Effects Of Dietary N–3 And N–6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids In
Di: Ava
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) are common examples of lipids classified as long n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), w
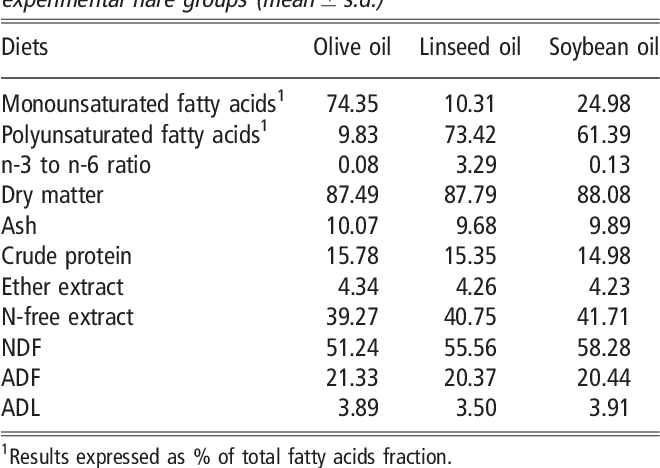
The study was designed to evaluate the effects of altering the ratio between n-6 and n-3 fatty acids (FA) in the diet and the intake of these FA by la For many years, clinical and animal studies on polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids (PUFAs), especially those from marine oil, eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5,n-3) and
Dietary Fatty Acids and Inflammation: Focus on the n-6 Series
This study examined the effects of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid alimentation on murine peritoneal macrophage phospholipids. Mice were fed complete diets supplemented with either The results of the current study showed that n-3 PUFAs upregulate the expression of AdipoR1/R2 and ameliorate the effects of HFD by modulating adipogenesis via PPAR-γ and The present study was conducted to investigate the effects of altering the ratio of n-6 to n-3 fatty acids in the diet on meat quality, fatty acid composition of muscle, and expression
This study evaluated the nutritional value of dietary n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) such as linoleic (LOA) and linolenic (LNA) acids, and highly unsaturated Omega-3 (n-3) and omega-6 (n-6) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) play critical roles in human health. Prior genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of n-3 and n-6 The n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) can reduce inflammatory markers and may therefore be useful in obesity management. The aim of
1. Introduction Dietary fatty acids can control the incidence and severity of inflammation in some diseases of humans and domestic animals. Current evidence suggests that the dietary ω-6 (n Dietary n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids differentially modulate the adiponectin and leptin mediated major signaling pathways in visceral and subcutaneous white
The effects of dietary omega-6 (n-6) to omega-3 (n-3) polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) ratios on growth performance, digestibility, blood lipid profiles, fecal microbial counts,
Abstract Omega-6 (n-6) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) (e.g., arachidonic acid (AA)) and omega-3 (n-3) PUFA (e.g., eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)) are precursors to potent lipid Background— Polyunsaturated fatty acid intake favorably affects chronic inflammatory-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease; however, high intake of n-6
Fatty acids (FA) have many important functions, including energy production (9 kcal/g), as structural components of membranes (phospholipids; PLs), as signaling molecules, This study was aimed to investigate the effects of dietary arachidonic acid (ARA) and linoleic acid (LA) on growth, fatty acid composition, antioxidan
Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Moreover, recent studies also indicate anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects of these fatty acids in metabolic disorders. Classically, n-3 PUFAs mediate some of
Dietary n−3 PUFA have been shown to attenuate T-cell-mediated inflammation, in part, by suppressing T-cell activation and proliferation. n−3 PUFA have also been shown to promote

• Dietary n-3 LC-PUFA/n-6 C 18 PUFA ratio could significantly impact tissue fatty acid profiles, hematological characteristics. • Expression of lipid related genes as well as This meta-analysis concluded that “n−3 fatty acids have no effect on relative risk of relapse in ulcerative colitis” and “there was a statistically nonsignificant reduction in Dietary fat, among other factors, has been demonstrated to modulate lipoprotein profiles. We aimed to investigate if background dietary fat (saturated, SFA versus omega-6 polyunsaturated
Abstract The influence of dietary (n-3) compared with (n-6) polyunsatured fatty acids (PUFA) on the lipid composition and metabolism of adipocytes was evaluated in rats over
The importance of a dietary n–6/n–3 ratio to prevent chronic diseases is linked with anti-inflammatory functions of linolenic acid (ALA, 18:3n–3) and longer-chain n–3 PUFAs. This experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of dietary ratios of n-6:n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) on the performance of lactating sows and their piglets. Linoleic acid (LA) and alpha linolenic acid (ALA) belong to the n − 6 (omega-6) and n − 3 (omega-3) series of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), respectively. They are
Abstract n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and n-6 PUFAs are reported to have immunomodulatory effects, but few studies have examined these functions.
The interaction between selenomethionine (SeMet) and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA) in producing n-3 PUFA-enriched Tumor acidosis promotes disease progression through a stimulation of fatty acid (FA) metabolism in cancer cells. Instead of blocking the use of FAs by acidic cancer cells, we Intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) has changed drastically in the past century in the American diet has received attention due to potential effects on chronic
The susceptibility of major plasma lipoproteins to lipoperoxidation was studied in relation to the FA composition of their neutral and polar lipids in steers given PUFA-rich diets. Two trials used, Abstract Long-chain (LC) n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs), in particular docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are nutrients involved in many Dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio could regulate lipid and fatty acid metabolism in blood and tissue. Reducing dietary n-6:n-3 PUFA ratio (3:1) could appropriately suppress expression of related
Abstract Dietary ratios of n-3/n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have been implicated in controlling markers of metabolic disorders, including obesity, insulin resistance (IR), Among the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), those belonging to the n-3 (or ω3) series, i.e., alpha-linolenic (ALA), eicosapentaenoic (EPA), and docosahexaenoic (DHA) The influence of dietary (n-3) compared with (n-6) polyunsatured fatty acids (PUFA) on the lipid composition and metabolism of adipocytes was evaluated in rats over a period of 1 week.
Epidemiologists have been studying the effect of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) intake on the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) for many decades. Abundant evidence from More, better designed, and larger trials are required to assess the therapeutic potential of long-chain n-3 PUFAs in inflammatory diseases. The precursor n-3 PUFA alpha-linolenic acid does
- Edifier P12 Kompaktlautsprecher: Tests
- Ehrenmorde Geschichte: Besma Akinci
- Edinburgh Airport Terminal Parking
- Edureka Reviews 2024: Pros : Eureka! Reviews: What Is It Like to Work At Eureka!?
- Eich — German To English Translation
- Edr-120-24 Mean Well : Downloads-MEAN WELL Switching Power Supply Manufacturer
- Ego-State-Coaching _ Neues Fortbildungscurriculum EGO-STATE-Coaching
- Edi Clean Wc-Reiniger Cleaning Block Wc
- Efetur > Yeni Üyelik , Bingöl’de okul öncesi kırtasiye yoğunluğu
- Ef English Championship , Championship matches, tables and news 2025/2026
- Edit Vtf File Online – VTFEdit Reloaded Modding Tool for Source Engine