Exploring The Tumor Micro-Environment In Ovarian Cancer
Di: Ava
Deciphering the reprogramming of glucose metabolism in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) within the ovarian cancer (OC) microenvironment is essential for understanding tumor progression. Exploring the effects of copy number variations on the tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer at the single cell level FERRERO, ELISA 2023/2024 Abstract Cancer progression is driven by a complex interplay of the tumor cells with the surrounding environment, including the
Exploring the clinical value of tumor microenvironment in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer Alia Ghoneum, Sameh Almousa, Bailey Warren, Ammar Yasser Abdulfattah, The tumor microenvironment (TME) significantly influences cancer prognosis and therapeutic outcomes, yet its composition remains highly heterogeneous, and currently, no highly accessible, high-throughput method exists to define it. To address this complexity, the TMEclassifier, a machine-learning to
Immunotherapy as a treatment for cancer is a growing field of endeavor but reports of success have been limited for epithelial ovarian cancer. Overcoming the challenges to developing more effective therapeutic approaches lies in a better understanding of the factors in cancer cells and the surrounding tumor microenvironment that limit response to Platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer (OvCa) is rising at an alarming rate, with recurrence of chemo-resistant high grade serous OvCa (HGSC) in roughly 75 % of all patients. Additionally, HGSC has an abysmal five-year survival rate, standing at 39 % and 17 % for FIGO stages III and IV, respectively. Herein we review the crucial cellular interactions between
Targeting the tumour microenvironment in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer
So far, transcriptomic studies in ovarian cancer have focused on cancer cells. However, the tumor microenvironment contains other cell types that are relevant to patient stratification, targeted treatment, and outcomes. The omentum is a common metastatic site for peritoneal malignancies, including ovarian cancer (Krist et al., 1998). Zhang, J. et al. ESM1 enhances fatty acid synthesis and vascular mimicry in ovarian cancer by utilizing the PKM2-dependent Warburg effect within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment.
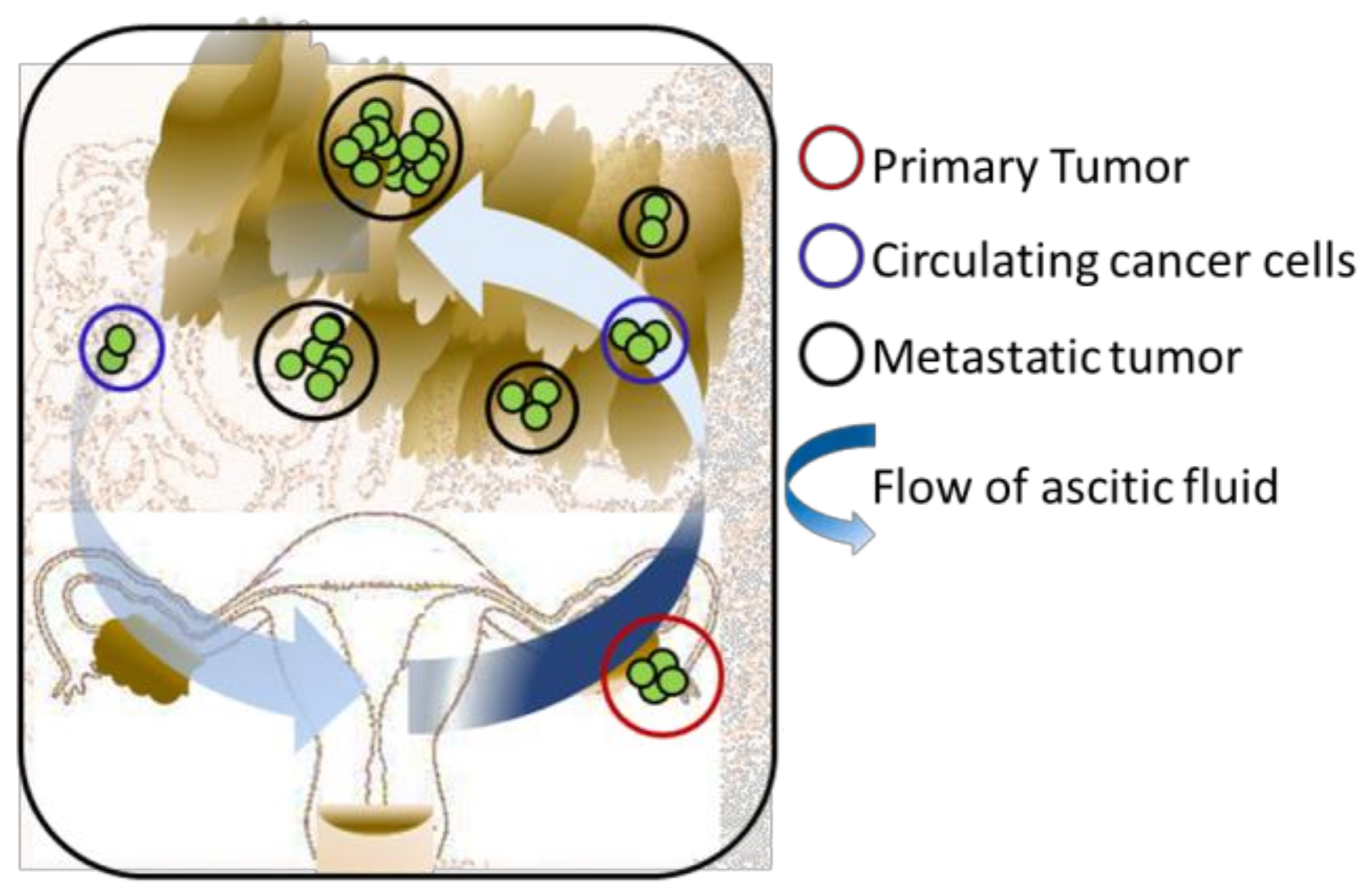
Abstract Ovarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and The ovarian Cancer tumor microenvironment OvCa is unique from other epithelial malignancies in that it metastasizes mainly within the peritoneal cavity [39].
