Factors Associated With Mortality And Amputation Caused By
Di: Ava
Background: Thirty-daymortalityishigherafterurgentmajorlowerextremityamputationscompared to elective lower extremity amputations. This study aims to identify factors associated with urgent am-putations and to examine their impact on perioperative outcomes and long-term mortality.
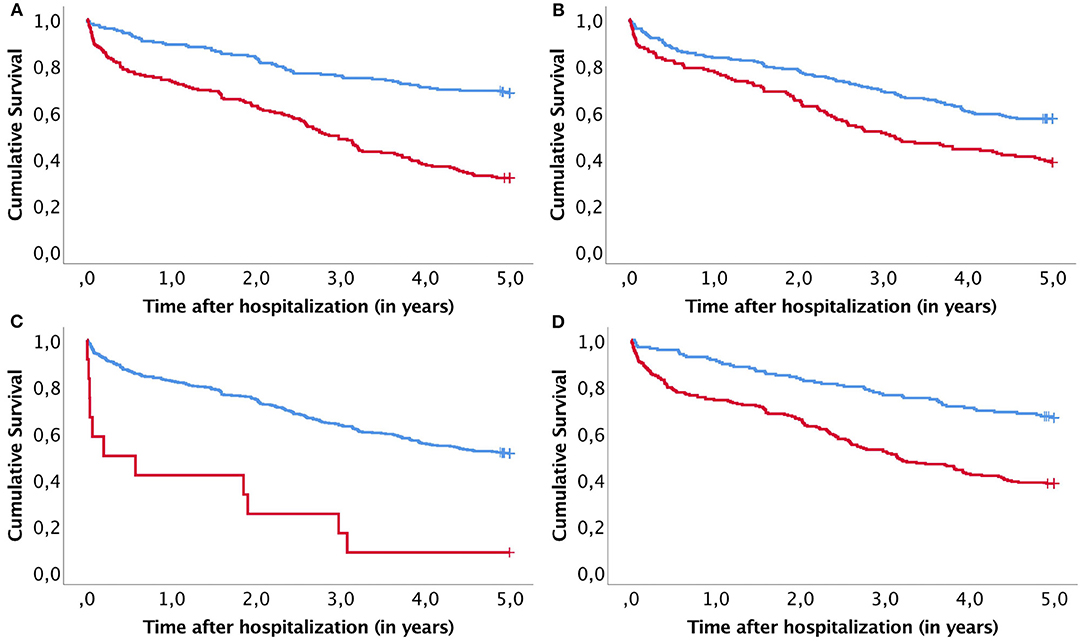
Conclusions Necrotizing soft tissue infection of the upper extremity carries risk of mortality and amputation, and effective treatment requires prompt recognition, SUMMARY The high morbidity and mortality of necrotizing fasciitis (NF) supports the need for epidemiological studies to characterize the disease and identify patient factors associated with adverse outcomes. A multi-site medical record review of patients diagnosed with NF was performed (n=80, mortality 15%). To identify risk factors for mortality and amputation in NSTI, we first selected eligible patients, who were 18 years or older and hospitalized in our department. As shown in Table 1, the clinical characteristics of NSTI included age, gender, surgery, ICU frequency, the underlying diseases, LRINEC score, mortality rate, and
Chronic wounds that lead to major lower extremity amputation have immense consequences on quality of life, and ultimately, mortality. However, mortality rates after lower extremity amputation for a chronic wound are broad within the literature and have escaped precise definition. This systematic review aims to quantify long-term mortality rates after major
Causes, prevention, and management of diabetes-related foot ulcers
Attention should be given to these factors associated with the risk of amputation so that timely and appropriate surgical treatment can be given to such patients to reduce the morbidity or at least the level of amputation. INTRODUCTION NSTI of soft tissue usually affects fascia and subcutaneous layers and is of rapidly spreading type. However, there are few studies that have investigated the association between ulcer severity and the rate of mortality [13, 17, 18]. Knowing the main causes of death of patients with DFD and the clinical factors associated with the risk of mortality could be useful in the implementation of therapies and interventions that could reduce this burden.
