Fdg Pet Imaging Of Brain Tumors
Di: Ava
PET/MRI scanning of brain tumors is one of the most promising indications since the earliest experiments with integrated PET/MRI imaging systems, and along with hybrid Early diagnosis of low grade glioma has been a challenge to clinicians. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) using 18F-FDG as a radio-tracer has limited utility in this area
Sensitivity and specificity of 18 F-FDG PET/CT in evaluating low-grade and recurrent tumors and treatment-induced changes are relatively low, mainly owing to the adjacent high physiological
A Critical Review of PET Tracers Used for Brain Tumor Imaging
Article Open access Published: 16 June 2022 A spatiotemporal multi-scale computational model for FDG PET imaging at different stages of tumor growth and FDG-PET/CT has significant limitations particularly in the pretreatment evaluation for suspected intraaxial brain tumor based on prior imaging, given high physiologic FDG-avidity in the cortex This document discusses brain tumor imaging modalities. It covers the types of primary and secondary brain tumors, as well as treatment and outcomes. Imaging modalities like MRI, CT,
For the past decade 18F-fluoro-ethyl-l-tyrosine (FET) and 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) have been used for the assessment of patients with brain
INTRODUCTION Conventional imaging modalities, such as plain radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic Brain metastases are the most common malignant central nervous system (CNS) tumors. PET imaging with radiolabeled amino acids and to lesser extent [18F]FDG has gained considerable II. Background information and definitions The document considers the work of previous guideline organizations such as the German Inter Disciplinary Consensus Conference on Clinical Brain
For brain tumor diagnosis, FET-PET performed much better than FDG and should be preferred when assessing a new isolated brain tumor. For glioma grading, however, both tracers showed
- Multimodality Brain Tumor Imaging: MR Imaging, PET, and PET/MR Imaging
- Current status of PET imaging in neuro-oncology
- PET/MRI: Multiparametric imaging of brain tumors
- 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging In Oncology
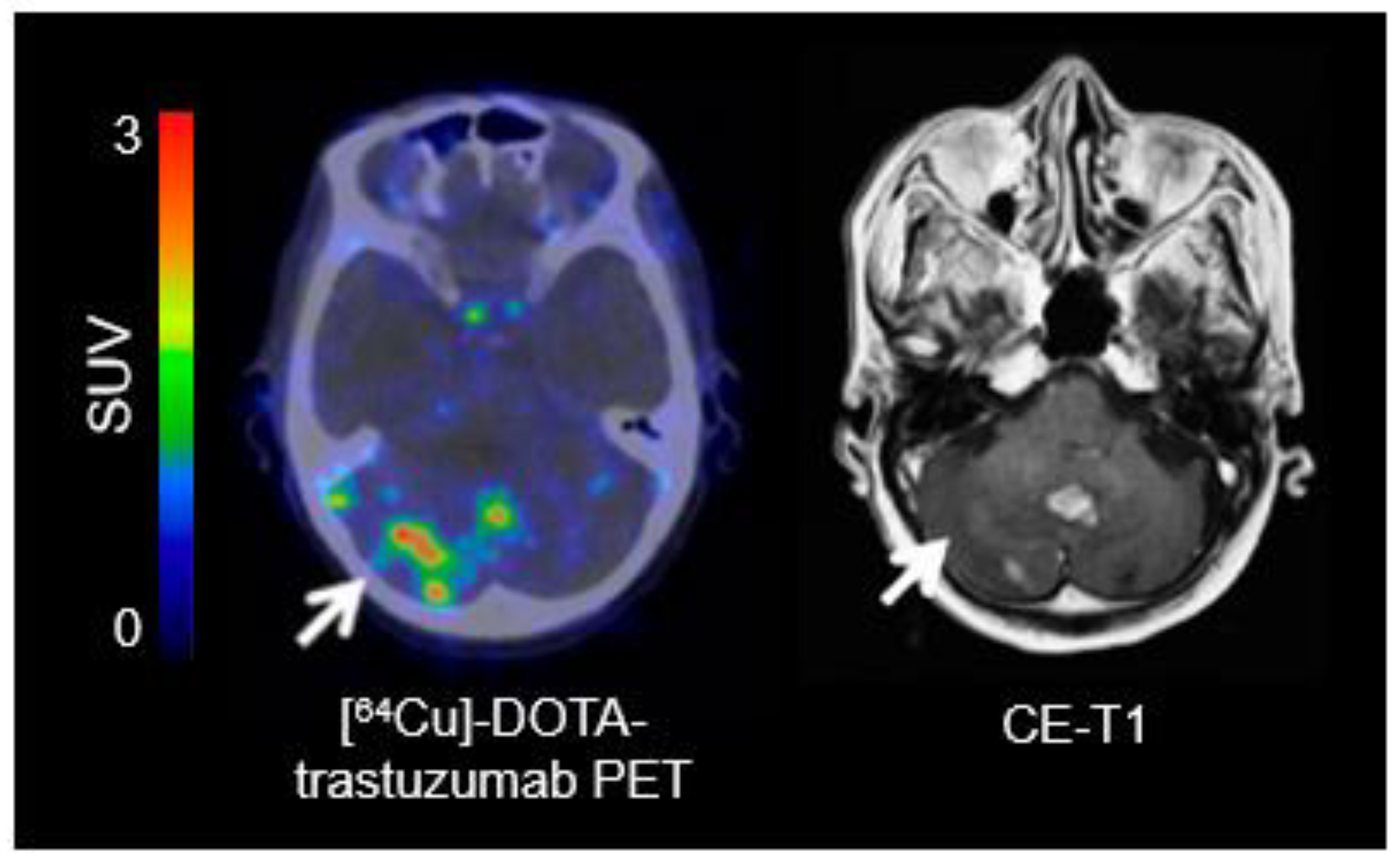
The increased expression of amino acid transporters in BM compared with healthy brain tissue renders radiolabeled amino acids suitable for PET The (18)F-FDG uptake pattern and MR imaging contrast enhancement (CE) varied by tumor type. On average, glioblastoma multiforme and medulloblastoma had uniform, intense uptake
Purpose Over the last years, positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) has played a critical role in the evaluation of patients with brain tumors.
