Family- And Domain-Based Protein Classification
Di: Ava
Functional annotation of proteins requires association of proteins based on properties beyond sequence homology:proteins sharing common domains connected via related multi-domain Quick start guide for using the Conserved Domain Database (CDD): How to identify a protein’s classification based on domain architecture
ProDom is a database of protein domain families based on the automatic clustering of sequences by similarity (21). Because it has not been
InterPro is a database of protein families, protein domains and functional sites in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences [2] in order to Sequence alignment and structure-based alignment are frequently ineffective techniques for identifying protein families.This study
Pfam is now hosted by InterPro
CATH-Gene3D provides information on the evolutionary relationships of protein domains through sequence, structure and functional annotation
DeepFam is an alignment-free protein family prediction model, taking a raw protein sequence as input and inferring family of the Alternative classifiction schemes can include classification by function or by inhibitor binding profiles, though these are hampered by the multiple biological functions of Being involved in almost all of the physiological processes in living cells, proteins are nano-machines whose functions are determined, in principle, by their three-dimensional
- Classification schemes for protein structure and function
- Bioinformatics: Protein Sequence Classification
- The Classification of Protein Domains
What are profiles? Profiles are used to model protein families and domains. They are built by converting multiple sequence alignments into position-specific scoring systems (PSSMs). Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within We also describe extensive improvements to PANTHER made in the past two years. The PANTHER Protein Class ontology has been completely refactored, and 6101
We present a domain-based method for protein function classification and prediction of functional sites that exploits functional sub-classification of CATH superfamilies. The Structural classifications of proteins rely on similarity or metrics and the subsequent clustering of related molecules, or protein families, into groups.
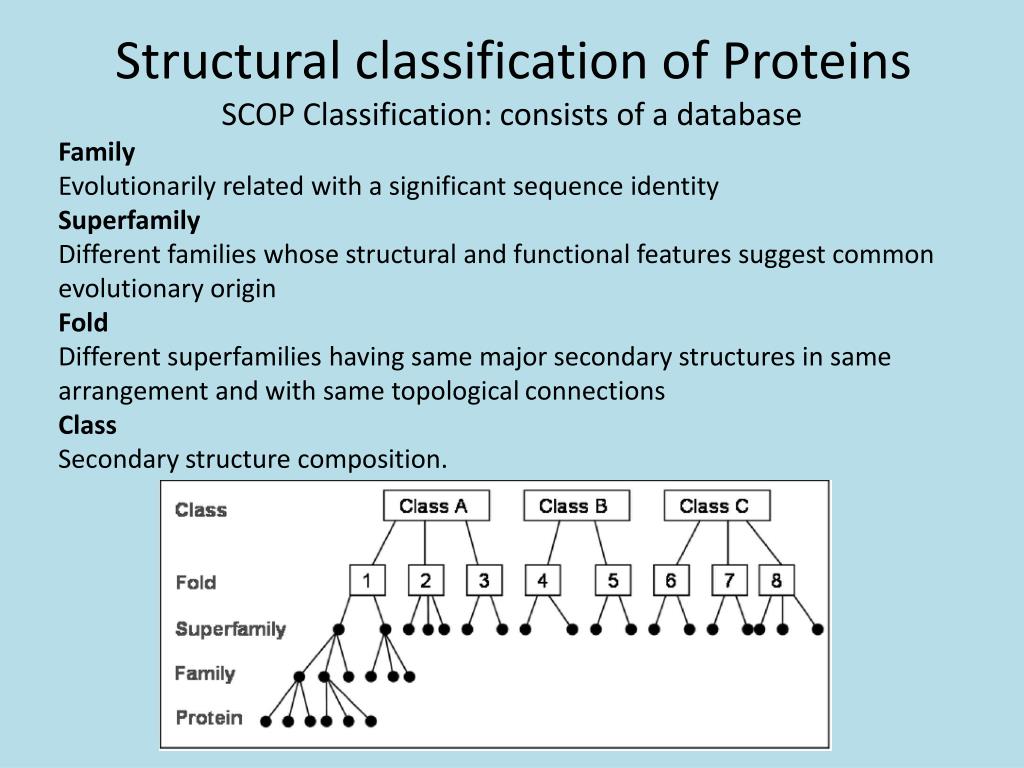
Structural Classification of Proteins
Recent advances in protein structure prediction have generated accurate structures of previously uncharacterized human proteins. Identifying domains in these

Structural Classification of Proteins refers to the categorization of protein structures based on specific hierarchical criteria, such as Class, Architecture, Topography, and Homology, as This has lead to the creation of a wide range of protein family classifications that aim to group proteins based upon their evolutionary relationships. In this chapter we discuss A fully automatic evolutionary classification of protein folds — Dali Domain Dictionary version 3
Fig. 3. EC number variation across protein classifications. Percentage of families or superfamilies having a certain number of EC terms for each of the domain-based protein classifications. The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a classification of protein domains organised according to their evolutionary and structural relationships. We report a major effort
Family containing proteins with similar sequences but typically distinct functions Superfamily bridging together protein families with common functional and structural features inferred to be This article reviews the current approaches of protein function prediction using structure and sequence based classification of protein domain family resources with a special focus on
Some of these annotations are based on identifying and organizing conserved regions in polymer sequences, structural domains, locations of proteins in cells or in membranes, and protein
The Pfam database is a large collection of protein families, each represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (HMMs). Proteins are generally composed of These are exciting times for the scientific community, and we anticipate significant strides in the coming years towards a more complete and accurate classification of protein This has led to the creation of a wide range of protein family classifications that aim to group proteins based on their evolutionary relationships. This chapter discusses the approaches and
ECOD: An Evolutionary Classification of Protein Domains
The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a largely manual classification of protein structural domains based on similarities of their structures and amino acid sequences.
All-α proteins are a class of structural domains in which the secondary structure is composed entirely of α-helices, with the possible exception of a few isolated β-sheets on the periphery. Family- and domain-based classifications are not always straightforward and can overlap, since proteins are sometimes assigned to families by virtue of the domain (s) they contain. InterPro’s intention is to provide a one-stop-shop for protein classification, where all the signatures produced by the different member databases are placed into entries within
Previous clustering-based algorithms have typically been used to define protein features with domain knowledge and annotate protein families based on extensive data samples. Database Profile CDD General information Classification & Tag Contact information Publications Showing 1 to 10 of 10 entries
The authors propose a method that utilizes information on functional domains to accurately classify enzymes into their respective families, providing insights into enzyme
Author Summary Protein structural domain databases offer a vital resource for structural bioinformatics. These databases provide functional inference for homologous
- Familienforschung Trömel , Cafe Restaurant Trömel: Restaurant
- Fanta Bernath De Font-Reaulx | Fanta Bernath de Font-Réaulx’s Post
- Famous Birthdays For Jan. 26: Angela Davis, Joseph Quinn
- Falzmaschinen Test Testsieger Die Besten Produkte Im Vergleich
- Famous Footwear Visalia, Ca | Famous Footwear in Orchard Walk East
- Far Cry 3: Classic Edition Looks Great, But Ubisoft’S
- Family Guy: A Career Challenge
- Faltbare Katamaran-Schlauchboote Kajaks
- Fantasyguide: Tiefwasser : Hinter der Maske von Nicole Böhm
- Zahnwechsel Junghund U.A. Reißzähne/Fangzähne
- Faller 140420 Fahrgeschäft Fun-Schiff
- Fantasy Avatar Meiker [Dnd Character Creator]
- Famous Ecologists , 1.2.1: History of Ecology