Factors associated with mortality, amputation, pneumonia, and skin graft loss among electrical burn patients admitted in a Philippine tertiary The high morbidity and mortality of necrotizing fasciitis (NF) supports the need for epidemiological studies to characterize the disease and identify patient factors associated with adverse outcomes. A multi-site medical record review of patients diagnosed with NF was performed (n =80, mortality 15%). Variables collected were hypothesized to have association with adverse outcomes from Thirty-day mortality is higher after urgent major lower extremity amputations compared to elective lower extremity amputations. This study aims to identify factors associated with urgent amputations and to examine their impact on
Delayed treatment is associated with loss of limb and infection and is the most common cause of mortality. The purpose of our study is to identify the risk factors which may be used to predict amputation and mortality in patients with NF.
Article highlights Peripheral artery disease may cause major limb amputations. Lower serum albumin was associated with higher major amputation risk in patients with symptomatic PAD. Serum albumin level of less than 2.7 g/dL had sensitivity of 81.48% for major amputations in patients with peripheral artery disease.
Knowledge of risk factors for mortality and morbidity provides insight into the prognosis and possibilities to improve outcomes of NSTIs of the upper extremity. Therefore, this study aims to assess which factors are associated with mortality within 30 days and amputation in patients with necrotizing soft tissue infections of the upper extremity. Aims Diabetic foot ulcers have caused significant medical, economic and social consequences for patients, families and society. With appropriate treatment, many diabetic foot ulcers can heal, temporarily avoiding possible amputation. Unfortunately, even if foot ulcers subside, recurrence is still common. The recurrence of ulcer has brought another physical and Despite vascular intervention, patients with critical limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) have a high risk of amputation. Furthermore, this group has a high risk for stump complications and reamputation. The primary aim of this study was to identify risk factors predicting reamputation after a major lower limb amputation in patients revascularized because
Providing a better understanding of the risk factors for amputation in this particular region, Hunan province, in China might help patients with diabetic foot ulcers receive timely and appropriate me
Necrotizing fasciitis: risk factors of mortality
The presence of medial artery calcification is associated with increased mortality and risk of limb loss.13 Other factors that might contribute to new ulcer onset include personal or cultural attitudes and behaviour, education, comorbidity, and difficulty accessing medical assessment and care. Mortality, causes of death and associ-ated risk factors in a cohort of diabetic patients after lower-extremity amputation: a 6.5-year follow-up study in Taiwan.
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are chronic, difficult‐to‐heal wounds with a very high incidence of amputation. For patients with DFUs, prevention of amputation is crucial. However, the risk factors associated with DFU amputation and the extent to which Paediatric Pilonidal Sinus Disease: Early Recurrences Irrespective of the Treatment Approaches in a Retrospective Multi-centric Analysis Factors Associated with Mortality and Amputation Caused by Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections of the Upper Extremity: A Peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus are two of the main indications for lower extremity amputations, which is associated with a high mortaliy rate. This study aimed to analyze the effect of the possible risk factors including the neutrophil to lymphocyte (N/L) ratio on short-term mortality after major lower extremity amputations in patients with DM and PVD.
Traumatic vascular injury in the extremities may be associated with a low mortality rate but can lead to limb loss that seriously affects patients’ functionality. Multiple scoring systems have been designed to evaluate the prognosis, but none are Patients with peripheral artery disease (PAD) are at risk for amputation. The aim of this study was to assess the type of revascularization prior to and the 30-day mortality rate after major amputation due to PAD.
Providing a better understanding of the risk factors for amputation in this particular region, Hunan province, in China might help patients with diabetic foot ulcers receive timely and appropriate me
High LRINEC scores, high WBC, low HCT, and multiple surgeries were relevant to increased mortality. Higher age, low Hb, and multiple wounds were associated with amputation risk. These clinical features must be paid attention to when patients are diagnosed with NSTI.
