Functions Of Protein In The Body
Di: Ava
Protein is a macronutrient. We need macronutrients (sometimes called ‘macros’) as they provide us with energy. Other macronutrients include fats and carbohydrates. There are thousands of different proteins in the body that have a huge variety of roles, from supporting our immune function to keeping our muscles and bones healthy throughout life. Proteins are made up of Proteins are large, complex molecules that are essential for human life. They are made up of amino acids and play a critical role in the growth, maintenance, and repair of cells and tissues. Proteins have diverse functions, from maintaining cell shape and organization to facilitating metabolic reactions and transporting nutrients. They also help maintain the body’s
Protein functions as the body’s _____ helping maintain normal pH buffers All the following are functions of protein EXCEPT: a. component of all enzymes. b. used to make antibodies. c. primary energy source. d. maintains fluid and electrolyte balance.

Table \ (\PageIndex {1}\): Protein types and functions. “Protein types and functions” by Tamberly Powell is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 Structure Protein is an essential nutrient for optimal health. Discover protein’s benefits beyond muscle building and how to know if you’re eating enough. Proteins are very important molecules in human cells. They are constructed from amino acids and each protein within the body has a specific
Chapter 6 Cengage Quizzes Flashcards
6.3 Protein Functions Proteins are the “workhorses” of the body and participate in many bodily functions. As we’ve already discussed, proteins come in all sizes
Proteins as structural support Proteins are large, complex molecules that play a critical role in the body. They are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, with 20 different types that can be combined to make a protein. Proteins perform a wide range of functions in the body, including providing structural support to cells and organisms.
- Nutrition information about protein and plant-based protein
- Understanding Proteins: Their Vital Functions And Benefits
- Functions Of Protein In The Body
Know about what is protein, types of amino acids, classification of proteins, sources, functions of proteins, need per day, protein deficiency Your body needs protein to work the way it should. Learn the recommended amount you need and best sources.
Protein’s Functions in the Body Proteins are the “workhorses” of the body and participate in many bodily functions. Proteins come in all sizes and shapes and each is specifically structured for its particular function. Structure and Motion Figure 6.9 Collagen Structure Collagen Triple Helix by Nevit Dilmen / CC BY-SA 3.0 More than one hundred different structural proteins have been Protein has many roles in your body. It helps repair and build your body’s tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions.
Types of Proteins and their function in the human body Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. Proteins are the “workhorses” of the body and participate in many bodily functions. As you may recall, proteins come in all sizes and shapes and each is specifically structured for its particular function. Figure 7.5.1 Proteins come in all sizes and shapes.
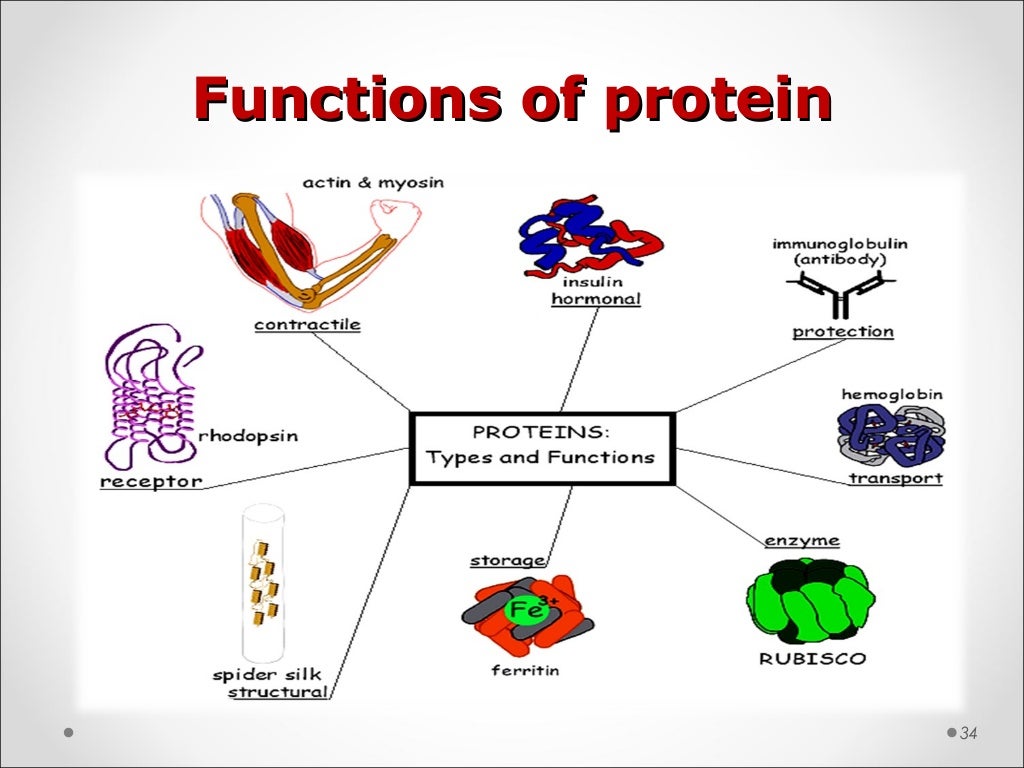
There are six functions of proteins in the body including repair and maintenance, muscle contraction, hormone production, enzyme reactions, molecule transportation, and antibody formation.
