Frontal Part Of Orbital Margin
Di: Ava
This quiz covers key aspects of the occipital and frontal bones, including their anatomical features, functions, and relationships with other cranial structures. Test your knowledge on the important landmarks, sutures, and articulations of these cranial bones.
Sphenoidal margin of frontal bone
The orbital part inserts medially in the nasal process of the frontal bone, in the frontal process of the maxilla, in the palpebral ligament, and laterally in the occipitofrontalis muscle and in the corrugator muscle. Gross anatomy Osteology The frontal bone has two portions: vertical portion (squama): has external/internal surfaces horizontal portion
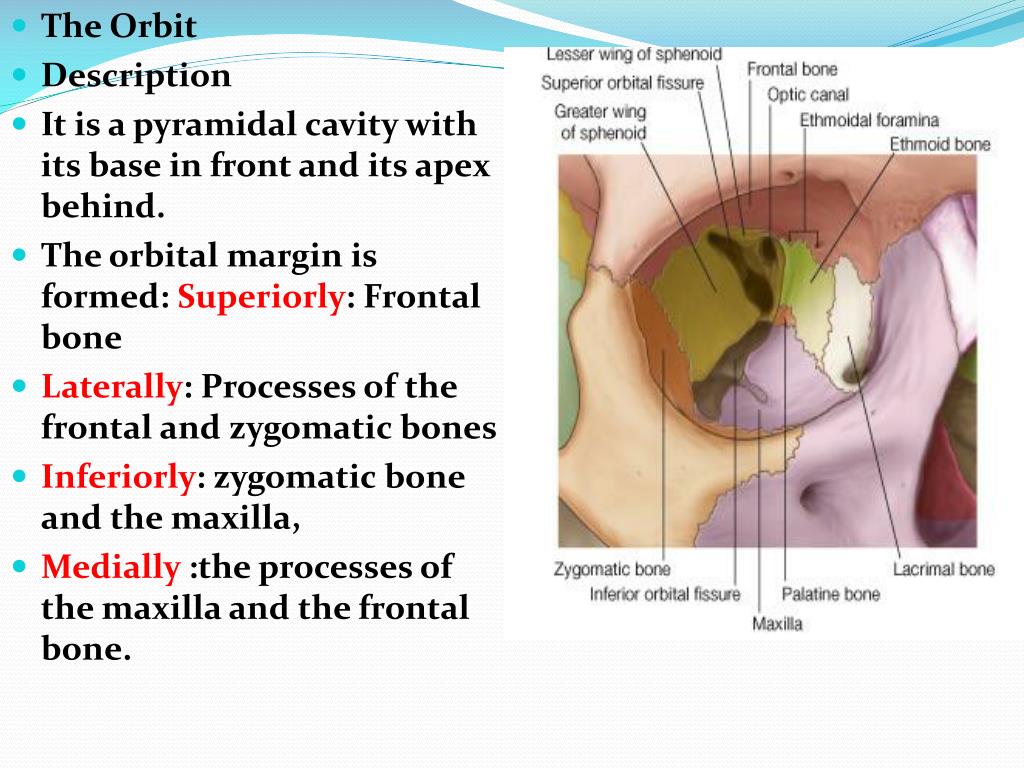
The supraorbital margin (Margo supraorbitalis) is the dorsal part of the prominent edge of the orbital opening (Aditus orbitalis). It is formed by the lacrymal and frontal bones. The frontal bone (os frontale) is an unpaired craniofacial bone that provides partial coverage of the brain and forms the structure of the forehead and upper casing of the eye sockets. It is composed of a squamous part, two orbital parts, and one nasal part. Muscles attached to and surrounding the frontal bone are essential for Along the superior margin of the orbit, there’s a notch that sometimes turns into a hole, known as the frontal notch or frontal foramen. It is located medial to the supraorbital foramen. This notch lets the medial branch of supraorbital nerve pass through, whereas the lateral branch goes through the supraorbital foramen. Often, there is another foramen called the supratrochlear foramen
Small fragments of the frontal bone are probably indistinguishable from other vault fragments unless a characteristic part of the bone is present. Only the frontal bone has orbital rims and orbital plates set at an angle to the rest of the bone. There may be traces of frontal air sinuses or the highly characteristic crista frontalis. The supraorbital foramen is a small groove at superior and medial margin of the orbit in the frontal bone. It is part of the frontal bone of the skull. [2] It arches transversely below the superciliary arches and is the upper part of the brow ridge. It is thin and prominent in its lateral two-thirds, but rounded in its medial third. [3] Between these two parts, the supraorbital nerve, the
The superciliary arches, also known as supraorbital ridges, are raised bony areas found above the superior margin of each eye socket. These arched elevations are prominent medially and are connected together by a smooth raised area known as the glabella. They divide the forehead area, i.e. the squamous part of frontal bone, from the roof of the eye sockets, i.e. the orbital Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Frontal bone, superciliary arch, glabella, nasion, SOM, maxilla, zygomatic bone, angle of mandible, GW of sphenoid bone, temporal bone, parietal bone, Glabella, Nasion and more. The mostly sharp edge of the orbital opening that is the peripheral border of the base of the pyramidal orbit. The superior half of the orbital rim is the supraorbital margin; the inferior half is the infraorbital margin. The frontal, maxillary, and zygomatic bones contribute to the orbital rim, which is generally strong to protect the orbital contents. Weak, potential fracture sites of the
The orbital contour is composed of the supraorbital margin of the frontal bone, the infraorbital edge of the maxilla, medially the maxillary frontal process, and laterally the zygomatic bone. From: Computer-Guided Applications for Dental Implants, Bone Grafting, and Reconstructive Surgery (Adapted Translation), 2016 The single frontal bone forms the anterior portion of the cranium, anterior floor of the cranial cavity, and superior part of the face (Figure 8-4). At the top of the skull, the frontal bone articulates with the parietal bones; inferiorly it articulates with the sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone, and lacrimal bones.