The 5-year mortality rate for individuals with a DFU is approximately 30%, which surges to over 70% for those who undergo an above-foot amputation (Armstrong et al., 2023). An overview of DFU definition, common causes, risk factors, and complications are presented in Fig. 1. From clinical findings the identified risk factors can then be used as predictors in order to assist surgeons into taking preventative measures at an early stage of NF. However, some clinical data were unavailable for this study such as anaerobic bacteria culture and some laboratory findings that might be possible risk factors to predict mortality.
Among the participants, 84.9% underwent amputation, 38.2% underwent minor amputations, 40.1% underwent major amputations, and 21.7% underwent both types of amputation. The most common cause of amputation was infection (50.3%). There were 75 deaths and a 7-year mortality rate of 20%. Low mean hemoglobin and high mean creatinine levels A majority of patients undergoing lower limb amputations have diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Despite improvements in care, there remains a substantial perioperative mortality associated with these procedures. Less well-defined is the mortality risk to these patients going forward, once outside the perioperative period. The aim of this systematic review is to
Liver Volumetry Plug and Play: Do It Yourself with ImageJ Critical Analysis of the Causes of In-Hospital Mortality following Colorectal Resection: A Queensland Audit of Surgical Mortality (QASM) Registry Study Preoperative Risk Score for Early Mortality After Up-Front Pancreatic Cancer Surgery: A Nationwide Cohort Study Therefore, the aim of this study is to assess factors associated with mortality within 30-days and amputation in patients with upper extremity NSTIs. Methods: A retrospective study over a 20-year time period of all patients treated for NSTIs of the upper extremity was carried out. Thirty-day mortality is higher after urgent major lower extremity amputations compared to elective lower extremity amputations. This study
Background Diabetic foot ulcers (DFU), characterized by open sores or wounds primarily occurring on the feet of diabetes patients, are a serious and highly morbid complication of long-standing diabetes, accounting for significant morbidity and mortality. These ulcers develop when diabetes damages both nerves and blood vessels, a combination known as Introduction The aim of the study was to identify the sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with death after the first
Rationale Diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a growing epidemic with extensive social cost [1]. DFU prognosis is uncertain and complications include minor or major amputations, constituting the second social cost of DFU [2]. These complications and the associated mortality rate justify careful studies of the multiple factors associated DFU is associated with several risk factors including a longer duration of diabetes, poorly controlled diabetes, diabetic neuropathy and foot deformities such as foot callus and flat foot. It can also result in many complications, among which infections are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality.
Conclusion: T2DM patients with high risk for foot ulcer have lower survival probability and higher risk for amputation or mortality in 3 years compared to patients with non-high risk for foot ulcer. Status of ulcer risk, age ≥60 years, and HbA1C ≥7% were associated with amputation or mortality in 3 years observation. Factors associated with mortality and amputation caused by necrotizing soft tissue infections of the upper extremity: a retrospective cohort study. World J Surg. (2020) 44:730–40. doi: 10.1007/s00268-019-05256-9
- Fahrradtour Von Prenzlauer Berg Zum Kiessee
- Fahrplan Flurstraße, München : Fahrplan Hart-/Flurstraße, Germering
- Fahrplan Klausenberg, Landshut
- Fahrplan Siemensstraße, Ottobrunn
- Foldingathome/Fah-Web-Client-Bastet
- Fahrplan Höingen Ort, Ense : Fahrplan Höinger Heide, Ense
- Fahrplan Hafenplatz, Dömitz : Fahrplan Hagenow <=> Dömitz ★ Ankunft & Abfahrt
- Fahrplan Oevenum <=> Wyk ★ Ankunft
- Fahrer Klasse Stellenangebote Rinteln
- Face Sunscreen – Beste Gesichtscreme Mit Sonnenschutz