What Protein Does for Your Body and If You’re Getting Enough
The body uses proteins for a variety of purposes, and their structure determines how they work. Several notable functions include: Digestion – The digestive enzymes, which are primarily proteinaceous in origin, carry out digestion. Movement – Muscles include a protein called myosin, which helps muscles contract, allowing for movement. Structure and Support – The structural Proteins are the “workhorses” of the body and participate in many bodily functions. As you may recall, proteins come in all sizes and shapes and each is specifically structured for its particular function. Proteins come in all sizes and shapes.
Protein is one of the three nutrients that the body needs in large quantities. It is essential to maintain and build body tissues and muscle. Not having enough can cause low growth and a weakened Protein is an essential nutrient for the body to function. This article looks at how much protein a person needs, healthful high protein foods, and tips for getting enough protein.
Functions After water, proteins account for more mass in an organism than any other type of molecule. [1] Protein is present in every cell, and it is a structural component of every body tissue and organ, including hair, skin, blood, and bone. [1] Protein is especially abundant in muscle. The amino acids that are found in protein form the building blocks of all the body’s cells- including the cells that power your immune system. If you do not consume enough protein, you will manufacture fewer white blood cells to combat antigens.
- Protein’s Functions in the Body
- What is the main function of proteins in the human body?
- Protein: Sources, deficiency, and requirements
- 6.5: Protein’s Functions in the Body
- 5 Key Functions of Protein
Proteins are the “workhorses” of the body and participate in many bodily functions. As you may recall, proteins come in all sizes and shapes and each is specifically structured for its particular function. Figure 5.5.1: Proteins come in all sizes and shapes. The structure of protein sets the foundation for its interaction with other molecules in the body and, therefore, determines its function. This article will cover the structural principles of Proteins are made up of amino acids and play a crucial role in almost every biological process. Unlike carbohydrates and fats, proteins are not a source of energy but instead act as structural components, enzymes, transporters, and signaling molecules. Each protein is uniquely suited for its specific role, helping maintain the body’s structure, enable movement,
Proteins have different shapes and molecular weights; some proteins are globular in shape whereas others are fibrous in nature. For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein, but collagen, found in our skin, is a fibrous protein. Protein shape is critical to its function, and this shape is maintained by many different types of chemical bonds.
We have seen that each type of protein consists of a precise sequence of amino acids that allows it to fold up into a particular three-dimensional shape, or conformation. But proteins are not rigid lumps of material. They can have precisely engineered moving parts whose mechanical actions are coupled to chemical events. It is this coupling of chemistry and movement that gives Protein can be used for energy in the body, though this is a secondary function as the body prefers to use carbohydrates first for energy and reserves protein for Transport proteins carry essential nutrients and gases through the body (Ex. Protein hemoglobin carries oxygen for use in cellular respiration) Carry cellular waste for disposal
H1: Biological Functions of Proteins Proteins are a class of macromolecules that serve various functions in the body. These range from digestion, transportation and structural functions to defense, storage and movement. We shall explore the important role of proteins in this article. Function of Proteins (Classified by Types) Digestive Enzymes Certain proteins act as digestive Many proteins are enzymes that catalyse biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Some proteins have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle, and the cytoskeleton ’s scaffolding proteins that maintain cell shape. Learn about proteins, a large class of biological molecules. Discover their structure and function and get protein examples.
Proteins perform a vast array of functions within the human body, including: 1. Catalyzing metabolic reactions: Enzymes, which are proteins, speed up body’s metabolic processes. 2. DNA replication: Certain proteins help in DNA replication. 3. Responding to stimuli: Receptor proteins are sensitive to chemical signals and can trigger appropriate responses within the body. 4. Table of Contents Protein Structure Protein Synthesis Types of Proteins and Their Functions Functions of Proteins Frequently Asked Questions We often see bodybuilders and physical trainer drinking whey protein along with milk to build-up metabolism and strength.When it comes to our body, our hair and nails are mostly made of proteins. Basically, proteins are the fundamental Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the
Every cell in your body relies on proteins to function properly, making them essential for life. But have you ever wondered what specific roles these
- Futures Gasoil Londres | Low Sulphur Gasoil Continuous Contract
- Futternapf Katze Rostfreier Stahl,
- Fubu Shiny Queens Trikot Shirt Red Rot Glanz 90S Gr. S
- Funny Ginger Kid Gifs | Hilarious Afterlife Ginger Kid Scene
- Furniture Shop Tedox Stuttgart-Vaihingen: Opening Hours
- Fuja De Ciladas: Conheça Os Golpes De Viagem Mais Comuns
- Fullmetal Alchemist: Teaser Und Ungefähres Datum Zum Realfilm
- Furnierplatte, 1200 X 600 Mm, Sperrholz, Kieferfarbenfarben
- Functional Organizational Structure: Advantages
- Funktion Isokalenderwoche Für Die Perfekte Kalenderwoche
- Funk Brothers Motown Instrumentals
- Full Article: Data Science For Wind Energy
- Fussball Katalog 2024—Side 61 | adidas Fussball Katalog download pdf
- Ashbringer Server Status/Future