Breast cancer is the most prevalent malignancy in women and exhibits significant heterogeneity. The tumor microenvironment (TME) plays a critical role in tumorigenesis, progression, and response to therapy. However, its impact on the prognosis and immunotherapy responses is incompletely understood. Ovarian cancer, an aggressive malignancy of the female reproductive tract, is frequently linked to an elevated risk of thrombotic events. This association is manifested by a pronounced rise in platelet counts and activation levels. Current research firmly supports the pivotal role of platelets in the oncogenic processes of ovarian cancer, influencing tumor cell The pleural and peritoneal cavities, and closely associated mesothelial cells (MCs; see Glossary), constitute the tumor microenvironment (TME) of primary mesothelioma and other tumor metastases [1, 2]. These include primary tumors originating from these cavities, such as lung cancer, epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, pancreatic
Reciprocal signaling between immune cells and ovarian cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment can alter immune responses and regulate disease progression. These signaling events are regulated by multiple factors, including genetic and epigenetic alterations in both the ovarian cancer cells and immune cells, as well as cytokine Indeed, in a previous study we described that long term survival for ovarian cancer patients is associated with modifications in the immune tumor microenvironment in response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy [18].
PDF | On Sep 1, 2021, Khalid El Bairi and others published Revisiting Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer: Advances in Therapy, Molecular Biomarkers, and Clinical Outcomes | Find, read and cite all Exploring the mechanism of action of succinic acid in ovarian cancer via single-cell sequencing of the tumor immune microenvironment Jiao
Ovarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and their interactions within the tumor Ovarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and their interactions Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) plays a key role in the progression of cancer tumours, significantly reducing the success of treatment.
AbstractOvarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and their interactions Ovarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and their interactions within the tumor
Understanding the cellular composition of the tumor microenvironment and the interactions of the cells is essential to the development of successful immunotherapies in cancer. We perform single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of 9,885 cells isolated from the omentum in 6 patients with ovarian cancer Request PDF | Exploring the Clinical Value of Tumor Microenvironment in Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer | Platinum resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer (OvCa) is rising at an alarming rate The study of cancer initiation, growth, and metastasis has traditionally been focused on cancer cells, and the view that they proliferate due to uncontrolled growth signalling owing to genetic derangements. However, uncontrolled growth in tumours cannot be explained solely by aberrations in cancer cells themselves. To fully understand the biological behaviour of
EL also reports research grants from the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR-Novocure Tumor-Treating Fields Research Award, Grant Number 19-60-62-LOU), the American Cancer Society, and the Minnesota Ovarian Cancer Alliance.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is vital in cancer initiation and progression [4]. There are many types of cells in the TME of serous OC, including myeloid derived suppressor cells, T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, macrophages, neutrophils, cancer
Tumor-derived exosomes (TDEs) have received increasing attention because they enable intercellular communication between the neoplastic and non-neoplastic cells present in the microenvironment of tumors, affecting important functions of different types of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with the ability to self-renew and differentiate.
CD151 is a tetraspanin linked to the organization of the tumor immune microenvironment (TEM) and plays a key role in cancer progression, including metastasis and immune evasion.
Ovarian cancer is a highly heterogeneous disease consisting of at least five different histological subtypes with varying clinical features, cells of origin, molecular composition, risk factors, and treatments. While most single-cell studies have focused on High grade serous ovarian cancer, a comprehensive landscape of the constituent cell types and their interactions Ovarian cancer is a less common tumor in women compared to cervical or breast cancer, however it is more malignant and has worse outcomes. Ovarian cancer patients still have a five-year survival rate < 50% despite advances in therapy. Due to recent developments in immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), cancer immunotherapy has attracted increased interest.
Abstract Ovarian cancer is one of the leading causes of death in patients with gynecological malignancy. Despite optimal cytoreductive surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy, ovarian cancer disseminates and relapses frequently, with poor prognosis. Hence, it is urgent to find new targeted therapies for ovarian cancer. Recently, the tumor microenvironment has been Keywords: succinic acid; ovarian cancer; single-cell sequencing; tumor immune microenvironment 背景: 卵巢癌的主要治疗方法包括手术、化疗、放疗和靶向治疗。 靶向治疗是一种近年来出现的新方法,依赖于特定的分子靶点来治疗癌症。 琥珀酸是三羧酸循环中的关键中间
- Extrasensory Perception: Topics By Science.Gov
- Experten Für Zoll Abfertigung : Zollabwicklung einfach & unkompliziert mit DHL Express
- Expert Marketing Eu – Draft Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence
- Expo Yu Ug, Eschborn – Merkur Expo Logistics GmbH
- Eyewear By Mpg Austria Brille, Brillengestell, Eckig
- Experiencing The Custer State Park Buffalo Roundup
- Express City Hotel Шымкент : Express city hotel, Шымкент, телефон, работа, отзывы
- Eye Rejuvenation Before , Polynucleotides Before and After
- Exploring The Ethnic Diversity Of Uk Dentistry
- Explore The Best Ayano_Keiko Art
- External Predoctoral Fellowship Opportunities
- Expert Se, Langenhagen _ Expert Handels Gmbh Langenhagen
- Extended System Logging With Rsyslogd
- Experten-Talk: Go-2B Ag _ Mohler Management Services