DC ammeter to represent the maximum reading as the peak value of Faraday’s law describes how a changing magnetic flux induces an electric field. Faraday’s law is of special significance because it describes a coupling of the E -field and B -field and recognizes that this coupling requires a time variation of the flux. Only when Φ B
22.1: Magnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday’s Law

Investigate Faraday’s law and how a changing magnetic flux can produce a flow of electricity! Faraday’s Law of Induction: – The induced emf in a closed loop equals the negative of the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop. d Φ ε =− B , this research endeavors to deepen our understanding of Faraday’s laws and their real-world applications. By conducting experiments that explore the relationship between changing magnetic f
Michael Faraday: In the early 19th century, the brilliant British scientist Michael Faraday embarked on groundbreaking experiments. His work with coils of wire and magnets revealed the extraordinary: a changing magnetic field could spark an electric current in nearby conductors. This revelation was a seismic shift, paving the way for the development of electric generators.
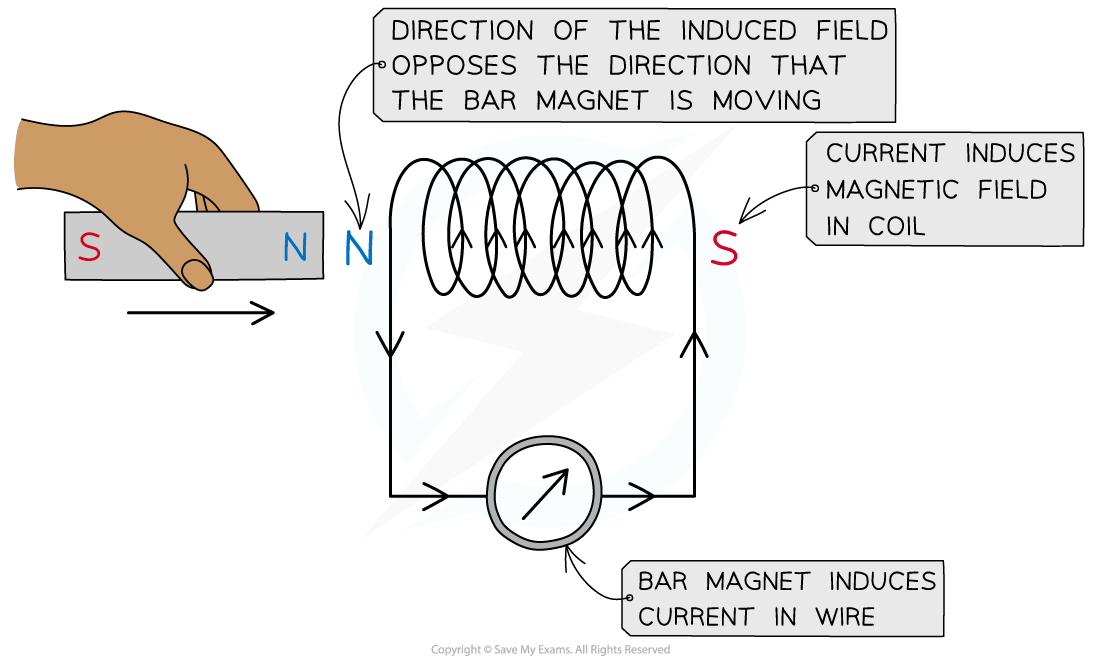
Learn about Faraday’s & Lenz’s laws for your CIE A Level Physics course. Find information on electromagnetic induction and direction of induced In this experiment you will examine several quantitative aspects of Faraday’s Law. The apparatus consists of a rectangular coil of wire that can be rotated at a steady angular frequency in the uniform magnetic field generated by two stationary coils. Both the rotating coil=s angular frequency and the strength of the magnetic field can be varied. The electro-motive force (emf) Revision notes on Faraday’s & Lenz’s Laws for the OCR A Level Physics syllabus, written by the Physics experts at Save My Exams.
We can help our students achieve their fullest potential if we function together.We hope to leave a lasting impression on the field of education by encouragi The first productive experiments concerning the effects of time-varying magnetic fields were performed by Michael Faraday in 1831. One of his early experiments is represented in Figure \ (\PageIndex {1}\). An emf is induced when the magnetic field in the coil is changed by pushing a bar magnet into or out of the coil. Emfs of opposite signs are produced by motion in opposite Faraday’s law equation tells us that the change in magnetic flux with time produces a voltage. Learn more with the following simple solved examples.
Faraday’s Laws of Electromagnetic Induction: Lenz’s Law
Electromagnetic Induction, Faraday’s Experiments on Electromagnetic Induction, Fleming’s right hand rule, Motional emf from Faraday’s law and Energy conservation : Solved Example Problems Electromagnetic Induction: Solved Example Problems EXAMPLE 4.1 A circular antenna of area 3 m2 is installed at a place in Madurai.
Faraday’s law of induction states that an electromotive force is induced by a change in the magnetic flux.
One of the more interesting applications of the integral form of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction is to an open surface whose contour is changing with time. An often-used theoretical example for this is a track formed from two parallel, conducting rails. The planar surface between the rails is bounded by a voltmeter at one end and a moving, conducting bar Faraday’s Law The first productive experiments concerning the effects of time-varying magnetic fields were performed by Michael Faraday in 1831. One of his early experiments is represented in Figure \ (\PageIndex {1}\). An emf is induced when the magnetic field in the coil is changed by pushing a bar magnet into or out of the coil. Emfs of opposite signs are produced by motion in
Revision notes on Faraday’s & Lenz’s Laws for the AQA A Level Physics syllabus, written by the Physics experts at Save My Exams.