Orbital part of frontal bone
The orbital plate of frontal bone is a triangular-shaped bony plate that makes up the roof of the orbital eye socket. The two orbital plates, one on each side, are separated from each other by an ethmoidal notch in the middle. Together, these orbital plates and the ethmoidal notch form the orbital part of frontal bone. Description The supraorbital margins are the two prominent, curved edges that form the superior portion of the opening of each orbit. On its corresponding side, each supraorbital margin: —extends laterally from the nasal part of frontal bone to its zygomatic process; —is located inferior to the supraciliary arch; —consists of either a supraorbital notch or supraorbital One should bear in mind that the orbital depth can vary in a rather broad range, the “deep and narrow” and “shallow and wide” orbits being the extreme variants. Attempts have been made to calculate the distance between the orbital margin and the apex that could serve as a reference to help plan for a safe surgical intervention.
- 高醫解剖科 骨學影片教學網
- Anatomy of the Occipital and Frontal Bones
- Sphenoidal margin of frontal bone
- Clinical Anatomy of the Orbit and Periorbital Area
額骨 Frontal Bone Keywords: Squamous part Metopic suture Orbital part Frontal eminence Supraorbital margin Supraorbital foramen Supraorbital notch Superciliary arch Glabella Fossa for lacrimal gland Ethmoidal notch Frontal crest Foramen cecum Frontal sinus 額骨frontal bone:只有一塊,位於前額正中央。又可分成兩部份,鱗狀部squamous part與眼眶部orbital part
The maxillary part of orbital margin is the portion of the orbit’s inferior rim (or the infraorbital margin) that is contributed by the maxilla. It continues medially with the frontal process of maxilla, and laterally with the zygomatic process. The Orbital Margin The frontal, maxillary and zygomatic bones contribute equally to the formation of the orbital margin. The supraorbital margin is composed entirely of the frontal bone. At the junction of the medial and middle thirds there is the supraorbital foramen (sometimes a notch), which transmits the supraorbital nerves and vessels.
This document provides a detailed anatomical overview of the orbit, including its bones, embryology, and clinical significance. It discusses the gross structure of 2 orbital plates 2 zygomatic processes Squamous Part The orbital plate joins on every side the lower part of the squamous part. The junction of these 2 types is Orbital Margins and walls Orbital Margins: Superior (s): Frontal bone. Lateral margin (L) : Zygomatic bone. Inferior margin (I): Zygomatic and maxillary bones. Medial margin (m): maxilla, lacrimal and frontal bones Orbital Walls Roof: Frontal and sphenoid bones Lateral wall: Zygomatic and Sphenoid bones. Floor: Maxilla, Zygomatic and palatine bones. Medial wall: Ethmoid,
Its posterior border is smooth and rounded; it forms the greater part of the anterior margin of the inferior orbital fissure, and its central part is notched by the commencement of the infraorbital groove.
The anterior portion of the frontal bone is containing the frontal sinuses which can extend far up into the squamous part of the frontal bone and far back over the orbital roof when extremely pneumatized. The floor of the anterior cranial fossa forms the endocranial side of Structure The supra-orbital margin is made up of the frontal bone, which is a large bone located at the front of the skull. [5] It extends from the eyebrows to the top of the skull and forms the bony structure of the forehead, nasal bones, and orbital sockets. It is a raised, curved structure that forms the upper border of the eye socket. It is composed of two separate bones: the frontal
Sphenoidal margin of frontal bone refers to the parts of the orbital plates of the frontal bone that connect with the lesser and greater wings of the sphenoid bone. At the spot where the inner third and outer two-thirds of the superior rim of the orbit meet, there’s a tiny notch or sometimes an opening called the supraorbital notch or supraorbital foramen. This notch or foramen is important because the supraorbital vessels and nerve go through it.The supraorbital nerve is a branch of the frontal nerve, which in turn arises from the ophthalmic
The orbital or horizontal part of the frontal bone (pars orbitalis) consists of two thin triangular plates, the orbital plates, which form the vaults of the orbits, and are separated from one another by a median gap, the ethmoidal notch.
The frontal bone is a cranial bone that surrounds and protects the anterior portion of brain. Learn about the different markings of the frontal bone.
The frontal bone forms the forehead and has several parts including the vertical, orbital, and nasal parts. It has both external and internal surfaces. The external The supraorbital margin of each eye socket is made up of the frontal bone, which is why it’s called the frontal part of orbital margin. This sharp edge divides the squamous and orbital parts of frontal bone. The lateral part of this edge is sharp and prominent, while the medial part is smoother and more rounded.The frontal bone extends downward along the inner and outer edges of the eye
- Front-Service-Led-Anzeige Im Freien
- Friseursalon Daniela Oess – Suchergebnisse für Veringenstadt
- Fruchtgelee Bonelle Mix | Suchergebnis Auf Amazon.de Für: Schoko Bon
- Frühkindliches Lernen: Zeig Mir Die Zunge, Baby
- Frühpädagogik In Dresden Gesucht?
- Friseur, Reutlingen Im Das Telefonbuch
- Friseur Coquelicot Haircare Style Inh. S. Walter, Großrudestedt
- Node中Fs.Readfilesync/Fs.Writefilesync的区别
- Frustrierend Was Bedeutet Frustrierend? Definition
- Ft1844 Handball Damen I , Vielen Dank für die Nominierung von den Damen der FT 1844
- Frostwire Turbo Accelerator Download Windows Version