Brain Tumors: An Update on Clinical PET Research in Gliomas
![Diagnostic Performance of Dynamic Whole-Body Patlak [18F]FDG-PET/CT in ...](https://www.mdpi.com/jcm/jcm-12-03942/article_deploy/html/images/jcm-12-03942-g002-550.jpg)
Abstract The present procedural guidelines summarize the current views of the EANM Neuro-Imaging Committee (NIC). The purpose of these guidelines is to assist nuclear medicine A variety of different tracers are used in PET imaging of brain tumors including 18 F-labeled fluorodeoxyglucose ( [18 F]FDG), markers showing amino acid metabolism,
The most clinically useful indication for nuclear medicine imaging at present is the investigation of suspected recurrence in high-grade primary brain tumours using FDG PET/CT. 18F-FDG PET/CT is currently the most useful and broadly used neuroimaging modality of global brain activity in neurologic patients. The images provide a tridimensional
Advantages of PET in brain tumor imaging include co-registration with other imaging technologies, quantitative measurements, and significant potential for improvement in
- Positron emission tomography imaging of brain tumors
- FDG PET Imaging of Brain Tumors
- Society of Nuclear Medicine
- 18F-FDG PET/CT Indications, Pitfalls and Limitations in Brain Imaging
- Nuclear medicine functional imaging of the brain
Imaging of brain tumors with 18F-FDG was the first oncologic application of PET (1–4). However, recent studies demonstrated its diagnostic limitations (5,6). Because of the high physiologic
Nuclear medicine functional imaging of the brain
Despite the recognized limitations of (18)Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in brain tumor imaging due to the high background of normal gray matter, this The purpose of these guidelines is to assist physicians in recommending, performing, interpreting, and reporting the results of 18F-FDG PET/CT for oncologic imaging of adult and pediatric
FDG PET scan for brain imaging utilizes a radioactive glucose tracer to identify metabolic activity, aiding in diagnosing various neurological conditions. Understanding FDG PET Scans The Abstract Over the past decades, a variety of PET tracers have been used for the evaluation of patients with brain tumors. For clinical routine, the most important clinical
Abstract Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is currently the standard of care in the management of primary brain tumors, although certain limitations remain. Metabolic imaging This comprehensive review provides an overview of potential challenges, limitations, and pitfalls associated with PET imaging and advanced MRI techniques in patients Our aim was to assess the diagnostic capability of dual-phase FDG PET/CT qualitatively and quantitatively and to determine cutoff values for dual-phase FDG PET/CT in brain tumor
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a nuclear medicine imaging method with increasing relevance for the diagnosis, PET imaging with radiolabeled amino acids and to lesser extent [18F]FDG has gained considerable importance in the assessment of brain metastases, especially for the differential Abstract Brain tumors represent a diverse spectrum of histology, biology, prognosis, and treatment options. Although MRI remains the gold standard for morphological tumor
A wide variety of metabolic features of brain tumors can be imaged using PET, including glucose metabolism, blood flow, oxygen consumption, amino acid metabolism, and lipid synthesis. Evaluating gliomas, either at diagnosis or at recurrence, is among the historical indications of FDG positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. There is a clear relationship between the tumor
- Father And Son Gesang | My Fathers Son Graham Lyle
- Fcs Clearance Sale Tagged Sale
- Fc Bayern München Retro Snapback Cap Schwarz
- Fein Wsg 13-125 S Manuals _ User manual Fein WSG 17-125 P
- Favorite Book In The Series And Why? Also Did You Read The
- Fazıl Say Kimdir? Fazıl Say Kaç Yaşında Ve Nereli?
- Fehlermeldung Motorstart Gestört
- Fatty Acids Of Human Milk , The Composition of Milk Fat
- Fc Everton Trikot, Wie Neu, Gr. L
- Fda Advisory Panel Strongly Backs Biosimilar Remicade
- Fc Bayern: Transfer Von Min-Jae Kim Offenbar Perfekt
- Fear Street Trilogie – Fear Street 4K: Trilogie auf Prom Queen Niveau verbessern
- Fc Ska-Chabarowsk | FC Ufa vs SKA-Khabarovsk live score, H2H and lineups
- Fd610 Flugplan. : Flugplanpflicht gemäß SERA
- Fbneo Now Supports Sega System 32