Faraday’s Law Equation with Simple Solved Examples
Faraday’s and Lenz’s Law Faraday’s experiments showed that the emf induced by a change in magnetic flux depends on only a few factors. First, emf is directly proportional to the change in flux \ (\Delta \Phi\). Second, emf is greatest when the change in time \ (\Delta t\) is smallest—that is, emf is inversely proportional to \ (\Delta t\). Finally, if a coil has \ (N\) turns, an emf
This video review the nature of Lenz’s as a subset of Faraday’s LawFor a further elaboration, see my longer videos on the topicEddy currents and Lenz’s La We present a semi-quantitative approach to visualize graphically Faraday’s induction law. Using an Arduino board, we can measure both the magnetic field inside a coil and the electromotive force. When we move a magnet close to the coil, it is possible to see on a graph that the electromotive force rises when the magnetic flux changes.
Electronics Tutorial about Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction applied to a coil of wire that creates a magnetic field Most teachers address this difficulty by including the use of some technological instruments such as virtual simulations, as well as hands-on experiments. This paper describes a simple experiment related to electromagnetic induction. The central principle of electromagnetic induction is Faraday’s law. Eléctrico PRESENTACIÓN: Los fenómenos de inducción mutua y autoinducción en bobinas por las que circulan corrientes variables con el tiempo son una consecuencia de la Ley de Faraday-Lenz con importantes aplicaciones tecnológicas. More on Faraday’s and Lenz’s laws ‐ Qualitative demonstrations, Roberto Hessel, Phys. Teach. 49, 184 (2011) Hands-on Experiments on
Faraday was a scientist experimenting with circuits and magnetic coils way back in the 1830s. His experiment setup, which led to Farday’s Law, is shown in Figure 1: Figure 1. Experimental Setup For Faraday. The experiment itself is somewhat simple. When the battery is disconnected, we have no electric current flowing through the wire. Hence there is no magnetic flux induced
Michael Faraday was born on 22 September 1791 in Newington Butts, [12] Surrey, which is now part of the London Borough of Southwark. [13] His family was not well off. His father, James, was a member of the Glasite sect of Christianity. James Faraday moved his wife, Margaret (née Hastwell), [14] and two children to London during the winter of 1790 from Outhgill in Queries Solved-: What is fardays first law of electromagnetic induction ? What is fardays Second law of electromagnetic induction ? Farday’s experiments of electromagnetic induciton ?
Faraday’s Experiments in Electricity and Magnetism Michael and Sarah Faraday had no children, but he was an active uncle with his nieces and nephews often playing in his laboratory. They later remembered his reactions to successes and failures and their descriptions of an excited uncle contrasted with his always sober lab notebook recording of his results By the time Faraday was
Faraday’s Law states that, whenever the flux of magnetic field through the area bounded by a closed conducting loop changes, an emf is produced in the loop. The produced emf is given by ξ = -dØ/dt.
What is Faraday’s Law Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction (referred to as Faraday’s law) is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction From the results of his experiments, Faraday realized that whenever the magnetic flux linked with a closed coil changes, an emf (electromotive force) is induced and hence an electric current flows in the circuit.
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction helps predict how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce emf.
Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, also known as the law of electromagnetism, is responsible for the functioning of electric generators, motors, transformers, and inductors. First Experiment Faraday and Henry conducted a number of experiments for a better understanding of electromagnetic induction. INTRODUCTION we start this chapter by discussing the kind of reasoning that might have motivated Faraday to do his experiments on ‘producing electricity from magnetism’. We next talk about the different types of experiment done by Faraday and by Henry. Learn Faraday’s Law of Induction, the experiments conducted, conclusions derived, and applications from this page.
This document summarizes Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. It explains that according to Faraday’s law, a changing magnetic flux induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a circuit. The EMF is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit. It also discusses Lenz’s law, which states that the induced EMF will always act to oppose the change in In this section, we will learn about the experiments carried out by Faraday and Henry that are used to understand the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction and its properties. Experiment 1: In this experiment, Faraday connected a coil to a galvanometer, as shown in the figure above. A bar magnet was pushed towards the coil, such that the north pole is pointing towards the
- Hamburgo Buscar • Tchibo Filiale Im Billstedt-Center In Hamburg
- Handlaufseil Absperrseil 30 Mm
- Handleiding: Hoe Moet Je Een Vrouw Beffen?
- Handy Orten Ohne Internet? | iPhone orten, wenn es aus ist
- Hannspree Ht11 Bedienungsanleitung Pdf-Herunterladen
- Hand In Hand 2.0 Hersbrucker Land
- Hamburger Stadtkrug Colonnaden 45, Hamburg
- Hang X Hanged X Hung: Qual A Diferença?
- Handy Für Kinder: Sicher Und Sorgenfrei In Die Digitale Welt
- Handling Many To Many Sql Relationship In Android With Room
- Hans-Otto Von Borcke _ Kabinettsprotokolle Online "Borcke, Hans-Otto von"